
In September last year, we at Sanyi Life took the lead in “interpreting” Intel’s latest generation mobile processor architecture for everyone with reference to the latest architecture information at the time and some exclusive internal data.

Of course, everyone now knows that the object we were "analyzing" at that time was an ES version of the first-generation Core Ultra processor that had just been released.
To be honest, the information we obtained was relatively early. Although it was very detailed, there was still a certain gap between it and the final version. Therefore, we are very concerned about Intel’s new products released on December 15, 2023. The final result is that this event did not disappoint us
Bigger and stronger, the fifth generation can be expanded to the most powerful "big killer"
The biggest difference between Intel's new product launch conference and previous ones is that they almost put together new cloud server CPU products for enterprises and new end-side computing device CPU products for consumers for the first time. This press conference can be described as unique

The new generation of Xeon scalable processors has been unveiled. This processor, codenamed "Emerald Rapide-SP", uses the Intel 7 process and has significantly redesigned the architecture. According to relevant technical information, compared with the fourth generation Xeon scalable processor, this processor has higher performance

Rewritten content: The latest generation of Xeon Scalable processors showed off its new specifications at this appearance. It has 64 cores, an increase from the 60 cores of the previous generation. These cores are now divided into 2 MCM modules instead of 4 modules in the previous generation. This also means that each CPU module has more than twice the number of cores of the previous generation

On this basis, the basic architecture of the fifth-generation Xeon scalable processor has also been updated from Golden Cove to Raptor Cove, which means that it has the same requirements for cache and memory as the familiar 13th and 14th generation Cores. The subsystem has been significantly enhanced. For example, if you compare the new Xeon 8592 with the previous generation Xeon 8490H, you will find that its L3 Cache has increased from 112.5MB to 320MB in one go. At the same time, compared with the previous generation DDR5-4800, the starting memory frequency of the eight-channel DDR5-5600 also means that its memory bandwidth has been significantly enhanced.
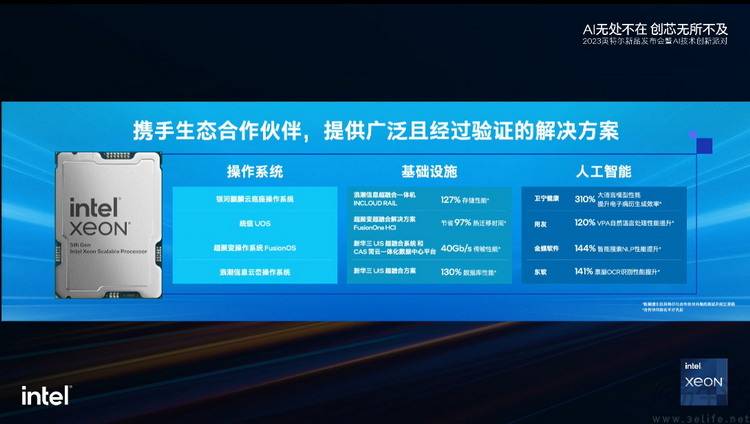
Of course, the above content is mainly aimed at cloud service providers, such as JD.com, Alibaba, Baidu, etc. The purpose of these architecture and performance improvements is to accelerate the iteration and application efficiency of large AI models in the cloud. In addition, everyone also knows that Intel also has a product line for enthusiasts, Xeon W. Therefore, the fifth-generation scalable Xeon architecture actually reveals a lot of information about the next-generation Xeon W
More cores, stronger graphics, and NPU, Core Ultra is here
The next step is the highlight of this conference-the new Intel Core Ultra processor

In terms of architecture, Intel's first-generation Core Ultra processor is designed with a multi-module, multi-process hybrid packaging. Each core contains four modules, including a CPU module using Intel 4 process, a GPU module using TSMC 5nm process, and an SoC module and IO module using TSMC 6nm process

What are the benefits of such a design? First, it allows the processor to integrate more functional components. Taking the Core i9-185H as an example, its CPU module integrates 6P 8E, with a total of 14 CPU cores. At the same time, there are 2 additional E cores in the SoC module, which can completely shut down the CPU module when running extremely low loads, thereby achieving more power saving purposes

For another example, Core Ultra’s ARC GPU module now has a more “complete” Xe architecture. It has up to 128 execution units (instead of the 96 of the previous generation), can run at a frequency of up to 2250MHz, and has 64 texture units and 32 raster units. In addition, it also supports hardware ray tracing and XeSS hardware AI super-resolution anti-aliasing. Under such a configuration, the performance of the new core display FP32 can be as high as 4.608TFlops, which is twice the performance of the previous generation.

In addition, Core Ultra has also become Intel’s first mobile processor solution with integrated NPU. According to relevant technical information, its NPU computing power can reach 10TOPs. At the same time, the processor also has a built-in Thunderbolt 4 controller
After substantial improvements, Core Ultra has significantly improved its architecture and design. A very noteworthy highlight of this release is that the default TDP of its standard voltage version is only 28-45W, and the maximum TDP is only 115W. You know, since the 11th generation, the standard mobile version of Core has not had such a low official TDP parameter for a long time. For example, the high-end standard-voltage mobile CPU 14900HX even has an official maximum TDP setting of 157W. Judging from the various information currently exposed, the ultra-high energy efficiency ratio is likely to become the highlight of the first-generation Core Ultra in actual use
How to make “AI PC” truly practical, Intel has indeed taken a good lead
If you have paid attention to recent relevant information, you must know that in fact, Intel's competitors, such as Qualcomm and AMD, have previously released mobile CPU product lines with independent NPUs. In contrast, Intel's Core Ultra series arrived relatively late.

Intel is not later than its competitors on the "AI PC" technology route. In fact, as early as 2019, Intel introduced the DL Boost instruction set for the first time in the then Core X series processors (Cascade Lake) to accelerate deep learning calculations
Subsequently to the 10th and 11th generation Core mobile versions, DL Boost and AVX-512 instruction sets were further popularized into more popular products, so that many laptop products at that time had similar camera centering, AI experiences such as microphone noise reduction and video super resolution.

As Intel introduces the Xe architecture into the core displays of Core processors, these core displays also have AI acceleration capabilities. For example, on some 12th and 13th generation Core laptops and desktop computers, you can see functions such as AI voice assistant and AI background blur based on core graphics computing power

Because of this, in the first-generation Core Ultra processor, although on the surface, its "AI unit" seems to be an NPU. But in fact, Intel has long figured out a heterogeneous acceleration system that allows CPU, GPU, and NPU to undertake different AI tasks according to different codes, and sometimes can even perform collaborative calculations, and they call this technology "XPU."

At today’s press conference, it can be seen that Intel has attracted many domestic software manufacturers to participate and demonstrated the effect of their products running through AI acceleration on Core Ultra. According to Intel, although Core Ultra has just been released, more than 100 software has been officially adapted to the product and can exert the AI acceleration effect

It can be said that compared with its competitors in Core Ultra, Intel's unique heterogeneous processing design and the large number of adaptations they have made to promote the popularity of "AI PC" may be the most obvious advantages. Compared with simply adding a hardware AI acceleration unit to the CPU, this processing method is more efficient
The above is the detailed content of Opening the door to a new era of PCs, analysis of Intel's new 'AI processor”. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Computer screen shows no signal
Computer screen shows no signal
 What does legacy startup mean?
What does legacy startup mean?
 Introduction to Document in JS
Introduction to Document in JS
 Euro-Italian Exchange official app
Euro-Italian Exchange official app
 How to download and save today's headline videos
How to download and save today's headline videos
 Reasons why website access prompts internal server error
Reasons why website access prompts internal server error
 Implementation method of VUE next page function
Implementation method of VUE next page function
 Bitcoin exchange
Bitcoin exchange
 What to do if the chm file cannot be opened
What to do if the chm file cannot be opened




