 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 A complete analysis of Spring design patterns: building maintainable and scalable applications
A complete analysis of Spring design patterns: building maintainable and scalable applications
A complete analysis of Spring design patterns: building maintainable and scalable applications

Full analysis of Spring design patterns: building maintainable and scalable applications requires specific code examples
Introduction:
In modern software development , building maintainable and scalable applications is an important goal. Design patterns are a widely accepted software development methodology that provide solutions to common problems. As a powerful Java development framework, the Spring framework provides the implementation of many design patterns to help developers build efficient, flexible and maintainable applications.
This article will comprehensively analyze the commonly used design patterns in the Spring framework, focusing on their principles and example codes. By deeply understanding these design patterns, developers can better apply them to build maintainable and scalable applications.
1. Singleton Pattern
The singleton pattern is one of the most common design patterns and is often used in applications. Its main purpose is to ensure that there is only one instance of a class and to provide a global access point.
Sample code:
public class Singleton {
private static Singleton instance;
private Singleton() {}
public static synchronized Singleton getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new Singleton();
}
return instance;
}
}2. Factory Pattern
Factory pattern is a creational design pattern that separates the creation and use of objects. By introducing the factory class, we can create objects by calling the methods of the factory class.
Sample code:
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
public class Circle implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Drawing a circle");
}
}
public class Square implements Shape {
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Drawing a square");
}
}
public class ShapeFactory {
public static Shape getShape(String shapeType) {
if (shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("circle")) {
return new Circle();
} else if (shapeType.equalsIgnoreCase("square")) {
return new Square();
}
return null;
}
}3. Observer Pattern
The Observer pattern is a behavioral design pattern that defines a one-to-many The dependency relationship allows multiple objects to monitor the status changes of a theme object at the same time.
Sample code:
public interface Observer {
void update(String message);
}
public interface Subject {
void registerObserver(Observer observer);
void removeObserver(Observer observer);
void notifyObservers(String message);
}
public class WeatherStation implements Subject {
private List<Observer> observers;
private String weather;
public WeatherStation() {
observers = new ArrayList<>();
}
@Override
public void registerObserver(Observer observer) {
observers.add(observer);
}
@Override
public void removeObserver(Observer observer) {
observers.remove(observer);
}
@Override
public void notifyObservers(String message) {
for (Observer observer : observers) {
observer.update(message);
}
}
public void setWeather(String weather) {
this.weather = weather;
notifyObservers(weather);
}
}
public class User implements Observer {
private String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void update(String message) {
System.out.println(name + " received a weather update: " + message);
}
}
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeatherStation weatherStation = new WeatherStation();
User user1 = new User("Alice");
User user2 = new User("Bob");
weatherStation.registerObserver(user1);
weatherStation.registerObserver(user2);
weatherStation.setWeather("Sunny");
}
}Conclusion:
By learning and applying the design patterns in the Spring framework, we can build maintainable and scalable applications. This article introduces the principles of singleton pattern, factory pattern and observer pattern and the corresponding sample code. Of course, the Spring framework provides more design pattern implementations to help developers solve various practical problems. By continuing to learn and practice, we can better apply these design patterns to develop excellent software applications.
The above is the detailed content of A complete analysis of Spring design patterns: building maintainable and scalable applications. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Shazam app not working in iPhone: Fix
Jun 08, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
Shazam app not working in iPhone: Fix
Jun 08, 2024 pm 12:36 PM
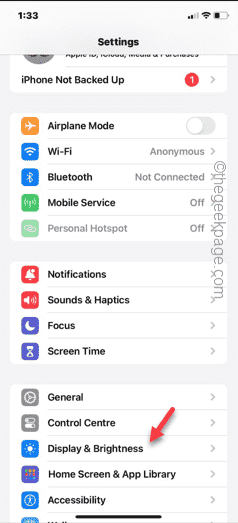
Having issues with the Shazam app on iPhone? Shazam helps you find songs by listening to them. However, if Shazam isn't working properly or doesn't recognize the song, you'll have to troubleshoot it manually. Repairing the Shazam app won't take long. So, without wasting any more time, follow the steps below to resolve issues with Shazam app. Fix 1 – Disable Bold Text Feature Bold text on iPhone may be the reason why Shazam is not working properly. Step 1 – You can only do this from your iPhone settings. So, open it. Step 2 – Next, open the “Display & Brightness” settings there. Step 3 – If you find that “Bold Text” is enabled
 The difference between design patterns and architectural patterns in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
The difference between design patterns and architectural patterns in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
In the Java framework, the difference between design patterns and architectural patterns is that design patterns define abstract solutions to common problems in software design, focusing on the interaction between classes and objects, such as factory patterns. Architectural patterns define the relationship between system structures and modules, focusing on the organization and interaction of system components, such as layered architecture.
 Location not available on iPhone: Fix
Jun 02, 2024 pm 05:19 PM
Location not available on iPhone: Fix
Jun 02, 2024 pm 05:19 PM
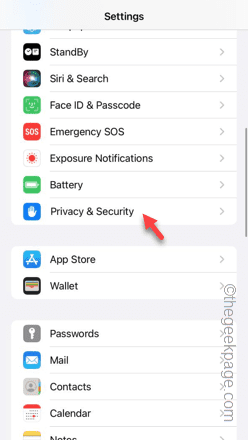
Suppose you're about to go on a hike you planned a long time ago, but the location seems to have stopped working on your phone? While it may not seem like much, the wrong location settings can be very problematic. Start searching for restaurants near you from a weather app, the wrong location settings can be very frustrating. In this case, these fixes will be useful. Fix 1 – Enable location settings You must enable location settings on your phone. Step 1 – Start the process by opening the Settings page. Step 2 – Later, open the Privacy & Security settings. Step 3 – Next, open the Location Services settings. Step 4 – Enable the “Location Services” option. Go back to the offending app and check if it can access the location. Fix 2 – Enable airplane mode and test enabling
 Analysis of the Decorator Pattern in Java Design Patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
Analysis of the Decorator Pattern in Java Design Patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 03:12 PM
The decorator pattern is a structural design pattern that allows dynamic addition of object functionality without modifying the original class. It is implemented through the collaboration of abstract components, concrete components, abstract decorators and concrete decorators, and can flexibly expand class functions to meet changing needs. In this example, milk and mocha decorators are added to Espresso for a total price of $2.29, demonstrating the power of the decorator pattern in dynamically modifying the behavior of objects.
 The wonderful use of the adapter pattern in Java design patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 12:54 PM
The wonderful use of the adapter pattern in Java design patterns
May 09, 2024 pm 12:54 PM
The Adapter pattern is a structural design pattern that allows incompatible objects to work together. It converts one interface into another so that the objects can interact smoothly. The object adapter implements the adapter pattern by creating an adapter object containing the adapted object and implementing the target interface. In a practical case, through the adapter mode, the client (such as MediaPlayer) can play advanced format media (such as VLC), although it itself only supports ordinary media formats (such as MP3).
 PHP Design Patterns: Test Driven Development in Practice
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:14 PM
PHP Design Patterns: Test Driven Development in Practice
Jun 03, 2024 pm 02:14 PM
TDD is used to write high-quality PHP code. The steps include: writing test cases, describing the expected functionality and making them fail. Write code so that only the test cases pass without excessive optimization or detailed design. After the test cases pass, optimize and refactor the code to improve readability, maintainability, and scalability.
 How design patterns deal with code maintenance challenges
May 09, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
How design patterns deal with code maintenance challenges
May 09, 2024 pm 12:45 PM
Design patterns solve code maintenance challenges by providing reusable and extensible solutions: Observer Pattern: Allows objects to subscribe to events and receive notifications when they occur. Factory Pattern: Provides a centralized way to create objects without relying on concrete classes. Singleton pattern: ensures that a class has only one instance, which is used to create globally accessible objects.
 What are the advantages and disadvantages of using design patterns in java framework?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
What are the advantages and disadvantages of using design patterns in java framework?
Jun 01, 2024 pm 02:13 PM
The advantages of using design patterns in Java frameworks include: enhanced code readability, maintainability, and scalability. Disadvantages include complexity, performance overhead, and steep learning curve due to overuse. Practical case: Proxy mode is used to lazy load objects. Use design patterns wisely to take advantage of their advantages and minimize their disadvantages.



