 System Tutorial
System Tutorial
 LINUX
LINUX
 Detailed explanation of Win10 and Ubuntu 18.04 dual system installation tutorial
Detailed explanation of Win10 and Ubuntu 18.04 dual system installation tutorial
Detailed explanation of Win10 and Ubuntu 18.04 dual system installation tutorial
Foreword:
Due to development needs, many users need to install a Linux environment. If you use a virtual machine to operate, it will consume a lot of memory, and ordinary computers will appear laggy, thus affecting development efficiency. Here I share some installation experience, hoping to help everyone.
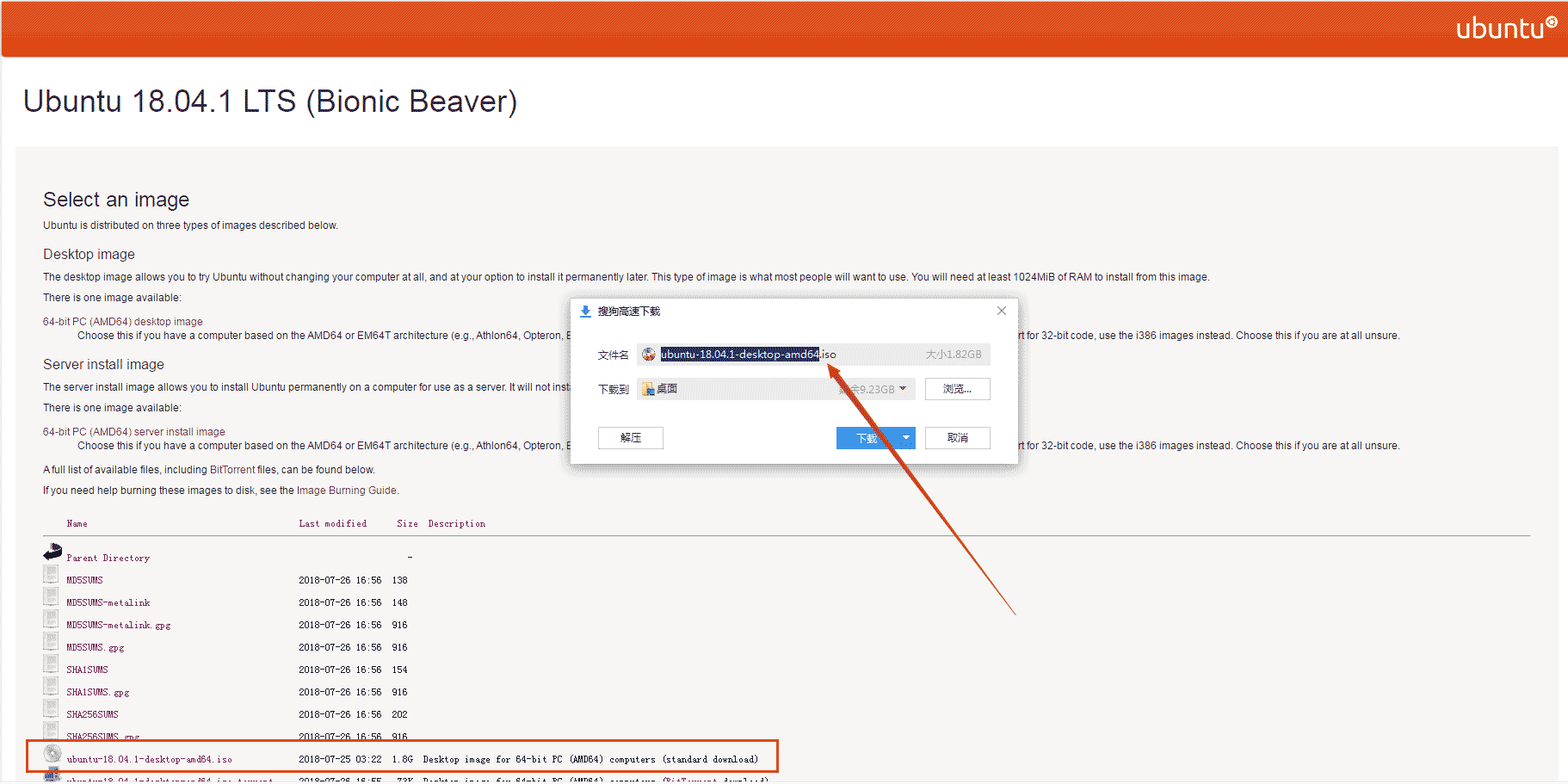
Tutorial: Step 1: Download the image file
Download the system iso image file from the Ubuntu official website http://releases.ubuntu.com/18.04/. There is no need to decompress it after downloading. The process is as follows:
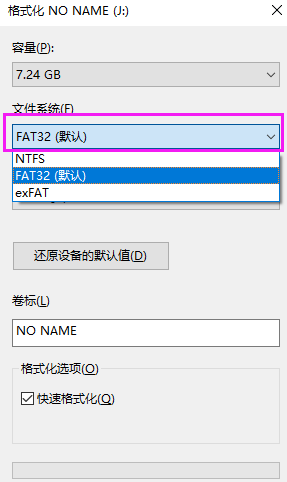
Step 2: Format U disk
Format your USB flash drive. When formatting, select FAT32 format. The specific process is as follows:
Note: Don’t forget to back up before formatting. You can first backup it on the Windows 10 desktop, which is the C drive.
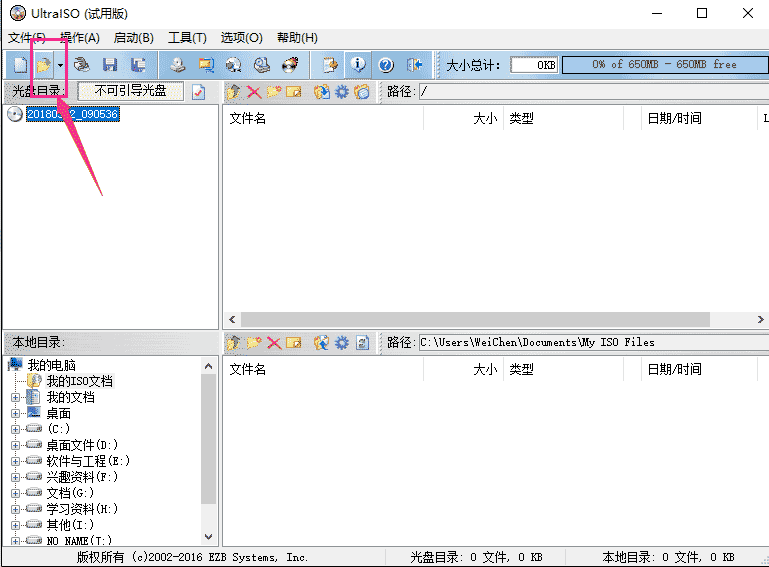
Step 3: Make a boot disk
Download the UltraISO software installation from the Internet https://www.php.cn/link/a4017a78440df3ea7890934b5247dde9, and select "Continue Trial" to open the software.
Click the file icon in the picture below to select the image file you just downloaded.
After selection, the interface is shown in the figure below:
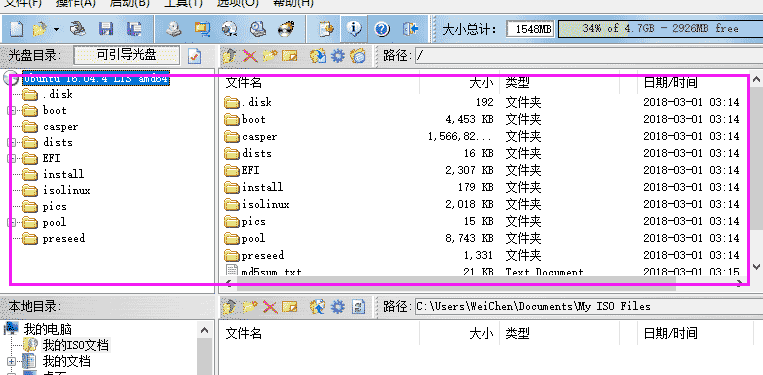
Then proceed with the following steps:
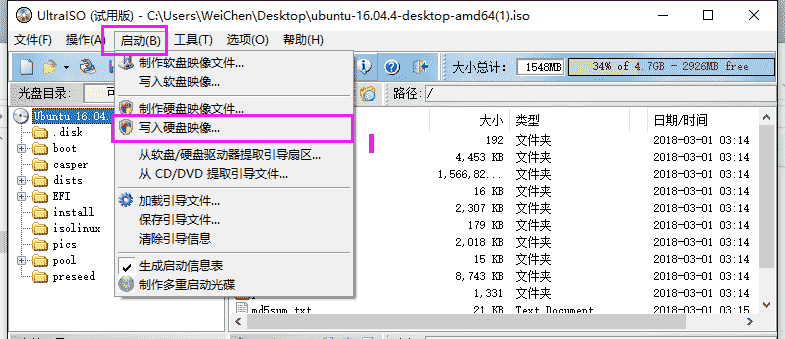
Then set the following options:
Note: Writing sysLinux boot is very important! ! ! Otherwise, there will be an error message later.
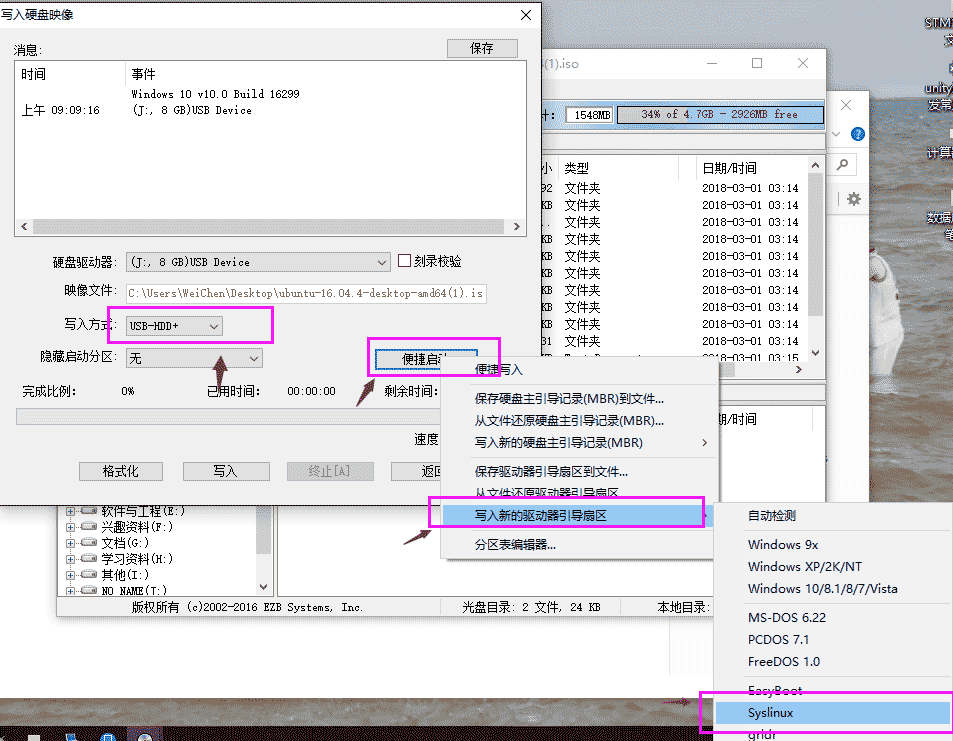
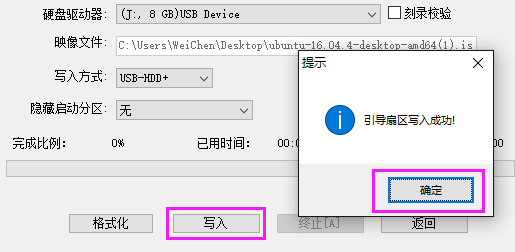
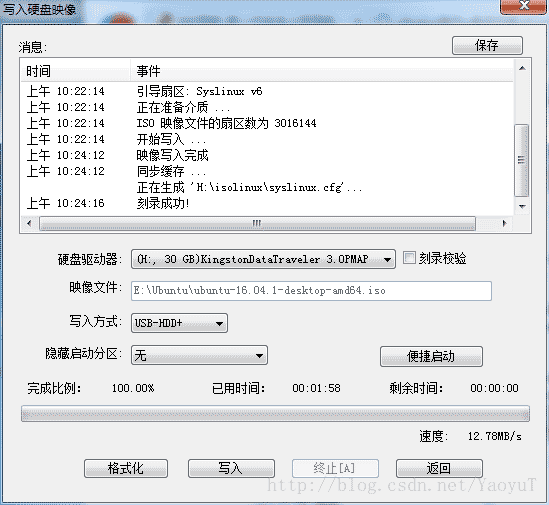
Then click "Yes", and finally click Write to start writing the file. When completed, close it. The U disk creation is completed.
Step 4: Disk partitioning for ubuntu
Note: The Windows 10 64-bit version I installed can be compressed through disk (the method is Baidu's, recommended: https://www.jizhuba.com/kejiyouxi/20170929/5721.html) to get a disk of about 30G, but Do not create a partition, make it a free partition so that it can be recognized by Ubuntu installation! ! !
Click My Computer-->Management-->Disk Management to partition (you can use Baidu here, there are many online tutorials, it is very simple) and separate a free disk that is almost larger than 30G. Be sure not to allocate a disk to it. symbol (such as the one shown in green)
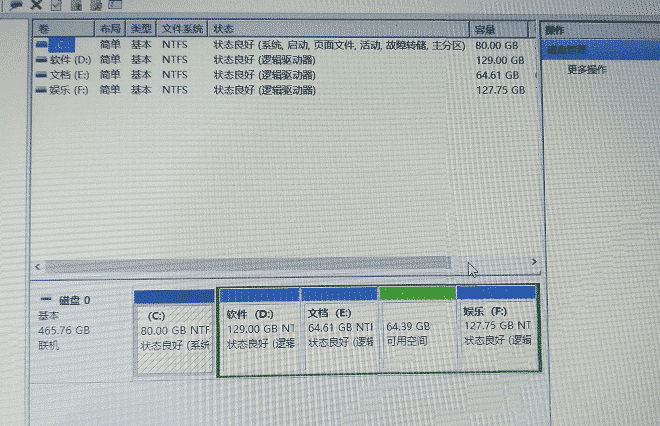
Step 5: Start installing the system (be sure to insert the USB flash drive before booting)
①Enter the BIOS to perform Secure Boot settings (generally press F2 or Fn F2 when turning on the computer), enter Boot, and if the Boot Mode is UEFI, we will set the following Secure Boot to Disable. If Boot Mode is Legacy, skip this step.
②Then put the USB HDD startup item at the top, which means to boot from the U disk first. (There are certain differences in the content of different computers in this process. I will not show the picture here. Anyway, you can think about it for a while or refer to it. Several online blogs, I tried several times before entering the Ubuntu installation interface).
③After setting, save and exit, you will enter the Ubuntu interface and select installation (if you choose trial, you will directly enter the Ubuntu trial environment).
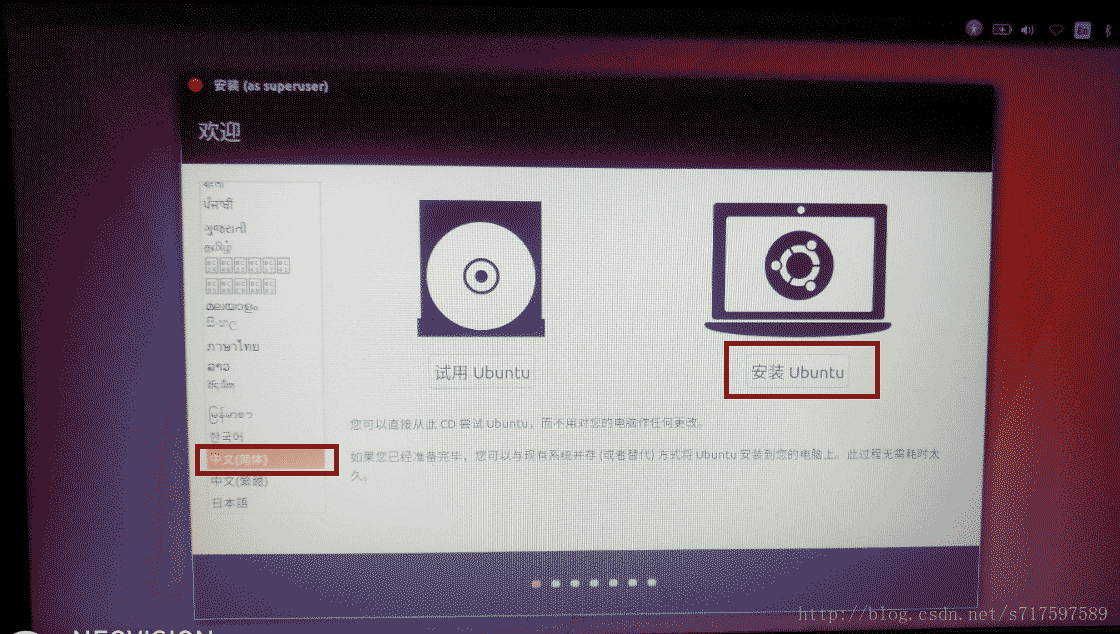
④ Then connect to the Internet (it is best to connect, because some files will be automatically downloaded from the Internet later)

⑤When you get to the installation type, select other options
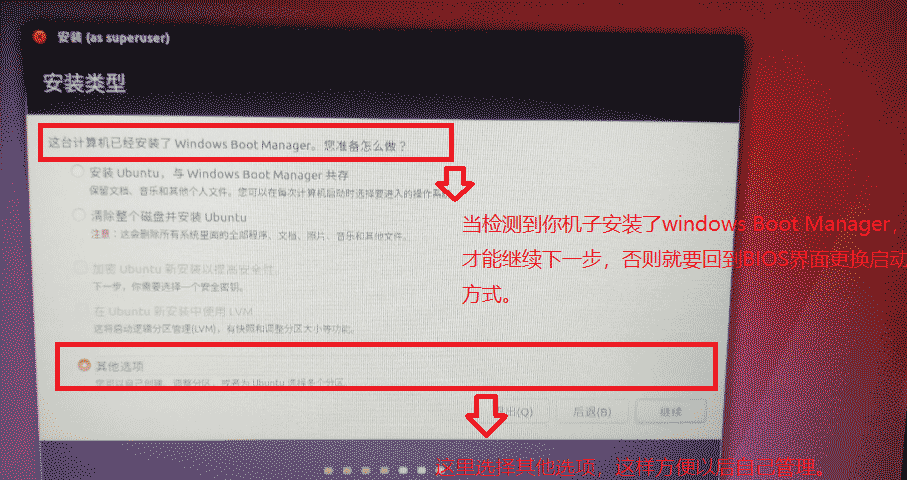
⑥The next step is to partition the Ubuntu system:
Find the disk whose size we compressed before (the disk that has not been used), double-click to enter the partition settings
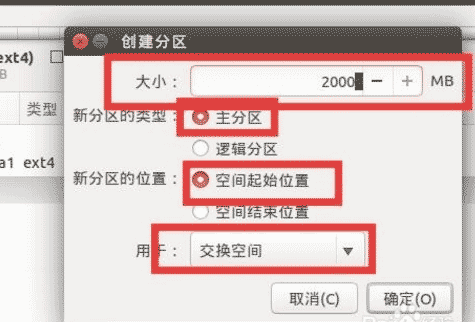
Set up swap space
Used as virtual memory, this is generally 1 to 2 times the physical memory (memory) of your own, of course it can be larger (mine is 6G memory, the picture below is an online picture, the size is allocated according to your own situation ).
Settings /Partition (root partition)
Then double-click the remaining free disk and double-click to create the /: partition, which is mainly used to store Linux system files. Specific steps are as follows
Select the logical partition here, the starting position of the space, for the Ext4 log file, the mount point: /, the size is recommended to be 8-16G, you can set it according to your own situation, I set it here to 10G.
Set the home partition (personal file storage)
Set home, we select the logical partition, the starting position of the space, used for Ext4 log files, the mount point: /home, the size can be based on your own situation. Pictures refer to the settings above.
Set the boot partition (start boot storage)
This partition contains the kernel of the operating system and files used in the process of starting the system. It is necessary to build this partition. The size of the partition is about 150MB-200MB, and it cannot be larger. Select the ext4 log file, mount point: /boot.
Set swap (swap space):
Logical partition, the size is set to the computer memory size (it can also be 1-2 times the computer memory), the function is equivalent to virtual memory, if it is too small, it may slow down the system.
#Set /usr partition (optional)
#You decide where to store the system and personal software. If there are many installation programs, use more points. Select the ext4 log file, mount point: /usr.
⑦Select the device for installing the bootloader below to the device corresponding to the boot area just separated, and then click Install.
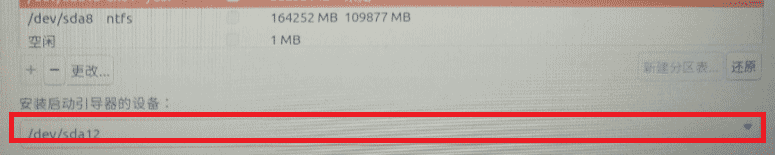
⑧ Complete the corresponding simple operations according to the prompts
Step 6: Add system boot
After unplugging the U disk, the computer restarts. At this time, the previous Windows system is usually entered. After entering, download EasyBCD (you can find it by searching online). When opening the software, it is recommended to complete the following steps ( If this method doesn't work, Baidu will use other methods):
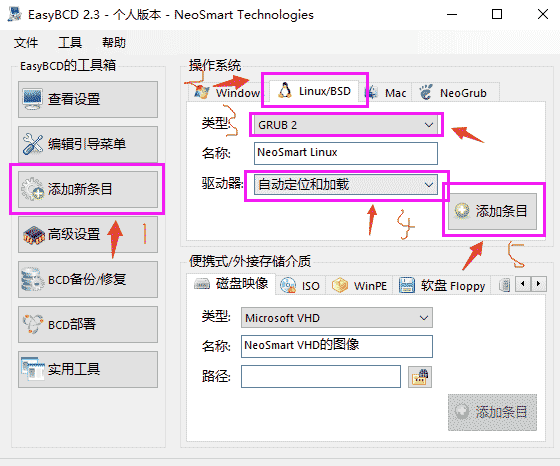
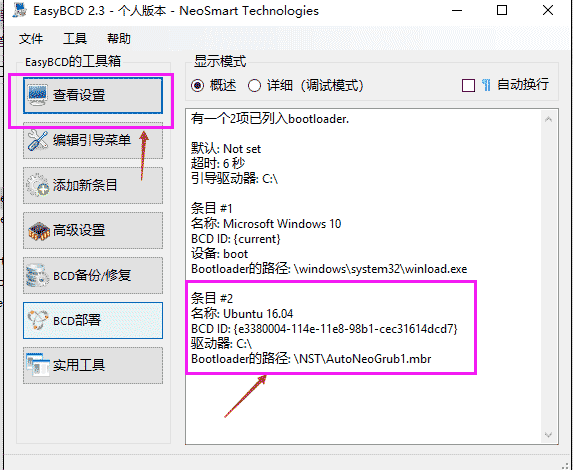
Then you can see the newly added guide in the view settings, save and exit
Step 7: Shut down and restart, you will see two system options on the startup interface. The installation is now complete
Note: If there are some other problems, please solve them on Baidu yourself;
refer to:
Some of the pictures in this blog are from Baidu resources. Some improvements have been made by referring to the two blogs.
https://www.php.cn/link/48abd1b3f5452995d995eb78a77013c8
https://www.php.cn/link/5cc33dfe7e069a757ca0fcbe6b95c89e
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Win10 and Ubuntu 18.04 dual system installation tutorial. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1381
1381
 52
52
 System Restore prompts that you must enable system protection on this drive
Jun 19, 2024 pm 12:23 PM
System Restore prompts that you must enable system protection on this drive
Jun 19, 2024 pm 12:23 PM
The computer has a restore point, and when the system is restored, it prompts "You must enable system protection on this drive." This usually means that the system protection function is not turned on. System protection is a feature provided by the Windows operating system that can create system restore points to back up system files and settings. That way, if something goes wrong, you can revert to a previous state. When the system fails and you cannot enter the desktop to start it, you can only try the following method: Troubleshooting-Advanced Options-Command Prompt Command 1 netstartvssrstrui.exe/offline:C:\windows=active Command 2 cd%windir%\system32 \configrenSYSTEMsy
 What should I do if win10 does not switch users? Win10 login interface does not have the option to switch users. Solution
Jun 25, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
What should I do if win10 does not switch users? Win10 login interface does not have the option to switch users. Solution
Jun 25, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
A problem that Windows 10 users may encounter is that they cannot find the switch user option on the login interface. So what should I do if there is no switch user option on the win10 login interface? Let this site give users a detailed explanation of the problem of not switching user options in the win10 login interface. Detailed solution to the problem of switching user options on the Win10 login interface: Check user account settings: First, make sure you have multiple user accounts on your computer and that these accounts are enabled. You can check and enable the account by following these steps: a. Press Win+I keys to open Settings and select "Accounts". b. Select "Family & Others" or &ld in the left navigation bar
 How to restore the default wallpaper in win10? One trick to quickly restore the default wallpaper in Windows 10 system
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:07 PM
How to restore the default wallpaper in win10? One trick to quickly restore the default wallpaper in Windows 10 system
Jun 02, 2024 pm 02:07 PM
In Windows 10 system, if you want to return to the system default wallpaper, you can follow the following steps: 1. Right-click a blank space on the desktop and select Personalize in the pop-up menu. 2. This will open the Personalization window in Settings. In the left menu, click Background. 3. Under the "Background" settings, find and click the drop-down menu next to "Choosepicture", and then select Windows Default (Windows Default) or directly select a picture that looks like the default wallpaper in the picture preview below ( if there are multiple options). 4. If your system has multiple versions
 How to permanently turn off real-time protection in win10? How to disable real-time protection function in win10 computer 0
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:46 PM
How to permanently turn off real-time protection in win10? How to disable real-time protection function in win10 computer 0
Jun 05, 2024 pm 09:46 PM
Although the comprehensive anti-virus software that comes with Windows 10 system can continuously protect the security of your personal computer, sometimes it may also affect certain downloaded files. For some users, it may be more appropriate to temporarily turn off the real-time protection function. But many users don’t know how to permanently turn off the real-time protection feature on win10 system. 1. First, press the "Win+R" keys to open the run window, enter the "gpedit.msc" command to open the local Group Policy Editor interface; 2. Then, in the opened interface, click "Computer Configuration/Administrative Templates/ Windows Components/MicrosoftDef
 What should I do if Win10 takes a screenshot and crashes? How to solve the problem of Win10 flashing and then disappearing after taking a screenshot?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
What should I do if Win10 takes a screenshot and crashes? How to solve the problem of Win10 flashing and then disappearing after taking a screenshot?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
There are many reasons why the screenshot disappears after taking a screenshot in Win10. Users can first check the screenshot save location or adjust the screenshot settings, or check the animation effect to check it. If it really doesn't work, you can also choose to update the driver and operating system to perform the operation. Let this website carefully introduce to users the analysis of the problem of Win10 disappearing after taking a screenshot. Analysis of the problem after win10 takes a picture and it flashes and disappears 1. Check where the screenshot is saved: When you use the Win+PrtSc (PrintScreen) key combination to take a screenshot, the screenshot is usually saved in the C:\Users\YourUsername\Pictures\Screenshots folder. please
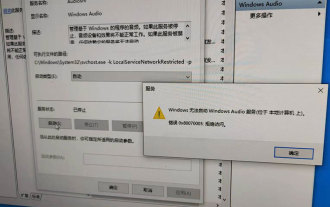 Windows cannot start the Windows Audio service Error 0x80070005
Jun 19, 2024 pm 01:08 PM
Windows cannot start the Windows Audio service Error 0x80070005
Jun 19, 2024 pm 01:08 PM
The guy's computer appears: Windows cannot start the WindowsAudio service (located on the local computer). Error 0x8007005: Access denied. This situation is usually caused by user permissions. You can try the following methods to fix it. Method 1: Modify the registry to add permissions through batch processing, create a new text document on the desktop, save it as .bat, and right-click the administrator to go far. Echo==========================EchoProcessingRegistryPermission.Pleasewait...Echo================== ========subinacl/subkey
 What to do if the Win10 Task Manager crashes? How to fix the Win10 Task Manager crash?
Jun 25, 2024 pm 04:31 PM
What to do if the Win10 Task Manager crashes? How to fix the Win10 Task Manager crash?
Jun 25, 2024 pm 04:31 PM
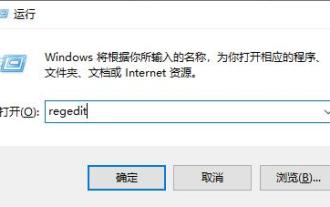
Hello everyone, have you ever encountered the situation where the Windows 10 Task Manager keeps crashing? This function helps us a lot, allowing us to quickly see all running tasks, which is very convenient to use, right? However, some friends said that they encountered this problem and didn’t know how to solve it, so let me share with you the specific solution! Solution to Win10 Task Manager crash 1. First, press and hold the "Win" + "R" keys on the keyboard to open Run, enter "regedit" and press the Enter key. 2. Expand the folders and find "HKEY_CURRENT_USERSoftwareMicros
 How to turn off popular searches in Windows 10 system? List of methods to close popular searches in Windows 10 system
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:46 PM
How to turn off popular searches in Windows 10 system? List of methods to close popular searches in Windows 10 system
Jun 03, 2024 pm 08:46 PM
In win10 system, hot search is one of the more practical methods, but sometimes it can cause certain troubles. So how to turn off hot search? Let’s take a look below! Step 1: Open the Settings app First, click on the Windows icon in the lower left corner of the screen and select the Settings app. Step 2: Enter "Personalization" settings In the "Settings" app, click the "Personalization" option. Step 3: Select the “Search” option In the “Personalization” settings, select the “Search” option. Step 4: Turn off popular searches. In the "Search" option, find the option "Show popular searches in search" and turn it off. Professional Tool Recommendation 1. Xiaozhi Soso Xiaozhi Soso—Quick Search and One-Click Positioning—Professional Computer Search Tool



