
Friends who have updated win101909, have you noticed that the new function "multi-core optimization" mentioned when 1909 was released actually has no practical effect. Some people feel that the computer's operating efficiency has become worse. In fact, there is a small bug here. Let’s take a look at the detailed introduction.
1. This is not the first time that Microsoft has intentionally or unintentionally harmed the performance of old hardware in order to optimize the performance of new hardware.
The new version of the Windows 10 1909 operating system, which will be launched on November 13 (optional installation), applies a new load rotation mechanism,
which allows the task process to more actively choose the system Run on better cores.
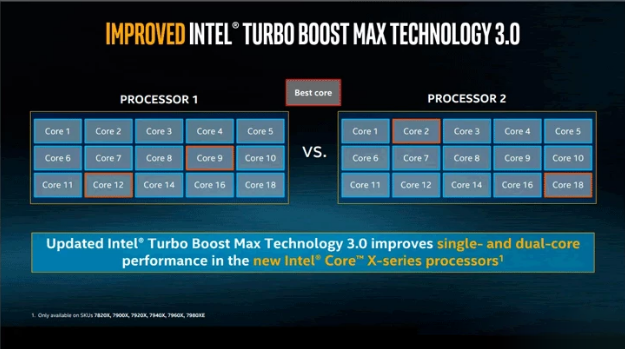
2. Theoretically, Intel Core X series and AMD third-generation Ryzen can benefit from this new thread scheduling algorithm (higher turbo frequency/ acceleration frequency).
However, there are more CPUs that do not support this feature (do not have Favored Core), but are also coerced into the new algorithm, resulting in performance damage!
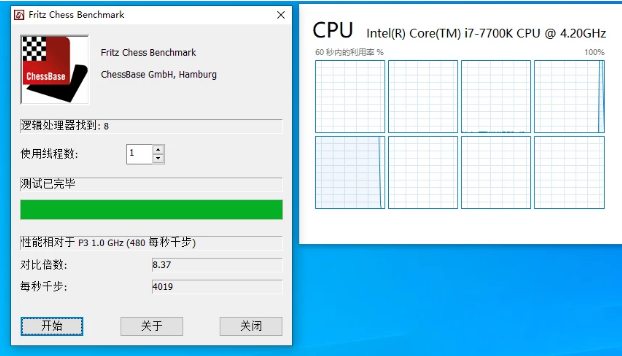
3. In 1903 and previous versions of the system, Windows tends to use a random single core to continuously execute single-threaded task loads.
As shown in the figure above, the entire process of the single-threaded chess test on Core i7-7700K only switched the running core once near the end.
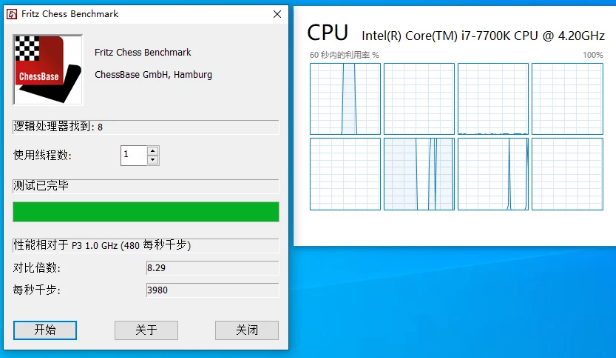
Starting from version 1909, Windows will frequently schedule the core used by the task. During a chess test, the core will usually be switched 3 to 5 times.
Switching tasks between cores will cause additional overhead in processor cache and other aspects, which will naturally lead to performance degradation.
As far as the chess test is concerned, the comparison multiple of Core i7-7700K dropped from 8.37 times to 8.29 times.
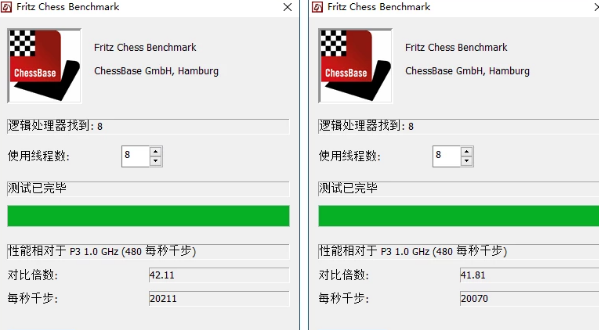
When choosing to use all 8 threads for testing, there are also very obvious differences between the 1903 and 1909 systems.
The new thread scheduling algorithm of 1909 drags down the CPU performance.
4. CineBench R20 score dropped from 2603 pts to 2534 pts.
In other words, the acceleration capabilities of different cores of these old CPUs (actually including the new 9900KS) are consistent.
If you use an algorithm suitable for the new CPU and frequently switch the CPU core where the thread is located, will hurt performance.
5. When it comes to CPU performance, it is often associated with high-speed NVMe solid-state drives.
The editor will use the recently launched Toshiba RD500 1TB as an example to compare and see the impact of the new system on storage performance.

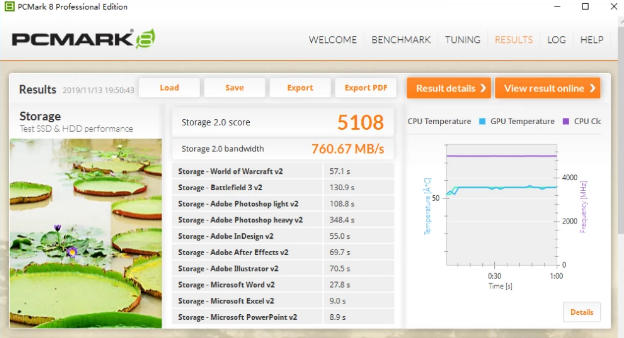
6. The PCMark 8 storage test plays back the hard disk read and write loads generated by real applications on the hard disk,
to measure the loading of common games on the computer by the solid state drive. , office software and the impact of time required for design work.
The RD500, which uses Toshiba's 96-layer stacked BiCS4 flash memory and the new TC58NC1201GST main control, can achieve a score of 5108 points under the Windows 1903 system, while it will drop to 5105 points on the 1909 system.

7. The three-thirds difference is not obvious, and is even within the normal error range for many mid- to low-end SSDs.
But it is different for RD500. Toshiba has optimized its firmware very well.
In particular, the performance consistency is excellent. Under normal circumstances, the error of multiple runs is within 1 part. Inside.
The 1909 system is 0.1 to 0.2 seconds slower than the 1903 system in individual test items.
Although the degree of degradation is not particularly large, it does quietly slow down the computer running speed.
Before Microsoft launches patches optimized for different CPUs, players using non-Intel X series and AMD third-generation Ryzen processors should try to avoid upgrading to Windows 10 1909 system.
The above is the detailed content of Detailed introduction to the bugs in win101909 version. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




