 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Can AI research also learn from Impressionism? These lifelike people are actually 3D models
Can AI research also learn from Impressionism? These lifelike people are actually 3D models
Can AI research also learn from Impressionism? These lifelike people are actually 3D models

The 19th century was the period when the Impressionism art movement flourished, which was influential in the fields of painting, sculpture, printmaking and other arts. Impressionism was characterized by the use of short, staccato brushstrokes with little pursuit of formal precision, which later evolved into the Impressionist art style. In short, the impressionist artist's brushstrokes are unmodified, showing obvious characteristics, not pursuing formal precision, and even being somewhat vague. Impressionist artists introduced the scientific concepts of light and color into paintings and revolutionized traditional color concepts.
In D3GA, the author has a unique goal. He hopes to create a photo-realistic performance effect by doing the opposite. In order to achieve this goal, the author creatively used Gaussian splattering technology in D3GA as a modern "segment brushstroke" to build the structure and appearance of virtual characters and achieve real-time and stable Effect.

"Sunrise·Impression" is the representative work of the famous Impressionist painter Monet.

## In order to create realistic human figures that can generate new content for animation, the construction of avatars currently requires a lot of work multi-view data. This is because monocular methods have limited accuracy. In addition, existing techniques require complex pre-processing, including accurate 3D registration. However, obtaining these registration data requires iteration and is difficult to integrate into an end-to-end process. In addition, there are methods that do not require accurate registration and are based on neural radiation fields (NeRFs). However, these methods are often slow at real-time rendering or have difficulty with clothing animation.
Kerbl et al. proposed a rendering method called 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS), which is improved on the basis of the classic Surface Splatting rendering method. Compared with state-of-the-art methods based on neural radiation fields, 3DGS is able to render higher quality images at faster frame rates and without the need for highly accurate 3D initialization.
However, 3DGS was originally designed for static scenes. At present, some people have proposed the Gaussian Splating method based on time conditions, which can be used to render dynamic scenes. This method can only play back what has been previously observed and is therefore not suitable for expressing new or previously unseen motion.
Based on the driven neural radiation field, the author models the appearance and deformation of 3D humans, placing them in a standardized space, but using 3D Gaussian rather than a radiation field. In addition to better performance, Gaussian Splatting eliminates the need to use the camera ray sampling heuristic.
The remaining problem is to define the signals that trigger these cage deformations. Current state-of-the-art technologies in driver-driven avatars require dense input signals, such as RGB-D images or even multiple cameras, but these methods may not be suitable for situations where transmission bandwidth is relatively low. In this study, the authors employ more compact input based on human poses, including skeletal joint angles and 3D facial keypoints in the form of quaternions.
By training individual-specific models on nine high-quality multi-view sequences, covering a variety of body shapes, movements, and clothing (not limited to intimate clothing), we can later The new posture of any subject drives the figure.
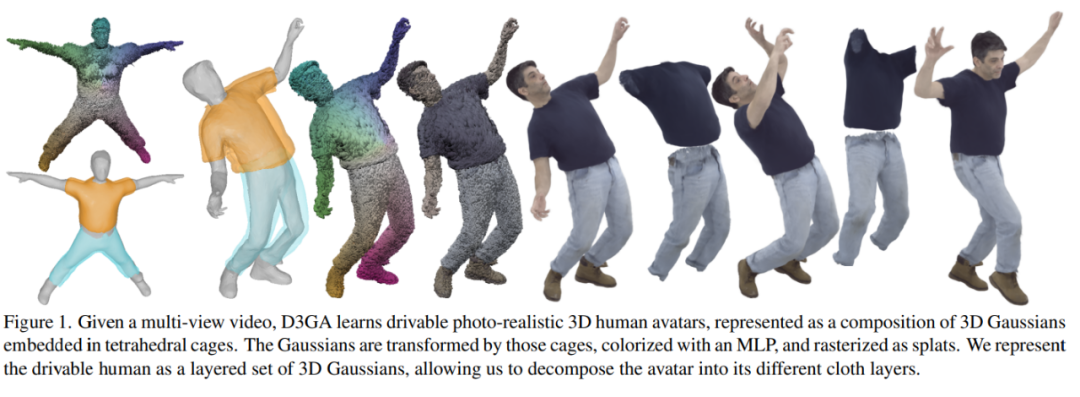


- Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2311.08581.pdf
- Project link: https ://zielon.github.io/d3ga/
Current methods for dynamically volumetricizing virtual characters either map points from deformation space to canonical space, Or just rely on forward mapping. Methods based on back mapping tend to accumulate errors in the canonical space because they require an error-prone back pass and are problematic in modeling perspective-dependent effects.
Therefore, the author decided to adopt a forward mapping only method. D3GA is based on 3DGS and extended through neural representation and cage to model the color and geometric shape of each dynamic part of the virtual character respectively.
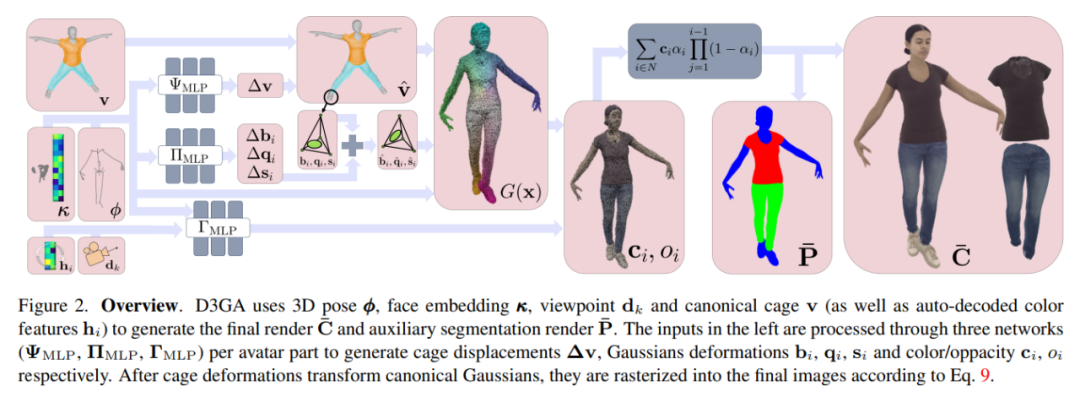
D3GA uses 3D pose ϕ, face embedding κ, viewpoint dk and canonical cage v (and automatically decoded color features hi) to generate the final Render C¯ and auxiliary segmentation render P¯. The input on the left is processed through three networks (ΨMLP, ΠMLP, ΓMLP) per virtual character part to generate cage displacement Δv, Gaussian deformations bi, qi, si, and color/transparency ci, oi.
After the cage deformation deforms the canonical Gaussian, they are rasterized into the final image via Equation 9.
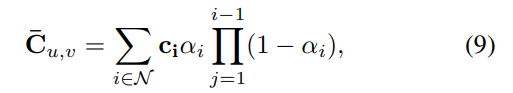
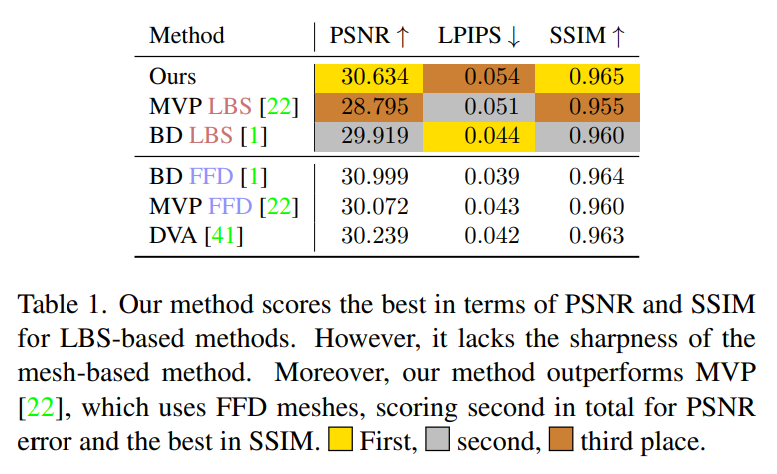
Experimental results
##D3GA in SSIM, PSNR and perceptual metric LPIPS Evaluate on other indicators. Table 1 shows that D3GA has the best performance in PSNR and SSIM among methods that only use LBS (that is, there is no need to scan 3D data for each frame), and outperforms all FFD methods in these indicators, second only to for BD FFD, despite its poor training signal and no test images (DVA was tested using all 200 cameras).
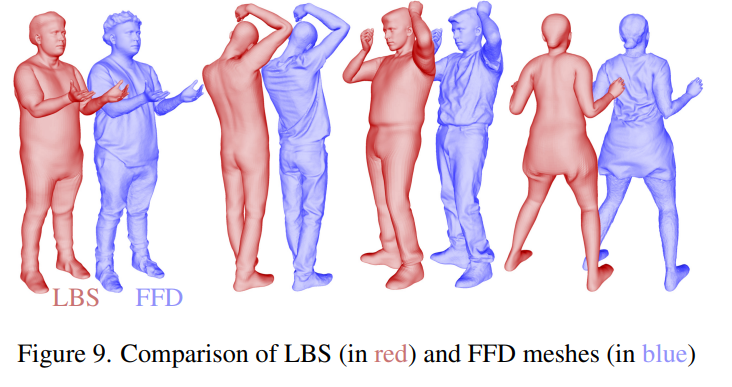
Qualitative comparison shows that D3GA can model clothing better than other state-of-the-art methods, especially Loose-fitting clothing like a skirt or sweatpants (picture 4). FFD stands for Free Deformation Mesh, which contains richer training signals than LBS meshes (Figure 9).

The above is the detailed content of Can AI research also learn from Impressionism? These lifelike people are actually 3D models. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
The return value types of C language function include int, float, double, char, void and pointer types. int is used to return integers, float and double are used to return floats, and char returns characters. void means that the function does not return any value. The pointer type returns the memory address, be careful to avoid memory leakage.结构体或联合体可返回多个相关数据。
 CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
Algorithms are the set of instructions to solve problems, and their execution speed and memory usage vary. In programming, many algorithms are based on data search and sorting. This article will introduce several data retrieval and sorting algorithms. Linear search assumes that there is an array [20,500,10,5,100,1,50] and needs to find the number 50. The linear search algorithm checks each element in the array one by one until the target value is found or the complete array is traversed. The algorithm flowchart is as follows: The pseudo-code for linear search is as follows: Check each element: If the target value is found: Return true Return false C language implementation: #include#includeintmain(void){i
 How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
Flexible application of function pointers: use comparison functions to find the maximum value of an array. First, define the comparison function type CompareFunc, and then write the comparison function compareMax(a, b). The findMax function accepts array, array size, and comparison function parameters, and uses the comparison function to loop to compare array elements to find the maximum value. This method has strong code reusability, reflects the idea of higher-order programming, and is conducive to solving more complex problems.
 What are c language function pointers and pointer functions? What's the difference?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
What are c language function pointers and pointer functions? What's the difference?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
A function pointer is a pointer to a function, and a pointer function is a function that returns a pointer. Function pointers point to functions, used to select and execute different functions; pointer functions return pointers to variables, arrays or other functions; when using function pointers, pay attention to parameter matching and checking pointer null values; when using pointer functions, pay attention to memory management and free dynamically allocated memory; understand the differences and characteristics of the two to avoid confusion and errors.
 What are the formats of function definition in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
What are the formats of function definition in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:51 PM
The key elements of C function definition include: return type (defining the value returned by the function), function name (following the naming specification and determining the scope), parameter list (defining the parameter type, quantity and order accepted by the function) and function body (implementing the logic of the function). It is crucial to clarify the meaning and subtle relationship of these elements, and can help developers avoid "pits" and write more efficient and elegant code.
 What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
The pointer parameters of C language function directly operate the memory area passed by the caller, including pointers to integers, strings, or structures. When using pointer parameters, you need to be careful to modify the memory pointed to by the pointer to avoid errors or memory problems. For double pointers to strings, modifying the pointer itself will lead to pointing to new strings, and memory management needs to be paid attention to. When handling pointer parameters to structures or arrays, you need to carefully check the pointer type and boundaries to avoid out-of-bounds access.
 Integers in C: a little history
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:09 AM
Integers in C: a little history
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:09 AM
Integers are the most basic data type in programming and can be regarded as the cornerstone of programming. The job of a programmer is to give these numbers meanings. No matter how complex the software is, it ultimately comes down to integer operations, because the processor only understands integers. To represent negative numbers, we introduced two's complement; to represent decimal numbers, we created scientific notation, so there are floating-point numbers. But in the final analysis, everything is still inseparable from 0 and 1. A brief history of integers In C, int is almost the default type. Although the compiler may issue a warning, in many cases you can still write code like this: main(void){return0;} From a technical point of view, this is equivalent to the following code: intmain(void){return0;}
 What do nested calls and recursive calls of c language functions mean respectively?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
What do nested calls and recursive calls of c language functions mean respectively?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:09 PM
C language function calls can be divided into nested calls and recursive calls. Nested calls refer to calling other functions within a function, nesting them layer by layer. Recursive calls refer to the function itself calling itself, which can be used to deal with self-similar structure problems. The key difference is that the functions in nested calls are called in sequence, with independent interaction scopes, while the functions in recursive calls are constantly called, so you need to pay attention to the recursive basis and stack overflow issues. Which calling method to choose depends on the specific requirements and performance requirements of the problem.





