Today I start a new series of courses about html5, which are my study notes from "The Definitive Guide to HTML5". I will sort out the chapters that I think are good or meaningful content for everyone to learn from.
An element can define its own attributes. For example, the a tag defines the href attribute. This is called a local attribute. Correspondingly, we can set common behaviors for all elements through global attributes. Of course, you can also set global attributes for individual elements, but this does not make much sense. I will introduce these global properties one by one below.
The following examples run normally in the Chrome browser. Some examples cannot run in Firefox. I have not tested other browsers, so I recommend that you use the Chrome browser as your preferred HTML5 browser. Instead of focusing on browser compatibility issues, I focused on learning and implementation. HTML5 is still being improved. With its popularity, I believe that mainstream browsers will support it better and better, and browser compatibility issues will be much better by then.
1.accesskey
The accesskey attribute allows you to set one or more keyboard shortcuts so that you can select elements on the page. Let’s look at the following example:
In this example, you can use key combinations to select elements on the page, such as in windows Under the operating system, you can use alt XXX to select an element.
Operating effect:

2.class I don’t want to say more about this attribute. It is a function of grouping elements. It is more often used in conjunction with CSS to set different display effects for different groups of elements. .
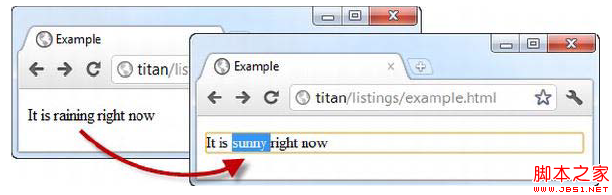
3.contenteditable This is a new attribute in html5. Add the contenteditable attribute to the html element. Set it to true to allow users to edit the element content; set it to false to not allow users to edit. .

4.contextmenu contextmenu allows users to set the right-click menu of html elements, and the menu will pop up when the user triggers it. No browsers yet support this attribute.
5.dir
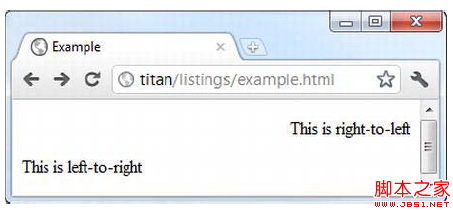
The dir attribute defines the alignment of the HTML element text and supports two values, ltr (left to right) and rtl (right to left).
Example
This is left-to-right

6. draggable draggable is the attribute that implements the drag and drop function of html elements in html5. We will introduce it in detail in the following courses.
7.dropzone dropzone is also an attribute that implements the drag and drop function of html elements in html5. We will introduce it in detail in the following courses.
8.hidden Everyone should be familiar with this attribute, which is to hide an html element.
9.id Everyone should know this attribute. It sets a unique identifier for the html element. Elements with the same id are not allowed to exist in an html page.
10.lang lang specifies the language used for the content of the html element. The value of lang must be a valid iso language code. You can visit the following address for more details, http://tools.ietf.org/html/bcp47. It should be noted that processing language is a rather complex and technical matter.
Example
Bonjour - comment êtes-vous?
Hola-¿ cómo estás?
11.spellcheck
When using the spellcheck attribute Sometimes, the browser will help you check whether the spelling of the text content of the html element is correct. The spellcheck attribute is meaningful only when the html element is editable.
Example