Find the storage location of installed pip packages

To explore the storage path of packages installed by pip, specific code examples are required
Introduction:
For Python developers, pip is indispensable Tool that can easily install and manage Python packages. However, sometimes we need to know the actual storage path of installed packages, which is very useful for debugging and locating problems. This article will show you how to explore the storage path of packages installed by pip through code examples.
Background:
When using pip to install a package, we usually only need to run a simple command, such as "pip install package_name". pip will then automatically download and install the required packages. However, pip's default behavior is to install packages into the system's default Python package directory, which is usually not what we want. Knowing the actual storage path of a package is very useful for understanding its internal structure, or modifying its contents.
Method:
To explore the storage path of packages installed by pip, we can use Python’s built-in modules site and sys. The following is a specific code example:
import site
import sys
def get_package_location(package_name):
# 获取当前 Python 解释器的 site-packages 路径
site_packages_path = site.getsitepackages()[0]
# 遍历 site-packages 目录下的所有包
for path in sys.path:
if path.startswith(site_packages_path):
package_path = path + '/' + package_name.replace('-', '_')
if package_path.endswith('.egg'):
package_path += '/EGG-INFO'
return package_path
# 调用示例:
package_name = 'requests'
location = get_package_location(package_name)
print(f"The location of package {package_name} is: {location}")This code first imports the site and sys modules. Then, a get_package_location function is defined, which accepts a package name as a parameter and returns the actual storage path of the package. In the
function, we first use the site.getsitepackages() method to obtain the site-packages path of the current Python interpreter. We then iterate through the sys.path list and find the path starting with the site-packages path. In this path, we replace the dashes in the package name with underscores and add the package suffix. If the package is an .egg file, we will also add /EGG-INFO to the path.
Finally, we use the example package name requests to call the get_package_location function, and then print out the storage path of the package.
Conclusion:
Through the above code example, we can easily obtain the actual storage path of the package installed by pip. This is useful for debugging, modifying, or inspecting the internal structure of a package. Mastering this skill will make our development work more efficient and flexible.
The above is the detailed content of Find the storage location of installed pip packages. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Solution to the problem that Win11 system cannot install Chinese language pack
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:48 AM
Solution to the problem that Win11 system cannot install Chinese language pack
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:48 AM
Solution to the problem that Win11 system cannot install Chinese language pack With the launch of Windows 11 system, many users began to upgrade their operating system to experience new functions and interfaces. However, some users found that they were unable to install the Chinese language pack after upgrading, which troubled their experience. In this article, we will discuss the reasons why Win11 system cannot install the Chinese language pack and provide some solutions to help users solve this problem. Cause Analysis First, let us analyze the inability of Win11 system to
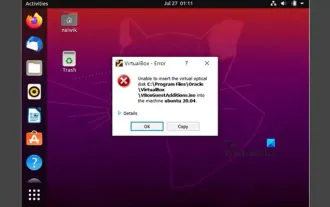 Unable to install guest additions in VirtualBox
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:34 AM
Unable to install guest additions in VirtualBox
Mar 10, 2024 am 09:34 AM
You may not be able to install guest additions to a virtual machine in OracleVirtualBox. When we click on Devices>InstallGuestAdditionsCDImage, it just throws an error as shown below: VirtualBox - Error: Unable to insert virtual disc C: Programming FilesOracleVirtualBoxVBoxGuestAdditions.iso into ubuntu machine In this post we will understand what happens when you What to do when you can't install guest additions in VirtualBox. Unable to install guest additions in VirtualBox If you can't install it in Virtua
 What should I do if Baidu Netdisk is downloaded successfully but cannot be installed?
Mar 13, 2024 pm 10:22 PM
What should I do if Baidu Netdisk is downloaded successfully but cannot be installed?
Mar 13, 2024 pm 10:22 PM
If you have successfully downloaded the installation file of Baidu Netdisk, but cannot install it normally, it may be that there is an error in the integrity of the software file or there is a problem with the residual files and registry entries. Let this site take care of it for users. Let’s introduce the analysis of the problem that Baidu Netdisk is successfully downloaded but cannot be installed. Analysis of the problem that Baidu Netdisk downloaded successfully but could not be installed 1. Check the integrity of the installation file: Make sure that the downloaded installation file is complete and not damaged. You can download it again, or try to download the installation file from another trusted source. 2. Turn off anti-virus software and firewall: Some anti-virus software or firewall programs may prevent the installation program from running properly. Try disabling or exiting the anti-virus software and firewall, then re-run the installation
 How to install Android apps on Linux?
Mar 19, 2024 am 11:15 AM
How to install Android apps on Linux?
Mar 19, 2024 am 11:15 AM
Installing Android applications on Linux has always been a concern for many users. Especially for Linux users who like to use Android applications, it is very important to master how to install Android applications on Linux systems. Although running Android applications directly on Linux is not as simple as on the Android platform, by using emulators or third-party tools, we can still happily enjoy Android applications on Linux. The following will introduce how to install Android applications on Linux systems.
 How to install Podman on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 22, 2024 am 11:26 AM
How to install Podman on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 22, 2024 am 11:26 AM
If you have used Docker, you must understand daemons, containers, and their functions. A daemon is a service that runs in the background when a container is already in use in any system. Podman is a free management tool for managing and creating containers without relying on any daemon such as Docker. Therefore, it has advantages in managing containers without the need for long-term backend services. Additionally, Podman does not require root-level permissions to be used. This guide discusses in detail how to install Podman on Ubuntu24. To update the system, we first need to update the system and open the Terminal shell of Ubuntu24. During both installation and upgrade processes, we need to use the command line. a simple
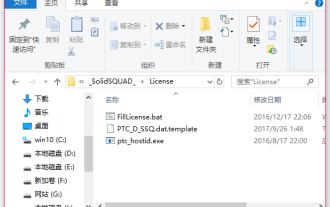 How to install creo-creo installation tutorial
Mar 04, 2024 pm 10:30 PM
How to install creo-creo installation tutorial
Mar 04, 2024 pm 10:30 PM
Many novice friends still don’t know how to install creo, so the editor below brings relevant tutorials on creo installation. Friends in need should take a look at it. I hope it can help you. 1. Open the downloaded installation package and find the License folder, as shown in the figure below: 2. Then copy it to the directory on the C drive, as shown in the figure below: 3. Double-click to enter and see if there is a license file, as shown below As shown in the picture: 4. Then copy the license file to this file, as shown in the following picture: 5. In the PROGRAMFILES file of the C drive, create a new PLC folder, as shown in the following picture: 6. Copy the license file as well Click in, as shown in the figure below: 7. Double-click the installation file of the main program. To install, check the box to install new software.
 How to Install and Run the Ubuntu Notes App on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 22, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
How to Install and Run the Ubuntu Notes App on Ubuntu 24.04
Mar 22, 2024 pm 04:40 PM
While studying in high school, some students take very clear and accurate notes, taking more notes than others in the same class. For some, note-taking is a hobby, while for others, it is a necessity when they easily forget small information about anything important. Microsoft's NTFS application is particularly useful for students who wish to save important notes beyond regular lectures. In this article, we will describe the installation of Ubuntu applications on Ubuntu24. Updating the Ubuntu System Before installing the Ubuntu installer, on Ubuntu24 we need to ensure that the newly configured system has been updated. We can use the most famous "a" in Ubuntu system
 Detailed steps to install Go language on Win7 computer
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
Detailed steps to install Go language on Win7 computer
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:00 PM
Detailed steps to install Go language on Win7 computer Go (also known as Golang) is an open source programming language developed by Google. It is simple, efficient and has excellent concurrency performance. It is suitable for the development of cloud services, network applications and back-end systems. . Installing the Go language on a Win7 computer allows you to quickly get started with the language and start writing Go programs. The following will introduce in detail the steps to install the Go language on a Win7 computer, and attach specific code examples. Step 1: Download the Go language installation package and visit the Go official website




