Best practices and optimization strategies for cookie settings

With the continuous development of Internet technology, user privacy protection has attracted more and more attention. As one of the most commonly used user tracking tools, cookies have also begun to be strictly regulated. This article will introduce cookie setting best practices and optimization strategies, and provide specific code examples.
What are cookies?
Cookie is a file that stores data on the user's computer, which contains user information sent by the browser to the server. By storing cookies on the user's computer, the server can track user behavior and provide a better user experience.
Best practices for setting cookies
Clear the purpose of use
Before using a cookie, you must clarify its purpose. For example, if you want to remember the user's login information the next time they visit, you can store the user's username or password in a cookie. However, before storing any user data, make sure you understand the relevant privacy policy and obtain the user's explicit consent.
Set the expiration time of Cookie
When setting a Cookie, its expiration time should be considered. The shorter the expiration time, the less likely user data will be stored on the computer for a long time, thus better protecting user privacy. However, the expiration time should not be too short, otherwise the user may have to log in again frequently.
Set the domain and path of the cookie
When setting the cookie, its domain and path must be specified. The domain defines the range of websites that can be accessed by the cookie, and the path defines the path of the web page that the cookie can access. By setting the correct domain and path, you can ensure that cookies are only sent to the correct website, thus enhancing security.
Disable Third-Party Cookies
Third-party cookies are cookies that are sent to the user's computer from other websites (not the website being visited). Since third-party cookies may be used for user tracking or advertising purposes, disabling third-party cookies can help protect user privacy.
Cookie optimization strategy
Limit the size of the cookie
If the size of the cookie exceeds the browser limit, then it will not be sent to the server. Therefore, to maximize cookie reliability, cookie size should be limited. Generally, the size of a cookie should not exceed 4KB.
Use the HttpOnly identifier
By using the HttpOnly identifier, you can effectively reduce the risk of cookies being used by attackers. After using the HttpOnly flag, JavaScript cannot use cookies, thus preventing common XSS attacks.
Sending Cookies in Encrypted Mode
User data can be protected from tampering or eavesdropping by sending Cookies in encrypted mode. Therefore, it is recommended to use encryption mode when transmitting cookies via SSL/TLS.
Specific code example
Set Cookie
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
|
Read Cookie
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
Delete Cookie
1 2 3 |
|
Conclusion
When using cookies, best practices and optimization strategies must be followed to protect user privacy and data security. By clarifying the purpose of use, setting the expiration time, domain and path, limiting the size, using the HttpOnly flag, and sending cookies in encrypted mode, you can ensure better performance and security of cookies.
The above is the detailed content of Best practices and optimization strategies for cookie settings. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to set the scheduled time for publishing works on Douyin? How does it set the video duration?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:11 PM
How to set the scheduled time for publishing works on Douyin? How does it set the video duration?
Mar 27, 2024 pm 06:11 PM
Publishing works on Douyin can attract more attention and likes, but sometimes it may be difficult for us to publish works in real time. In this case, we can use Douyin's scheduled release function. Douyin’s scheduled release function allows users to automatically publish works at a scheduled time, which can better plan the release plan and increase the exposure and influence of the work. 1. How to set the scheduled time for publishing works on Douyin? To set a scheduled release time, first go to Douyin's personal homepage, find the "+" button in the upper right corner, and click to enter the release page. There is a clock icon in the lower right corner of the publishing page. Click to enter the scheduled publishing interface. In the interface, you can choose the type of work you want to publish, including short videos, long videos, and live broadcasts. Next, you need to set a time for your work to be published. TikTok provides
 Setting up Chinese with VSCode: The Complete Guide
Mar 25, 2024 am 11:18 AM
Setting up Chinese with VSCode: The Complete Guide
Mar 25, 2024 am 11:18 AM
VSCode Setup in Chinese: A Complete Guide In software development, Visual Studio Code (VSCode for short) is a commonly used integrated development environment. For developers who use Chinese, setting VSCode to the Chinese interface can improve work efficiency. This article will provide you with a complete guide, detailing how to set VSCode to a Chinese interface and providing specific code examples. Step 1: Download and install the language pack. After opening VSCode, click on the left
 Where is the Douyin tag set? How can it be tagged so that it can be pushed accurately?
Mar 27, 2024 am 11:01 AM
Where is the Douyin tag set? How can it be tagged so that it can be pushed accurately?
Mar 27, 2024 am 11:01 AM
As one of the most popular short video platforms in the world, Douyin allows everyone to become a creator and share every moment of life. For Douyin users, tags are a very important function. It can help users better classify and retrieve content, and also allows the platform to push appropriate content to users more accurately. So, where are the Douyin tags set? This article will explain in detail how to set up and use tags on Douyin. 1. Where is the Douyin tag set? Using tags on Douyin can help users better classify and label their works, making it easier for other users to find and follow them. The method to set the label is as follows: 1. Open the Douyin APP and log in to your account. 2. Click the "+" sign at the bottom of the screen and select the "Publish" button. 3.
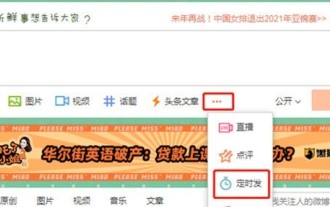 How to set up scheduled publishing on Weibo_Tutorial on how to set up scheduled publishing on Weibo
Mar 29, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
How to set up scheduled publishing on Weibo_Tutorial on how to set up scheduled publishing on Weibo
Mar 29, 2024 pm 03:51 PM
1. Open the Weibo client, click the three little dots on the editing page, and then click Scheduled Post. 2. After clicking on scheduled posting, there will be a time option on the right side of the publishing time. Set the time, edit the article, and click on the yellow words in the lower right corner to schedule posting. 3. The mobile version of Weibo does not currently support scheduled publishing. This function can only be used on the PC client!
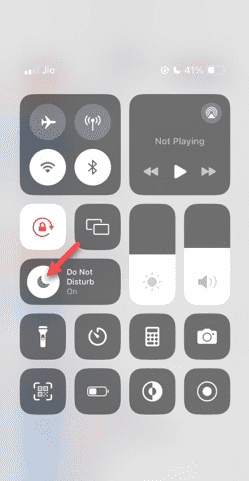 Do Not Disturb Mode Not Working in iPhone: Fix
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
Do Not Disturb Mode Not Working in iPhone: Fix
Apr 24, 2024 pm 04:50 PM
Even answering calls in Do Not Disturb mode can be a very annoying experience. As the name suggests, Do Not Disturb mode turns off all incoming call notifications and alerts from emails, messages, etc. You can follow these solution sets to fix it. Fix 1 – Enable Focus Mode Enable focus mode on your phone. Step 1 – Swipe down from the top to access Control Center. Step 2 – Next, enable “Focus Mode” on your phone. Focus Mode enables Do Not Disturb mode on your phone. It won't cause any incoming call alerts to appear on your phone. Fix 2 – Change Focus Mode Settings If there are some issues in the focus mode settings, you should fix them. Step 1 – Open your iPhone settings window. Step 2 – Next, turn on the Focus mode settings
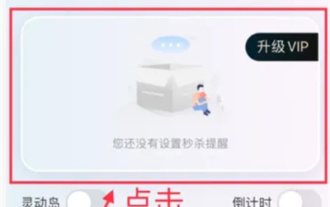 How to set the countdown to grab tickets in Damai
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:01 PM
How to set the countdown to grab tickets in Damai
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:01 PM
When buying tickets on Damai.com, in order to ensure that the ticket purchase time can be accurately grasped, users can set a floating clock to grab tickets. The detailed setting method is below, let us learn together. How to bind the floating clock to Damai 1. Click to open the floating clock app on your phone to enter the interface, and click on the location where the flash sale check is set, as shown in the figure below: 2. After coming to the page of adding new records, click on Damai.com Copy the ticket purchase link page copied in. 3. Next, set the flash sale time and notification time below, turn on the switch button behind [Save to Calendar], and click [Save] below. 4. Click to turn on [Countdown], as shown in the figure below: 5. When the reminder time comes, click the [Start Picture-in-Picture] button below. 6. When the ticket purchase time comes
 Where to set Douyin recommendations and selections
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:06 PM
Where to set Douyin recommendations and selections
Mar 27, 2024 pm 05:06 PM
Where are the recommendations and selections on Douyin? In Douyin short videos, there are two categories: selection and recommendation. Most users don’t know how to set up recommendations and selections. Next is the Douyin tutorial that the editor brings to users. Audio recommendations and selected setting method tutorials, interested users come and take a look! Douyin usage tutorial Where to set up Douyin recommendations and selections 1. First open the Douyin short video APP and enter the main page, click on the [Me] area in the lower right corner and select [three horizontal lines] in the upper right corner; 2. Then on the right The function bar will expand, slide the page to select [Settings] at the bottom; 3. Then on the settings function page, find the [Personal Information Management] service; 4. Finally jump to the personal information management page, slide [Personalized Content Recommendations] 】The buttons on the back can be set.
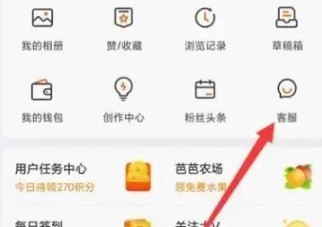 How to set the watermark in the middle on Weibo_How to set the watermark in the middle on Weibo
Mar 29, 2024 pm 03:31 PM
How to set the watermark in the middle on Weibo_How to set the watermark in the middle on Weibo
Mar 29, 2024 pm 03:31 PM
1. First enter Weibo, then click on me in the lower right corner and select [Customer Service]. 2. Then enter [Watermark] in the search box and select [Set Weibo Image Watermark]. 3. Then click [Link] in the interface. 4. Then click [Image Watermark Settings] in the newly opened window. 5. Finally, check [Picture Center] and click [Save].




