Numpy version selection guide: why upgrade?

With the rapid development of fields such as data science, machine learning, and deep learning, Python has become a mainstream language for data analysis and modeling. In Python, NumPy (short for Numerical Python) is a very important library because it provides a set of efficient multi-dimensional array objects and is the basis for many other libraries such as pandas, SciPy and scikit-learn.
In the process of using NumPy, you are likely to encounter compatibility issues between different versions. So how do we choose the NumPy version?
NumPy version update instructions
The most stable version of NumPy is currently 1.20.3, but there are also many people using older versions such as 1.16.x, 1.17.x and 1.19.x. What are the main differences between these versions?
On the NumPy official website, you can find the change log for each version. Taking version 1.19.0 as an example, we can see the following updates:
- New features: Added polynomial module polynomial, binomial distribution module binomial, beta distribution module beta, etc.
- Optimization: Improved the electrical detector function nextafter, and added more tools to support flags and subclasses of dtypes in the array methods mean, std, var, etc.
- Improvement: The array sorting method sort has been improved, and the performance has been increased by 100 times when the array needs to be updated.
- Removal: Removed some obsolete functions and modules, such as allow_unreachable, FreeList and umath.
It can be found that each version basically introduces new features, makes some optimizations and improvements, and removes some outdated content.
Why upgrade?
After understanding the updates between different versions, let’s think about it again: Why should we upgrade the NumPy version?
First, new versions usually fix some known problems or defects. If you encounter some serious problems in the old version and these problems have been solved in the new version, then it is necessary to upgrade to the new version.
Second, new versions usually add some new features or modules. These features may be more powerful, efficient, or easier to use and better meet our needs.
Third, new versions usually have some performance optimizations. These optimizations may make the NumPy library faster, allowing for faster calculations.
However, upgrading to a new version may also have some side effects. If your code ran fine in an older version but has some compatibility issues in the newer version, your code may not run properly.
Steps to upgrade to a new version
If you decide to upgrade to a new version of NumPy, you need to pay attention to the following steps:
1. Check the compatibility of old code
Before upgrading NumPy, it is best to first check whether the old code is compatible with the new version. The sample code is as follows:
import numpy as np a = np.arange(5) print(a)
If you are using version 1.16.x or older, the output should be: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4]). However, in 1.17.x and newer, arrays are displayed by default using a more compact format: [0 1 2 3 4]. If your code relies on printing array elements, you may need to change your code accordingly.
2. Install the new version
Next, you can upgrade NumPy through package managers such as pip. Take upgrading to 1.20.x as an example:
pip install numpy --upgrade
3. Modify the code
If you encounter some incompatibility problems with the new version after upgrading, then you need to modify the code accordingly. For example, some old APIs may have been removed or replaced with new APIs, or the default values of some parameters have been changed. Checking NumPy's official documentation can help you understand these changes and make corresponding modifications in a timely manner.
Summary
NumPy is a very important Python library in fields such as data science and machine learning. Choosing the right version is essential to properly implement data analysis and learning. When choosing a version of NumPy, we should understand the compatibility issues between different versions, as well as the new features, performance optimizations and fixes in the new version.
Although upgrading NumPy to a new version may cause some compatibility issues, generally speaking, upgrading to a new version can achieve better performance and stronger feature support. It is best to always keep the latest stable version of NumPy and pay attention to compatibility issues and make modifications in time.
The above is the detailed content of Numpy version selection guide: why upgrade?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Tutorial on updating curl version under Linux!
Mar 07, 2024 am 08:30 AM
Tutorial on updating curl version under Linux!
Mar 07, 2024 am 08:30 AM
To update the curl version under Linux, you can follow the steps below: Check the current curl version: First, you need to determine the curl version installed in the current system. Open a terminal and execute the following command: curl --version This command will display the current curl version information. Confirm available curl version: Before updating curl, you need to confirm the latest version available. You can visit curl's official website (curl.haxx.se) or related software sources to find the latest version of curl. Download the curl source code: Using curl or a browser, download the source code file for the curl version of your choice (usually .tar.gz or .tar.bz2
 Upgrading numpy versions: a detailed and easy-to-follow guide
Feb 25, 2024 pm 11:39 PM
Upgrading numpy versions: a detailed and easy-to-follow guide
Feb 25, 2024 pm 11:39 PM
How to upgrade numpy version: Easy-to-follow tutorial, requires concrete code examples Introduction: NumPy is an important Python library used for scientific computing. It provides a powerful multidimensional array object and a series of related functions that can be used to perform efficient numerical operations. As new versions are released, newer features and bug fixes are constantly available to us. This article will describe how to upgrade your installed NumPy library to get the latest features and resolve known issues. Step 1: Check the current NumPy version at the beginning
 Tutorial on how to solve the problem of being unable to access the Internet after upgrading win10 system
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
Tutorial on how to solve the problem of being unable to access the Internet after upgrading win10 system
Mar 27, 2024 pm 02:26 PM
1. Use the win+x shortcut key to open the menu and select [Command Prompt (Administrator) (A)], as shown below: 2. After entering the command prompt interface, enter the [ipconfig/flushdns] command and press Enter , as shown in the figure below: 3. Then enter the [netshwinsockresetcatalog] command and press Enter, as shown in the figure below: 4. Finally enter the [netshintipreset] command and press Enter, restart the computer and you can access the Internet, as shown in the figure below:
 How to easily check the installed version of Oracle
Mar 07, 2024 am 11:27 AM
How to easily check the installed version of Oracle
Mar 07, 2024 am 11:27 AM
How to easily check the installed version of Oracle requires specific code examples. As a software widely used in enterprise-level database management systems, the Oracle database has many versions and different installation methods. In our daily work, we often need to check the installed version of the Oracle database for corresponding operations and maintenance. This article will introduce how to easily check the installed version of Oracle and give specific code examples. Method 1: Through SQL query in the Oracle database, we can
 Check the Kirin operating system version and kernel version
Feb 21, 2024 pm 07:04 PM
Check the Kirin operating system version and kernel version
Feb 21, 2024 pm 07:04 PM
Checking the Kylin operating system version and kernel version In the Kirin operating system, knowing how to check the system version and kernel version is the basis for system management and maintenance. Method 1 to check the Kylin operating system version: Use the /etc/.kyinfo file. To check the Kylin operating system version, you can check the /etc/.kyinfo file. This file contains operating system version information. Execute the following command: cat/etc/.kyinfo This command will display detailed version information of the operating system. Method 2: Use the /etc/issue file Another way to check the operating system version is by looking at the /etc/issue file. This file also provides version information, but may not be as good as the .kyinfo file
 How to upgrade Xiaohongshu to a professional account
Mar 01, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
How to upgrade Xiaohongshu to a professional account
Mar 01, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
Many friends expressed that they want to know how to upgrade to a professional account in Xiaohongshu. Here I will introduce the operation method. If you are interested, come and take a look with me. Open the "Little Red Book" APP on your mobile phone, click the "My" option in the lower right corner after entering it, then find the "three horizontal lines" icon in the upper left corner of the My page and click to open it. 2. A menu page will pop up, in which click to select the "Creation Center" item to enter. 3. Next, find "More Services" in the options under "Creation Services" on the page you enter, and click on it to enter. 4. After the page jumps, click "Open a Professional Account" in the options under "Author Capabilities". 5. Finally, the Xiaohongshu Professional Account will be introduced on the entered page. Click "
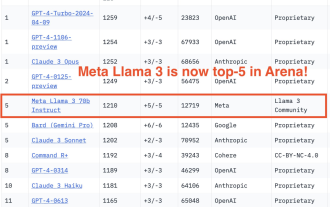 750,000 rounds of one-on-one battle between large models, GPT-4 won the championship, and Llama 3 ranked fifth
Apr 23, 2024 pm 03:28 PM
750,000 rounds of one-on-one battle between large models, GPT-4 won the championship, and Llama 3 ranked fifth
Apr 23, 2024 pm 03:28 PM
Regarding Llama3, new test results have been released - the large model evaluation community LMSYS released a large model ranking list. Llama3 ranked fifth, and tied for first place with GPT-4 in the English category. The picture is different from other benchmarks. This list is based on one-on-one battles between models, and the evaluators from all over the network make their own propositions and scores. In the end, Llama3 ranked fifth on the list, followed by three different versions of GPT-4 and Claude3 Super Cup Opus. In the English single list, Llama3 overtook Claude and tied with GPT-4. Regarding this result, Meta’s chief scientist LeCun was very happy and forwarded the tweet and
 Xiaoyi upgraded to an intelligent agent! HarmonyOS NEXT Hongmeng native intelligence opens a new AI era
Jun 22, 2024 am 01:56 AM
Xiaoyi upgraded to an intelligent agent! HarmonyOS NEXT Hongmeng native intelligence opens a new AI era
Jun 22, 2024 am 01:56 AM
On June 21, Huawei Developer Conference 2024 (HDC2024) gathered again in Songshan Lake, Dongguan. At this conference, the most eye-catching thing is that HarmonyOSNEXT officially launched Beta for developers and pioneer users, and comprehensively demonstrated the three "king-breaking" innovative features of HarmonyOSNEXT in all scenarios, native intelligence and native security. HarmonyOSNEXT native intelligence: Opening a new AI era After abandoning the Android framework, HarmonyOSNEXT has become a truly independent operating system independent of Android and iOS, which can be called an unprecedented rebirth. Among its many new features, native intelligence is undoubtedly the new feature that can best bring users intuitive feelings and experience upgrades.




