Optimization algorithm: Moth chasing light (MFO)
The moth into flame optimization algorithm (MFO) is a meta-heuristic algorithm that solves various optimization problems by imitating the movement of moths. The algorithm has been widely used in fields such as power and energy systems, economic dispatch, engineering design, image processing, and medical applications.
Inspiration for the Moth Fighting into the Flame Optimization Algorithm (MFO)
At night, moths often gather around lights. This is due to the fact that they rely on a mechanism of lateral positioning for specialized navigation. Moths need a distant light source to fly in a straight line, and they will maintain a fixed angle to the light source. Although lateral positioning is effective, moths are often observed flying in a spiral around the light. This is because moths are tricked by artificial light, causing them to exhibit this behavior. In order to maintain a constant angle to the light source, the moth will eventually circle around the light source.
Moth to Flame Optimization Algorithm (MFO) Flowchart

Moth to Flame Optimization Algorithm (MFO) Logic
In the Moth to Flame Optimization Algorithm ( In MFO), the candidate solution is assumed to be a moth, and the problem variable is the position of the moth in space. Therefore, moths can fly through space by changing their position vector.
It is important to note that both moths and flames are solutions, but they are processed and updated differently in each iteration.
The moth is a position that moves in the search space, and the flame represents the best position of the moth obtained so far. In other words, the flame can be seen as a central guiding point for the moths in their search, around which each moth searches and updates as it finds a better solution. This mechanism allows the moth algorithm to always maintain an optimal solution.
The above is the detailed content of Optimization algorithm: Moth chasing light (MFO). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1375
1375
 52
52
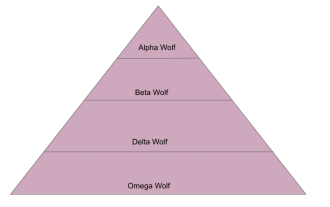 An in-depth analysis of the Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm (GWO) and its strengths and weaknesses
Jan 19, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
An in-depth analysis of the Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm (GWO) and its strengths and weaknesses
Jan 19, 2024 pm 07:48 PM
The Gray Wolf Optimization Algorithm (GWO) is a population-based metaheuristic algorithm that simulates the leadership hierarchy and hunting mechanism of gray wolves in nature. Gray Wolf Algorithm Inspiration 1. Gray wolves are considered to be apex predators and are at the top of the food chain. 2. Gray wolves like to live in groups (living in groups), with an average of 5-12 wolves in each pack. 3. Gray wolves have a very strict social dominance hierarchy, as shown below: Alpha wolf: Alpha wolf occupies a dominant position in the entire gray wolf group and has the right to command the entire gray wolf group. In the application of algorithms, Alpha Wolf is one of the best solutions, the optimal solution produced by the optimization algorithm. Beta wolf: Beta wolf reports to Alpha wolf regularly and helps Alpha wolf make the best decisions. In algorithm applications, Beta Wolf can
 Explore the basic principles and implementation process of nested sampling algorithms
Jan 22, 2024 pm 09:51 PM
Explore the basic principles and implementation process of nested sampling algorithms
Jan 22, 2024 pm 09:51 PM
The nested sampling algorithm is an efficient Bayesian statistical inference algorithm used to calculate the integral or summation under complex probability distributions. It works by decomposing the parameter space into multiple hypercubes of equal volume, and gradually and iteratively "pushing out" one of the smallest volume hypercubes, and then filling the hypercube with random samples to better estimate the integral value of the probability distribution. . Through continuous iteration, the nested sampling algorithm can obtain high-precision integral values and boundaries of parameter space, which can be applied to statistical problems such as model comparison, parameter estimation, and model selection. The core idea of this algorithm is to transform complex integration problems into a series of simple integration problems, and approach the real integral value by gradually reducing the volume of the parameter space. Each iteration step randomly samples from the parameter space
 Analyze the principles, models and composition of the Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA)
Jan 19, 2024 pm 10:27 PM
Analyze the principles, models and composition of the Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA)
Jan 19, 2024 pm 10:27 PM
The Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA) is a meta-heuristic optimization algorithm based on the anti-predation and foraging behavior of sparrows. The foraging behavior of sparrows can be divided into two main types: producers and scavengers. Producers actively search for food, while scavengers compete for food from producers. Principle of Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA) In Sparrow Search Algorithm (SSA), each sparrow pays close attention to the behavior of its neighbors. By employing different foraging strategies, individuals are able to efficiently use retained energy to pursue more food. Additionally, birds are more vulnerable to predators in their search space, so they need to find safer locations. Birds at the center of a colony can minimize their own range of danger by staying close to their neighbors. When a bird spots a predator, it makes an alarm call to
 What is the role of information gain in the id3 algorithm?
Jan 23, 2024 pm 11:27 PM
What is the role of information gain in the id3 algorithm?
Jan 23, 2024 pm 11:27 PM
The ID3 algorithm is one of the basic algorithms in decision tree learning. It selects the best split point by calculating the information gain of each feature to generate a decision tree. Information gain is an important concept in the ID3 algorithm, which is used to measure the contribution of features to the classification task. This article will introduce in detail the concept, calculation method and application of information gain in the ID3 algorithm. 1. The concept of information entropy Information entropy is a concept in information theory, which measures the uncertainty of random variables. For a discrete random variable number, and p(x_i) represents the probability that the random variable X takes the value x_i. letter
 Introduction to Wu-Manber algorithm and Python implementation instructions
Jan 23, 2024 pm 07:03 PM
Introduction to Wu-Manber algorithm and Python implementation instructions
Jan 23, 2024 pm 07:03 PM
The Wu-Manber algorithm is a string matching algorithm used to search strings efficiently. It is a hybrid algorithm that combines the advantages of Boyer-Moore and Knuth-Morris-Pratt algorithms to provide fast and accurate pattern matching. Wu-Manber algorithm step 1. Create a hash table that maps each possible substring of the pattern to the pattern position where that substring occurs. 2. This hash table is used to quickly identify potential starting locations of patterns in text. 3. Iterate through the text and compare each character to the corresponding character in the pattern. 4. If the characters match, you can move to the next character and continue the comparison. 5. If the characters do not match, you can use a hash table to determine the next potential character in the pattern.
 Numerical optimization principles and analysis of the Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA)
Jan 19, 2024 pm 07:27 PM
Numerical optimization principles and analysis of the Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA)
Jan 19, 2024 pm 07:27 PM
The Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) is a nature-inspired metaheuristic optimization algorithm that simulates the hunting behavior of humpback whales and is used for the optimization of numerical problems. The Whale Optimization Algorithm (WOA) starts with a set of random solutions and optimizes based on a randomly selected search agent or the best solution so far through position updates of the search agent in each iteration. Whale Optimization Algorithm Inspiration The Whale Optimization Algorithm is inspired by the hunting behavior of humpback whales. Humpback whales prefer food found near the surface, such as krill and schools of fish. Therefore, humpback whales gather food together to form a bubble network by blowing bubbles in a bottom-up spiral when hunting. In an "upward spiral" maneuver, the humpback whale dives about 12m, then begins to form a spiral bubble around its prey and swims upward
 Scale Invariant Features (SIFT) algorithm
Jan 22, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
Scale Invariant Features (SIFT) algorithm
Jan 22, 2024 pm 05:09 PM
The Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT) algorithm is a feature extraction algorithm used in the fields of image processing and computer vision. This algorithm was proposed in 1999 to improve object recognition and matching performance in computer vision systems. The SIFT algorithm is robust and accurate and is widely used in image recognition, three-dimensional reconstruction, target detection, video tracking and other fields. It achieves scale invariance by detecting key points in multiple scale spaces and extracting local feature descriptors around the key points. The main steps of the SIFT algorithm include scale space construction, key point detection, key point positioning, direction assignment and feature descriptor generation. Through these steps, the SIFT algorithm can extract robust and unique features, thereby achieving efficient image processing.
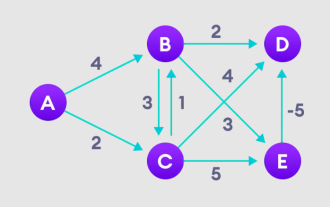 Detailed explanation of Bellman Ford algorithm and implementation in Python
Jan 22, 2024 pm 07:39 PM
Detailed explanation of Bellman Ford algorithm and implementation in Python
Jan 22, 2024 pm 07:39 PM
Bellman Ford algorithm can find the shortest path from the target node to other nodes in the weighted graph. This is very similar to the Dijkstra algorithm. The Bellman-Ford algorithm can handle graphs with negative weights and is relatively simple in terms of implementation. Detailed explanation of the principle of Bellman Ford algorithm The Bellman Ford algorithm iteratively finds new paths shorter than the overestimated paths by overestimating the path lengths from the starting vertex to all other vertices. Because we want to record the path distance of each node, we can store it in an array of size n, where n also represents the number of nodes. Example Figure 1. Select the starting node, assign it to all other vertices infinitely, and record the path value. 2. Visit each edge and perform relaxation operations to continuously update the shortest path. 3. We need



