What is the method to restore XP system boot?
How to restore the boot of XP system
Commonly used system fault recovery commands:
1. Bootcfg: used to configure and restore the startup file BOOT.INI (Win 2K does not have this command).
2. Disable and Enable: used to disable/enable system services or device drivers.
3. Expand: used to extract files from compressed files.
4. FixBoot: Rewrite the new partition boot area to the specified system partition.
5. FixMBR: Repair the master boot record of the startup disk.
6. Help: Display help.
7. Listsvc: List all system services and device drivers on the system (used with Disable/Enable).
8. Set: Display and set environment variables.
When a Windows 2000 or XP system fails, it can usually be repaired through "Last Known Good Configuration", "Safe Mode", and "System Restore" (only for XP). However, there are some situations that cannot be repaired through these methods, such as: system boot files are missing, BOOT.INI files are missing or misconfigured, system DLLs are missing, etc. At this time, although reinstalling the operating system is an effective method, it will take a long time. In fact, you can also make a final attempt by restoring the console. Using the recovery console, you can not only perform operations such as enabling and disabling system services, partitioning and formatting disks, repairing boot records, etc., but you can also repair errors such as missing system files by copying files from the source disc, etc.
How to establish dual system boot
It is very easy to install Windows 7 on XP! There should be no problem! One thing is that you must have XP before installing Windows 7. There will be two systems to choose from when you turn it on. You can use whichever one you like. Your current problem may be that you have turned off the dual boot setting!
1.[boot loader]
timeout=30
default=multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)WINDOWS
[operating systems]
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(1)WINDOWS="Microsoft Windows XP Professional"/fastdetect
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(2)WINNT="Microsoft Windows 2000 Professional"/fastdetect
2. After booting into the system, right-click My Computer-Properties-Advanced-Startup and Recovery-Settings-Edit, and add at the end:
multi(0)disk(0)rdisk(0)partition(2)\WINDOWS="Microsoft Windows XP
Professional" /noexecute=optin /fastdetect Then save and restart to try.
How to manually repair the boot file of XPVista dual system
Starting from Windows Vista, the startup manager of the operating system is no longer the NTLDR boot.ini used in Windows 2000/XP/Server 2003, but uses a new startup configuration database storage (BCD). When installing an earlier version of Windows operating system on a Windows Vista-based computer, the installer will overwrite everything in the MBR, boot sector, and boot files. In this case, we can no longer use the boot from the earlier version of Windows operating system. .ini file to boot Windows Vista. Even if you open the boot.ini file in Notepad, you will only see the prompt message shown in Figure 1 (please pay attention to the red frame in the figure).
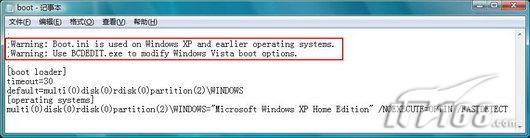
Figure 1 boot.ini file in the operating system
If the wrong facts have already been formed, we don’t have to worry at all. Here is an example of installing Windows Vista on the D drive and then formatting the C drive and reinstalling Windows XP due to some reasons. Follow the steps below to fix it manually:
Step 1: Restore MBR and restore boot manager
Use the Windows Vista installation CD to boot the computer, follow the order of selecting the installation language, time and currency format, keyboard and input method. After entering the installation program interface, select "Repair Computer" from the lower left corner, and then select "Repair Computer" on the next screen. Command Prompt" (see Figure 2), manually enter the following command in the command prompt environment and run: bootsect -nt60 all
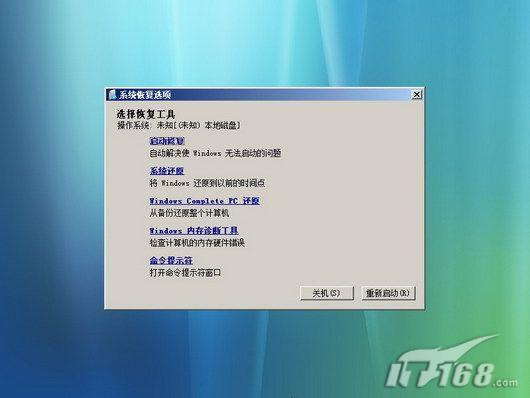
Figure 2 Vista System Recovery Tool
Step 2: Rebuild BCD
Still execute the "bootrec /RebuildBcd" command in the command prompt environment. This command will scan all disks for Windows Vista-compatible installations and re-add them to the newly generated BCD storage. Note here The rebuild of BCD is completely thorough.
Step 3: Manually add Windows XP projects
It should be pointed out that since "bootrec /RebuildBcd" only detects Windows Vista and Windows Server 2008, it cannot detect and discover Windows XP. Therefore, we can only add Windows XP to BCD manually, otherwise multi-boot will occur. Only Windows Vista will appear in the menu, not Windows XP.
The bcdedit.exe command line tool can modify the startup configuration data storage. We can enter the following commands in the command prompt environment and execute them. The content in parentheses indicates the explanation of the command. There is no need to enter during execution:
bcdedit /create {ntldr} /d "Early Versions of Windows" (Create a new item named "Early Versions of Windows" in the storage)
bcdedit /set {ntldr} device partition=C: (Set the item option value in storage and set the application device to the C: partition)
bcdedit /set {ntldr} path\ntldr
bcdedit /displayorder {ntldr} /addlast (Set the order in which multi-boot menus are displayed in the boot manager)
In the above command, the tag "{ntldr}" is used to specify the OS loader that can be used to start operating systems earlier than Windows Vista. The information of "early versions of Windows" can be changed freely; "PARTITION=C :" means the active partition of the hard disk where NTLDR is located. Please modify the command according to the actual situation; "/addlast" means adding the specified item identifier to the end of the display sequence. For more available parameters of bcdedit.exe, please view the help file.
Finally, of course you need to restart the system. At this time you will find that the problem has been solved. Friends who need this can give it a try.
The above is the detailed content of What is the method to restore XP system boot?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Discover How to Fix Drive Health Warning in Windows Settings
Mar 19, 2025 am 11:10 AM
Discover How to Fix Drive Health Warning in Windows Settings
Mar 19, 2025 am 11:10 AM
What does the drive health warning in Windows Settings mean and what should you do when you receive the disk warning? Read this php.cn tutorial to get step-by-step instructions to cope with this situation.
 How do I edit the Registry? (Warning: Use with caution!)
Mar 21, 2025 pm 07:46 PM
How do I edit the Registry? (Warning: Use with caution!)
Mar 21, 2025 pm 07:46 PM
Article discusses editing Windows Registry, precautions, backup methods, and potential issues from incorrect edits. Main issue: risks of system instability and data loss from improper changes.
 How do I manage services in Windows?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 07:52 PM
How do I manage services in Windows?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 07:52 PM
Article discusses managing Windows services for system health, including starting, stopping, restarting services, and best practices for stability.
 How to Fix the Steam Cloud Error? Try These Methods
Apr 04, 2025 am 01:51 AM
How to Fix the Steam Cloud Error? Try These Methods
Apr 04, 2025 am 01:51 AM
The Steam Cloud error can be caused by many reasons. To play a game smoothly, you need to take some measures to remove this error before you launch the game. php.cn Software introduces some best ways as well as more useful information in this post.
 Windows Metadata and Internet Services Problem: How to Fix It?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
Windows Metadata and Internet Services Problem: How to Fix It?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
You may see the “A connection to the Windows Metadata and Internet Services (WMIS) could not be established.” error on Event Viewer. This post from php.cn introduces how to remove the Windows Metadata and Internet Services problem.
 How do I change the default app for a file type?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 07:48 PM
How do I change the default app for a file type?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 07:48 PM
Article discusses changing default apps for file types on Windows, including reverting and bulk changes. Main issue: no built-in bulk change option.
 How to Resolve the KB5035942 Update Issues – Crashing System
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:16 PM
How to Resolve the KB5035942 Update Issues – Crashing System
Apr 02, 2025 pm 04:16 PM
KB5035942 update issues - crashing system commonly happens to users. Inflicted people hope to find a way out of the kind of trouble, such as crashing system, installation, or sound issues. Targeting these situations, this post published by php.cn wil
 How do I use the Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc)?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 07:48 PM
How do I use the Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc)?
Mar 21, 2025 pm 07:48 PM
The article explains how to use the Group Policy Editor (gpedit.msc) in Windows for managing system settings, highlighting common configurations and troubleshooting methods. It notes that gpedit.msc is unavailable in Windows Home editions, suggesting




