What is the role of information gain in the id3 algorithm?

The ID3 algorithm is one of the basic algorithms in decision tree learning. It selects the best split point by calculating the information gain of each feature to generate a decision tree. Information gain is an important concept in the ID3 algorithm, which is used to measure the contribution of features to the classification task. This article will introduce in detail the concept, calculation method and application of information gain in the ID3 algorithm.
1. The concept of information entropy
Information entropy is a concept in information theory that measures the uncertainty of random variables. For a discrete random variable
Among them, n represents the number of possible values of the random variable X, and p(x_i) represents the probability that the random variable X takes the value x_i. The unit of information entropy is bit, which is used to measure the minimum number of bits required to averagely encode a random variable.
The larger the value of information entropy, the more uncertain the random variable is, and vice versa. For example, for a random variable with only two possible values, if the probabilities of the two values are equal, then its information entropy is 1, which means that a coding length of 1 bit is needed to encode it; if the probability of one of the values is is 1, and the probability of another value is 0, then its information entropy is 0, which means that its value can be determined without coding.
2. The concept of conditional entropy
In decision tree learning, we need to calculate the contribution of features to the classification task. In order to measure the classification ability of a feature, we can calculate the uncertainty of classification with the feature given the feature, which is the conditional entropy. Assume that feature A has m values. For each value, we can calculate the probability distribution of the target variable under this value, calculate the corresponding information entropy, and finally find the conditional entropy, which is defined as follows:
H(Y|X)=\sum_{i=1}^{m}\frac{|X_i|}{|X|}H(Y|X=X_i)
Among them, |X| represents the size of the sample set is the information entropy of the target variable Y under the condition of A_i.
3. The concept of information gain
Information gain refers to using A to divide the sample set X under the condition that the feature A is known The amount of reduction in information entropy that can be obtained. The greater the information gain, the greater the information entropy obtained by using feature A to divide the sample set X is reduced, that is, the greater the contribution of feature A to the classification task. The definition of information gain is as follows:
IG(Y,X)=H(Y)-H(Y|X)
Where, H(Y) is the information entropy of the target variable Y, and H(Y|X) is the conditional entropy of the target variable Y under the condition of feature A.
4. Information gain calculation in ID3 algorithm
In the ID3 algorithm, we need to select the best features to divide the sample set X . For each feature A, we can calculate its information gain and select the feature with the largest information gain as the dividing point. Specifically, for each feature A, we can first calculate the number of samples with each value under the feature, then calculate the probability distribution of the target variable with each value under the feature, and calculate the corresponding information entropy . Then, we can calculate the conditional entropy of feature A, and subtract the conditional entropy from the information entropy to get the information gain. Finally, we select the feature with the largest information gain as the dividing point.
In practical applications, in order to prevent overfitting, we usually optimize the information gain, such as using gain ratio to select the best features. The gain ratio is the ratio of information gain to feature entropy, which represents the information gain obtained by using feature A to divide the sample set X relative to the information content of feature A itself. Gain ratio can solve the problem that information gain tends to select features with more values when features have more values.
In short, information gain is a very important concept in the ID3 algorithm, which is used to measure the contribution of a feature to the classification task. In the ID3 algorithm, we select the best split point by calculating the information gain of each feature, thereby generating a decision tree. In practical applications, we can optimize the information gain, such as using gain ratio to select the best features.
The above is the detailed content of What is the role of information gain in the id3 algorithm?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 15 recommended open source free image annotation tools
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:21 PM
15 recommended open source free image annotation tools
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:21 PM
Image annotation is the process of associating labels or descriptive information with images to give deeper meaning and explanation to the image content. This process is critical to machine learning, which helps train vision models to more accurately identify individual elements in images. By adding annotations to images, the computer can understand the semantics and context behind the images, thereby improving the ability to understand and analyze the image content. Image annotation has a wide range of applications, covering many fields, such as computer vision, natural language processing, and graph vision models. It has a wide range of applications, such as assisting vehicles in identifying obstacles on the road, and helping in the detection and diagnosis of diseases through medical image recognition. . This article mainly recommends some better open source and free image annotation tools. 1.Makesens
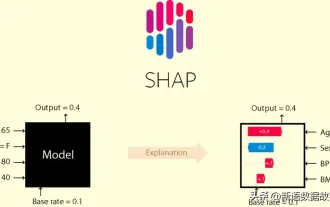 This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
In the fields of machine learning and data science, model interpretability has always been a focus of researchers and practitioners. With the widespread application of complex models such as deep learning and ensemble methods, understanding the model's decision-making process has become particularly important. Explainable AI|XAI helps build trust and confidence in machine learning models by increasing the transparency of the model. Improving model transparency can be achieved through methods such as the widespread use of multiple complex models, as well as the decision-making processes used to explain the models. These methods include feature importance analysis, model prediction interval estimation, local interpretability algorithms, etc. Feature importance analysis can explain the decision-making process of a model by evaluating the degree of influence of the model on the input features. Model prediction interval estimate
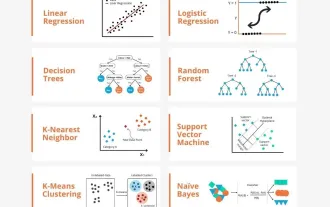 Transparent! An in-depth analysis of the principles of major machine learning models!
Apr 12, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
Transparent! An in-depth analysis of the principles of major machine learning models!
Apr 12, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
In layman’s terms, a machine learning model is a mathematical function that maps input data to a predicted output. More specifically, a machine learning model is a mathematical function that adjusts model parameters by learning from training data to minimize the error between the predicted output and the true label. There are many models in machine learning, such as logistic regression models, decision tree models, support vector machine models, etc. Each model has its applicable data types and problem types. At the same time, there are many commonalities between different models, or there is a hidden path for model evolution. Taking the connectionist perceptron as an example, by increasing the number of hidden layers of the perceptron, we can transform it into a deep neural network. If a kernel function is added to the perceptron, it can be converted into an SVM. this one
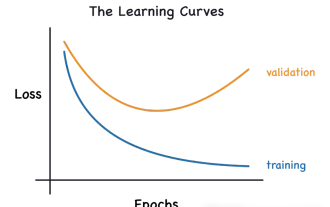 Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
This article will introduce how to effectively identify overfitting and underfitting in machine learning models through learning curves. Underfitting and overfitting 1. Overfitting If a model is overtrained on the data so that it learns noise from it, then the model is said to be overfitting. An overfitted model learns every example so perfectly that it will misclassify an unseen/new example. For an overfitted model, we will get a perfect/near-perfect training set score and a terrible validation set/test score. Slightly modified: "Cause of overfitting: Use a complex model to solve a simple problem and extract noise from the data. Because a small data set as a training set may not represent the correct representation of all data." 2. Underfitting Heru
 The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
In the 1950s, artificial intelligence (AI) was born. That's when researchers discovered that machines could perform human-like tasks, such as thinking. Later, in the 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense funded artificial intelligence and established laboratories for further development. Researchers are finding applications for artificial intelligence in many areas, such as space exploration and survival in extreme environments. Space exploration is the study of the universe, which covers the entire universe beyond the earth. Space is classified as an extreme environment because its conditions are different from those on Earth. To survive in space, many factors must be considered and precautions must be taken. Scientists and researchers believe that exploring space and understanding the current state of everything can help understand how the universe works and prepare for potential environmental crises
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Explainable AI: Explaining complex AI/ML models
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:08 PM
Explainable AI: Explaining complex AI/ML models
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:08 PM
Translator | Reviewed by Li Rui | Chonglou Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models are becoming increasingly complex today, and the output produced by these models is a black box – unable to be explained to stakeholders. Explainable AI (XAI) aims to solve this problem by enabling stakeholders to understand how these models work, ensuring they understand how these models actually make decisions, and ensuring transparency in AI systems, Trust and accountability to address this issue. This article explores various explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) techniques to illustrate their underlying principles. Several reasons why explainable AI is crucial Trust and transparency: For AI systems to be widely accepted and trusted, users need to understand how decisions are made
 Is Flash Attention stable? Meta and Harvard found that their model weight deviations fluctuated by orders of magnitude
May 30, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
Is Flash Attention stable? Meta and Harvard found that their model weight deviations fluctuated by orders of magnitude
May 30, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
MetaFAIR teamed up with Harvard to provide a new research framework for optimizing the data bias generated when large-scale machine learning is performed. It is known that the training of large language models often takes months and uses hundreds or even thousands of GPUs. Taking the LLaMA270B model as an example, its training requires a total of 1,720,320 GPU hours. Training large models presents unique systemic challenges due to the scale and complexity of these workloads. Recently, many institutions have reported instability in the training process when training SOTA generative AI models. They usually appear in the form of loss spikes. For example, Google's PaLM model experienced up to 20 loss spikes during the training process. Numerical bias is the root cause of this training inaccuracy,




