 Software Tutorial
Software Tutorial
 Office Software
Office Software
 The difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCEL
The difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCEL
The difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCEL

The difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCEL
The so-called absolute references and relative references are for cells. For example, $A$1 is an absolute reference and A1 is a relative reference ($A1 and A$1 are mixed references)
Assume A1=1,A2=2,A3=3,....
If you enter the formula =$A$1*2 in b1, and then drag it down to fill, the formula in each cell in column B is =$A$1*2, and its values are B1=2, B2 respectively. =2,B3=2,......
If you enter the formula =A1*2 in b1, and then drag down to fill, the formulas in the cells in column B are (B1)=A1*2, (B2)=A2*2, (B3)= A3*2,...their values are B1=2,B2=4,B3=6,...
Do you understand this clearly? For a formula that absolutely references a cell, the referenced cell will remain unchanged no matter where the formula is copied; for a formula that refers to a relative cell, the referenced cell will change depending on where the formula is copied.
How to achieve relative reference to rows when copying cells in Excel tables and absolute reference to rows when pulling down
1. The cell address can be written as $B1
2. Whoever $ precedes will definitely be quoted
A1 is a relative reference
$A1 absolute reference column is a mixed reference
A$1 absolute reference line is a mixed reference
$A$1 absolute reference row and column are absolute references
F4 is a shortcut key for switching between four types of references (press the F4 function key when entering a formula in the edit bar to switch)
three,
A1 (relative reference) will become references A2, A3, A4... when you pull down and drag the reference. When you drag it to the right, the reference will become B1, C1, D1....;
A$1 (Mixed Reference) When you want to ensure that only cell A1 is referenced when you pull down and copy, A1 must add a $ sign to become A$1, so that you can ensure a relative reference to the first row of column A when you pull down. (That is, keeping the line number unchanged when referencing);
$A1 (Mixed Reference) When you pull right to copy and want to ensure that only the A1 cell is referenced, A1 must add the $ symbol to become $A1, so that when you pull right to copy, you can ensure that the first row of column A is referenced. Relative reference (that is, keeping the column label unchanged when referencing);
$A$1 (absolute reference) When you want to ensure that only the A1 cell is referenced when copying in pull-down and right pull-down, A1 must add the $ symbol to become $A$1, so that it can be guaranteed in pull-down and right pull-down. An absolute reference to the first row of column A (that is, keeping the row number column label unchanged during the reference).
When to use relative references and absolute references in Excel functions
For example, the ranking function RANK.
If you want to get the ranking of column B data and only calculate cell B2, you can enter =RANK(B2,B2:B18) in cell C2, and the result is correct
B2 here is a relative reference cell, and B2:B18 is a relative reference area.
But if you copy the ranking formula of cell C2 downward, the result will be wrong,
Because in cell C3, the formula becomes =RANK(B3,B3:B19);
In cell C4, the formula becomes =RANK(B4,B4:B20);
Obviously, the relative reference of the previous cell is correct, but the later reference area has been changing, causing errors in the ranking results.
Therefore, when filling downwards, the subsequent reference area should be modified to an absolute reference or a relative-absolute mixed reference to ensure that the reference area will not change with copying or filling
The formula in cell C2 becomes
=RANK(B2,$B$2:$B$18)
or=RANK(B2,B$2:B$18)
I hope this example can help you improve your understanding of relative references and absolute references.
The above is the detailed content of The difference between absolute reference and relative reference of functions in EXCEL. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 5 Things You Can Do in Excel for the Web Today That You Couldn't 12 Months Ago
Mar 22, 2025 am 03:03 AM
5 Things You Can Do in Excel for the Web Today That You Couldn't 12 Months Ago
Mar 22, 2025 am 03:03 AM
Excel web version features enhancements to improve efficiency! While Excel desktop version is more powerful, the web version has also been significantly improved over the past year. This article will focus on five key improvements: Easily insert rows and columns: In Excel web, just hover over the row or column header and click the " " sign that appears to insert a new row or column. There is no need to use the confusing right-click menu "insert" function anymore. This method is faster, and newly inserted rows or columns inherit the format of adjacent cells. Export as CSV files: Excel now supports exporting worksheets as CSV files for easy data transfer and compatibility with other software. Click "File" > "Export"
 How to Use LAMBDA in Excel to Create Your Own Functions
Mar 21, 2025 am 03:08 AM
How to Use LAMBDA in Excel to Create Your Own Functions
Mar 21, 2025 am 03:08 AM
Excel's LAMBDA Functions: An easy guide to creating custom functions Before Excel introduced the LAMBDA function, creating a custom function requires VBA or macro. Now, with LAMBDA, you can easily implement it using the familiar Excel syntax. This guide will guide you step by step how to use the LAMBDA function. It is recommended that you read the parts of this guide in order, first understand the grammar and simple examples, and then learn practical applications. The LAMBDA function is available for Microsoft 365 (Windows and Mac), Excel 2024 (Windows and Mac), and Excel for the web. E
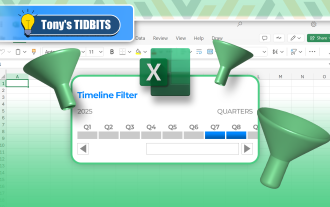 How to Create a Timeline Filter in Excel
Apr 03, 2025 am 03:51 AM
How to Create a Timeline Filter in Excel
Apr 03, 2025 am 03:51 AM
In Excel, using the timeline filter can display data by time period more efficiently, which is more convenient than using the filter button. The Timeline is a dynamic filtering option that allows you to quickly display data for a single date, month, quarter, or year. Step 1: Convert data to pivot table First, convert the original Excel data into a pivot table. Select any cell in the data table (formatted or not) and click PivotTable on the Insert tab of the ribbon. Related: How to Create Pivot Tables in Microsoft Excel Don't be intimidated by the pivot table! We will teach you basic skills that you can master in minutes. Related Articles In the dialog box, make sure the entire data range is selected (
 If You Don't Use Excel's Hidden Camera Tool, You're Missing a Trick
Mar 25, 2025 am 02:48 AM
If You Don't Use Excel's Hidden Camera Tool, You're Missing a Trick
Mar 25, 2025 am 02:48 AM
Quick Links Why Use the Camera Tool?
 Use the PERCENTOF Function to Simplify Percentage Calculations in Excel
Mar 27, 2025 am 03:03 AM
Use the PERCENTOF Function to Simplify Percentage Calculations in Excel
Mar 27, 2025 am 03:03 AM
Excel's PERCENTOF function: Easily calculate the proportion of data subsets Excel's PERCENTOF function can quickly calculate the proportion of data subsets in the entire data set, avoiding the hassle of creating complex formulas. PERCENTOF function syntax The PERCENTOF function has two parameters: =PERCENTOF(a,b) in: a (required) is a subset of data that forms part of the entire data set; b (required) is the entire dataset. In other words, the PERCENTOF function calculates the percentage of the subset a to the total dataset b. Calculate the proportion of individual values using PERCENTOF The easiest way to use the PERCENTOF function is to calculate the single
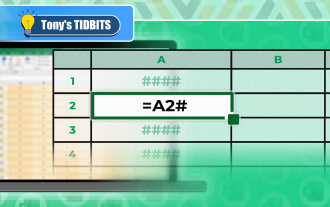 You Need to Know What the Hash Sign Does in Excel Formulas
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:55 AM
You Need to Know What the Hash Sign Does in Excel Formulas
Apr 08, 2025 am 12:55 AM
Excel Overflow Range Operator (#) enables formulas to be automatically adjusted to accommodate changes in overflow range size. This feature is only available for Microsoft 365 Excel for Windows or Mac. Common functions such as UNIQUE, COUNTIF, and SORTBY can be used in conjunction with overflow range operators to generate dynamic sortable lists. The pound sign (#) in the Excel formula is also called the overflow range operator, which instructs the program to consider all results in the overflow range. Therefore, even if the overflow range increases or decreases, the formula containing # will automatically reflect this change. How to list and sort unique values in Microsoft Excel
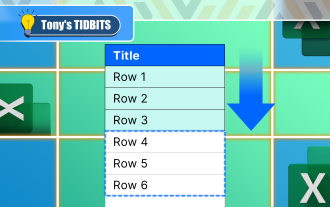 How to Format a Spilled Array in Excel
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
How to Format a Spilled Array in Excel
Apr 10, 2025 pm 12:01 PM
Use formula conditional formatting to handle overflow arrays in Excel Direct formatting of overflow arrays in Excel can cause problems, especially when the data shape or size changes. Formula-based conditional formatting rules allow automatic formatting to be adjusted when data parameters change. Adding a dollar sign ($) before a column reference applies a rule to all rows in the data. In Excel, you can apply direct formatting to the values or background of a cell to make the spreadsheet easier to read. However, when an Excel formula returns a set of values (called overflow arrays), applying direct formatting will cause problems if the size or shape of the data changes. Suppose you have this spreadsheet with overflow results from the PIVOTBY formula,




