 System Tutorial
System Tutorial
 LINUX
LINUX
 Answering questions about embedded Linux smartphone systems: a comprehensive analysis
Answering questions about embedded Linux smartphone systems: a comprehensive analysis
Answering questions about embedded Linux smartphone systems: a comprehensive analysis
The booming development of smart phones has made embedded Linux gradually become mainstream. Here, the author will give you detailed answers to hot questions about embedded Linux smartphone application systems from the perspective of an embedded system engineer.
Question 1: What is embedded linux?
Embedded Linux, as an operating system that can run stably in restricted embedded devices, is highly praised for its open source, customizable and high stability features.Smartphone applications based on embedded Linux System research, especially in mobile phones and other devices, is extremely widely used.
Question 2: Why choose embedded Linux as the operating system of smartphones?

Based on embedded Linux technology, this solution provides strong and friendly community support and a diverse ecosystem. No matter what manufacturer or user group you are, you can find suitable and satisfactory smartphone functions and performance. . In addition, the easy portability and high compatibility of this solution bring great convenience to developers, making it easy to develop and maintain applications.
Question 3: What are the core components of the embedded Linux smartphone application system?

The embedded Linux smartphone application system mainly includes important components such as kernel, driver, library and application program. The kernel is mainly responsible for allocating hardware resources and ensuring the smooth operation of system services; the driver is responsible for real-time information exchange with hardware devices; and the vast library of codes not only provides rich functional interfaces, but also implements various functions for applications. Provides strong support for the functions required by users.
Question 4: What are the processes for developing embedded Linux smartphone application systems?

The development process of the embedded Linux smartphone application system mainly includes requirements analysis, system design, software development, testing and verification, and release and launch. Among them, each link needs to cooperate closely to ensure the complete function and stability of the system.
Question 5: Have you encountered any common challenges when designing and developing embedded Linux smartphone applications?

The challenges faced by embedded Linux smartphone application projects cover many aspects such as resource limitations, power consumption control, real-time performance, and security protection. In the actual operation process, the development team must consider the project needs puppy linux, think comprehensively and adopt appropriate optimization strategies to deal with the above problems.
Question 6: How to improve the performance of embedded Linux smartphone application systems?

There are many methods to choose from to improve the performance of embedded Linux smartphone applications. For example, streamlining code, reducing resource consumption, taking advantage of hardware, etc. are all very effective. Of course, Research on Smartphone Application Systems Based on Embedded Linux, regularly upgrading the kernel and drivers, optimizing scheduling and memory management can steadily improve the overall performance.
Question 7: What are the prospects for embedded Linux smartphone application systems?
As technology becomes increasingly sophisticated, in the future, embedded Linux smartphone application systems will pay more attention to optimizing user experience, enhancing functional innovation, and ensuring information security. At the same time, the introduction of emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things will undoubtedly bring broader development space to this field.
In this Q&A event, we conducted a comprehensive exploration and analysis of smart phone application systems based on embedded Linux. I hope this discussion can provide some useful inspiration for readers to deeply understand and study related issues.
The above is the detailed content of Answering questions about embedded Linux smartphone systems: a comprehensive analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to list block devices of Linux system using lsblk command
Feb 15, 2024 am 08:10 AM
How to list block devices of Linux system using lsblk command
Feb 15, 2024 am 08:10 AM
sblk is a command used to list all available block device information in a Linux system. Block devices refer to devices that can transmit data in blocks, such as hard disks, optical drives, USB flash drives, etc. The lsblk command can display the dependencies between block devices, as well as various attributes such as size, type, file system, mount point, etc. The lsblk command obtains information from the /sys virtual file system and udev database. If there is no udev database or lsblk is not compiled with udev support, then it will try to read the label, UUID and file system type from the block device, which requires root privileges. In this article, we will explain how to use the lsblk command to list the block devices of a Linux system to
 Understand the four major IO scheduling algorithms of the Linux kernel in one article
Feb 14, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
Understand the four major IO scheduling algorithms of the Linux kernel in one article
Feb 14, 2024 pm 03:30 PM
The Linux kernel contains four types of IO schedulers, namely NoopIOscheduler, AnticipatoryIOscheduler, DeadlineIOscheduler and CFQIOscheduler. Typically, disk read and write latency is caused by the head moving to the cylinder. In order to solve this delay, the kernel mainly adopts two strategies: caching and IO scheduling algorithms. Scheduling Algorithm Concepts When a block of data is written to or read from a device, the request is placed in a queue waiting for completion. Each block device has its own queue. The I/O scheduler is responsible for maintaining the order of these queues to utilize the media more efficiently. The I/O scheduler will unordered I/O
 Secrets of the Linux root file system
Feb 15, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
Secrets of the Linux root file system
Feb 15, 2024 pm 01:42 PM
Linux is an open source, portable, and customizable operating system that is widely used in various fields, such as servers, desktops, embedded devices, etc. The core of Linux is the kernel, which is responsible for managing hardware resources and providing basic services. However, the kernel is not an independent entity and requires a file system to store and access various data and programs. A file system is a method of organizing and managing files. It defines the file's name, location, attributes, permissions and other information. In Linux, there are many different types of file systems, such as ext4, xfs, btrfs, etc., each of which has its own characteristics and advantages. However, among all file systems, there is a special file system, which is the foundation and core of the Linux system, which is
 What functions of the df command you don't know under Linux
Feb 14, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
What functions of the df command you don't know under Linux
Feb 14, 2024 pm 09:39 PM
Question: I want to use df command on Linux to check disk usage space. Can you give me some specific examples of the df command so I can make better use of it? On Linux, if you want to know how much space a specific file system takes up, or how much space is available for a specific file system, you can use the df command. The df command is a command that displays the available disk space of the file system for each filename parameter. If you do not specify any file names, the output will show the available space for all currently mounted file systems. By default, df displays disk space in 1K blocks. Linux has many command line or graphical interface tools that can tell you detailed information about current disk space usage, such as
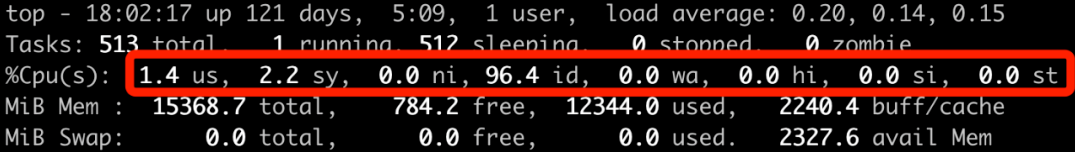 How is CPU utilization calculated in Linux?
Feb 15, 2024 am 11:15 AM
How is CPU utilization calculated in Linux?
Feb 15, 2024 am 11:15 AM
When observing the running status of online services on an online server, most people like to use the top command first to see the overall CPU utilization of the current system. For example, for a random machine, the utilization information displayed by the top command is as follows: This output result is simple to say, but complex, it is not so easy to understand it all. For example: Question 1: How is the utilization information output by top calculated? Is it accurate? Question 2: The ni column is nice. It outputs the CPU overhead when processing? Question 3: wa represents iowait, so is the CPU busy or idle during this period? Today we will conduct an in-depth study of CPU utilization statistics. Through today's study, you will not only understand c
 Black Box – A gorgeous looking Linux desktop terminal emulator
Feb 14, 2024 am 10:27 AM
Black Box – A gorgeous looking Linux desktop terminal emulator
Feb 14, 2024 am 10:27 AM
There are many terminal emulators available for Linux. From terminalemulators to Tilix, you have a variety of terminals to choose from. BlackBox is a terminal emulator that supports GTK4. The developer created this project so that he could use a good-looking terminal application on Linux. A new version of BlackBox, a gorgeous-looking Linux desktop terminal emulator that adds transparency and Sixel support, has been launched recently. The new version brings features you've been asking for, including support for customizable keyboard shortcuts. Users can edit keyboard shortcuts within the application to perform common operations such as copy and paste or switching tabs, as well as show/hide the title bar. also
 How is a Linux process created?
Feb 14, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
How is a Linux process created?
Feb 14, 2024 pm 09:21 PM
In Linux systems, processes are a concept that we are very familiar with. Even people who have only coded for a day have used it. But are you sure you know it well enough? Today, we will help you improve your understanding of processes by taking an in-depth look at how they are created. In this article, I will use Nginx to create a worker process as an example to guide you to understand the process's data structure task_struct, and then show you the execution process of fork. After studying this article, you will have an in-depth understanding of the key elements in the process, such as process address space, current directory, parent-child process relationship, file fd table opened by the process, process namespace, etc. You will also learn how the kernel optimizes memory usage when saving used pid numbers.
 Summary of Linux performance analysis tools
Feb 15, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Summary of Linux performance analysis tools
Feb 15, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Due to my interest in the Linux operating system and my desire for low-level knowledge, I compiled this article. It serves as a check for basic knowledge and covers all aspects of the system. The tools in the documentation cannot be fully mastered without complete knowledge of computer systems, networks, and operating systems. In addition, system performance analysis and optimization is a long-term series. This document is mainly a comprehensive article compiled by combining the updated Linux performance tuning tool blog post by Brendan Gregg, a Linux guru and Netflix senior performance architect, and collecting articles related to Linux system performance optimization. It mainly explains the principles and performance testing tools involved in conjunction with the blog post. Background knowledge: When analyzing performance issues,



