 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Meta's official Prompt project guide: Llama 2 is more efficient when used this way
Meta's official Prompt project guide: Llama 2 is more efficient when used this way
Meta's official Prompt project guide: Llama 2 is more efficient when used this way
As large language model (LLM) technology matures, prompt engineering (Prompt Engineering) becomes more and more important. Some research institutions have published LLM prompt engineering guidelines, including Microsoft, OpenAI, etc.
Recently, Meta provided an interactive prompt engineering guide specifically for their Llama 2 open source model. This guide covers quick engineering and best practices for using Llama 2.
The following is the core content of this guide.
Llama Model
In 2023, Meta launched the Llama and Llama 2 models. Smaller models are cheaper to deploy and run, while larger models are more capable.
Llama 2 series model parameter scale is as follows:

Code Llama is a code-centric LLM, built on Llama 2, also comes in various parameter sizes and fine-tuning variants:

Deploying LLM
LLM can be deployed and accessed in a variety of ways, including:
Self-hosting: using local hardware to run inference, For example, use llama.cpp to run Llama 2 on a Macbook Pro. Pros: Self-hosted is best if you have privacy/security needs, or if you have enough GPUs.
Cloud hosting: Rely on a cloud provider to deploy instances that host specific models, such as running Llama 2 through cloud providers such as AWS, Azure, GCP, etc. Advantages: Cloud hosting is the best way to customize your model and its runtime.
Managed API: Call LLM directly through the API. There are many companies offering Llama 2 inference APIs, including AWS Bedrock, Replicate, Anyscale, Together, and others. Pros: Hosted API is the easiest option overall.
Hosted API
Managed API usually has two main endpoints:
1. completion: Generate a response to the given prompt.
2. chat_completion: Generates the next message in the message list, providing clearer instructions and context for use cases such as chatbots.
token
LLM processes input and output in the form of blocks called tokens, and each model It has its own tokenization scheme. For example, the following sentence:
Our destiny is written in the stars.
The tokenization of Llama 2 is ["our", "dest", "iny", "is", "writing", "in", "the", "stars"]. Tokens are particularly important when considering API pricing and internal behavior (such as hyperparameters). Each model has a maximum context length that the prompt cannot exceed, Llama 2 is 4096 tokens, and Code Llama is 100K tokens.
Notebook Setup
As an example, we use Replicate to call Llama 2 chat and LangChain to easily set up the chat completion API.
First install the prerequisites:
pip install langchain replicate
from typing import Dict, Listfrom langchain.llms import Replicatefrom langchain.memory import ChatMessageHistoryfrom langchain.schema.messages import get_buffer_stringimport os# Get a free API key from https://replicate.com/account/api-tokensos.environ ["REPLICATE_API_TOKEN"] = "YOUR_KEY_HERE"LLAMA2_70B_CHAT = "meta/llama-2-70b-chat:2d19859030ff705a87c746f7e96eea03aefb71f166725aee39692f1476566d48"LLAMA2_13B_CHAT = "meta/llama-2-13b-chat:f4e2de70d66816a838a89eeeb621910adffb0dd0baba3976c96980970978018d"# We'll default to the smaller 13B model for speed; change to LLAMA2_70B_CHAT for more advanced (but slower) generationsDEFAULT_MODEL = LLAMA2_13B_CHATdef completion (prompt: str,model: str = DEFAULT_MODEL,temperature: float = 0.6,top_p: float = 0.9,) -> str:llm = Replicate (model=model,model_kwargs={"temperature": temperature,"top_p": top_p, "max_new_tokens": 1000})return llm (prompt)def chat_completion (messages: List [Dict],model = DEFAULT_MODEL,temperature: float = 0.6,top_p: float = 0.9,) -> str:history = ChatMessageHistory ()for message in messages:if message ["role"] == "user":history.add_user_message (message ["content"])elif message ["role"] == "assistant":history.add_ai_message (message ["content"])else:raise Exception ("Unknown role")return completion (get_buffer_string (history.messages,human_prefix="USER",ai_prefix="ASSISTANT",),model,temperature,top_p,)def assistant (content: str):return { "role": "assistant", "content": content }def user (content: str):return { "role": "user", "content": content }def complete_and_print (prompt: str, model: str = DEFAULT_MODEL):print (f'==============\n {prompt}\n==============')response = completion (prompt, model)print (response, end='\n\n')Completion API
complete_and_print ("The typical color of the sky is:")complete_and_print ("which model version are you?")## The #Chat Completion model provides additional structure for interacting with LLM, sending an array of structured message objects to the LLM instead of a single text. This message list provides LLM with some "background" or "historical" information on which to proceed.
Typically, each message contains a role and content:
Messages with system roles are used by developers to provide core instructions to the LLM.
Messages with user roles are usually human-provided messages.
Messages with the Assistant role are typically generated by LLM.
response = chat_completion (messages=[user ("My favorite color is blue."),assistant ("That's great to hear!"),user ("What is my favorite color?"),])print (response)# "Sure, I can help you with that! Your favorite color is blue."LLM hyperparameters
LLM API 通常会采用影响输出的创造性和确定性的参数。在每一步中,LLM 都会生成 token 及其概率的列表。可能性最小的 token 会从列表中「剪切」(基于 top_p),然后从剩余候选者中随机(温度参数 temperature)选择一个 token。换句话说:top_p 控制生成中词汇的广度,温度控制词汇的随机性,温度参数 temperature 为 0 会产生几乎确定的结果。
def print_tuned_completion (temperature: float, top_p: float):response = completion ("Write a haiku about llamas", temperature=temperature, top_p=top_p)print (f'[temperature: {temperature} | top_p: {top_p}]\n {response.strip ()}\n')print_tuned_completion (0.01, 0.01)print_tuned_completion (0.01, 0.01)# These two generations are highly likely to be the sameprint_tuned_completion (1.0, 1.0)print_tuned_completion (1.0, 1.0)# These two generations are highly likely to be differentprompt 技巧
详细、明确的指令会比开放式 prompt 产生更好的结果:
complete_and_print (prompt="Describe quantum physics in one short sentence of no more than 12 words")# Returns a succinct explanation of quantum physics that mentions particles and states existing simultaneously.
我们可以给定使用规则和限制,以给出明确的指令。
- 风格化,例如:
- 向我解释一下这一点,就像儿童教育网络节目中教授小学生一样;
- 我是一名软件工程师,使用大型语言模型进行摘要。用 250 字概括以下文字;
- 像私家侦探一样一步步追查案件,给出你的答案。
- 格式化
使用要点;
以 JSON 对象形式返回;
使用较少的技术术语并用于工作交流中。
- 限制
- 仅使用学术论文;
- 切勿提供 2020 年之前的来源;
- 如果你不知道答案,就说你不知道。
以下是给出明确指令的例子:
complete_and_print ("Explain the latest advances in large language models to me.")# More likely to cite sources from 2017complete_and_print ("Explain the latest advances in large language models to me. Always cite your sources. Never cite sources older than 2020.")# Gives more specific advances and only cites sources from 2020零样本 prompting
一些大型语言模型(例如 Llama 2)能够遵循指令并产生响应,而无需事先看过任务示例。没有示例的 prompting 称为「零样本 prompting(zero-shot prompting)」。例如:
complete_and_print ("Text: This was the best movie I've ever seen! \n The sentiment of the text is:")# Returns positive sentimentcomplete_and_print ("Text: The director was trying too hard. \n The sentiment of the text is:")# Returns negative sentiment少样本 prompting
添加所需输出的具体示例通常会产生更加准确、一致的输出。这种方法称为「少样本 prompting(few-shot prompting)」。例如:
def sentiment (text):response = chat_completion (messages=[user ("You are a sentiment classifier. For each message, give the percentage of positive/netural/negative."),user ("I liked it"),assistant ("70% positive 30% neutral 0% negative"),user ("It could be better"),assistant ("0% positive 50% neutral 50% negative"),user ("It's fine"),assistant ("25% positive 50% neutral 25% negative"),user (text),])return responsedef print_sentiment (text):print (f'INPUT: {text}')print (sentiment (text))print_sentiment ("I thought it was okay")# More likely to return a balanced mix of positive, neutral, and negativeprint_sentiment ("I loved it!")# More likely to return 100% positiveprint_sentiment ("Terrible service 0/10")# More likely to return 100% negativeRole Prompting
Llama 2 在指定角色时通常会给出更一致的响应,角色为 LLM 提供了所需答案类型的背景信息。
例如,让 Llama 2 对使用 PyTorch 的利弊问题创建更有针对性的技术回答:
complete_and_print ("Explain the pros and cons of using PyTorch.")# More likely to explain the pros and cons of PyTorch covers general areas like documentation, the PyTorch community, and mentions a steep learning curvecomplete_and_print ("Your role is a machine learning expert who gives highly technical advice to senior engineers who work with complicated datasets. Explain the pros and cons of using PyTorch.")# Often results in more technical benefits and drawbacks that provide more technical details on how model layers思维链
简单地添加一个「鼓励逐步思考」的短语可以显著提高大型语言模型执行复杂推理的能力(Wei et al. (2022)),这种方法称为 CoT 或思维链 prompting:
complete_and_print ("Who lived longer Elvis Presley or Mozart?")# Often gives incorrect answer of "Mozart"complete_and_print ("Who lived longer Elvis Presley or Mozart? Let's think through this carefully, step by step.")# Gives the correct answer "Elvis"自洽性(Self-Consistency)
LLM 是概率性的,因此即使使用思维链,一次生成也可能会产生不正确的结果。自洽性通过从多次生成中选择最常见的答案来提高准确性(以更高的计算成本为代价):
import refrom statistics import modedef gen_answer ():response = completion ("John found that the average of 15 numbers is 40.""If 10 is added to each number then the mean of the numbers is?""Report the answer surrounded by three backticks, for example:```123```",model = LLAMA2_70B_CHAT)match = re.search (r'```(\d+)```', response)if match is None:return Nonereturn match.group (1)answers = [gen_answer () for i in range (5)]print (f"Answers: {answers}\n",f"Final answer: {mode (answers)}",)# Sample runs of Llama-2-70B (all correct):# [50, 50, 750, 50, 50]-> 50# [130, 10, 750, 50, 50] -> 50# [50, None, 10, 50, 50] -> 50检索增强生成
有时我们可能希望在应用程序中使用事实知识,那么可以从开箱即用(即仅使用模型权重)的大模型中提取常见事实:
complete_and_print ("What is the capital of the California?", model = LLAMA2_70B_CHAT)# Gives the correct answer "Sacramento"然而,LLM 往往无法可靠地检索更具体的事实或私人信息。模型要么声明它不知道,要么幻想出一个错误的答案:
complete_and_print ("What was the temperature in Menlo Park on December 12th, 2023?")# "I'm just an AI, I don't have access to real-time weather data or historical weather records."complete_and_print ("What time is my dinner reservation on Saturday and what should I wear?")# "I'm not able to access your personal information [..] I can provide some general guidance"检索增强生成(RAG)是指在 prompt 中包含从外部数据库检索的信息(Lewis et al. (2020))。RAG 是将事实纳入 LLM 应用的有效方法,并且比微调更经济实惠,微调可能成本高昂并对基础模型的功能产生负面影响。
MENLO_PARK_TEMPS = {"2023-12-11": "52 degrees Fahrenheit","2023-12-12": "51 degrees Fahrenheit","2023-12-13": "51 degrees Fahrenheit",}def prompt_with_rag (retrived_info, question):complete_and_print (f"Given the following information: '{retrived_info}', respond to: '{question}'")def ask_for_temperature (day):temp_on_day = MENLO_PARK_TEMPS.get (day) or "unknown temperature"prompt_with_rag (f"The temperature in Menlo Park was {temp_on_day} on {day}'",# Retrieved factf"What is the temperature in Menlo Park on {day}?",# User question)ask_for_temperature ("2023-12-12")# "Sure! The temperature in Menlo Park on 2023-12-12 was 51 degrees Fahrenheit."ask_for_temperature ("2023-07-18")# "I'm not able to provide the temperature in Menlo Park on 2023-07-18 as the information provided states that the temperature was unknown."程序辅助语言模型
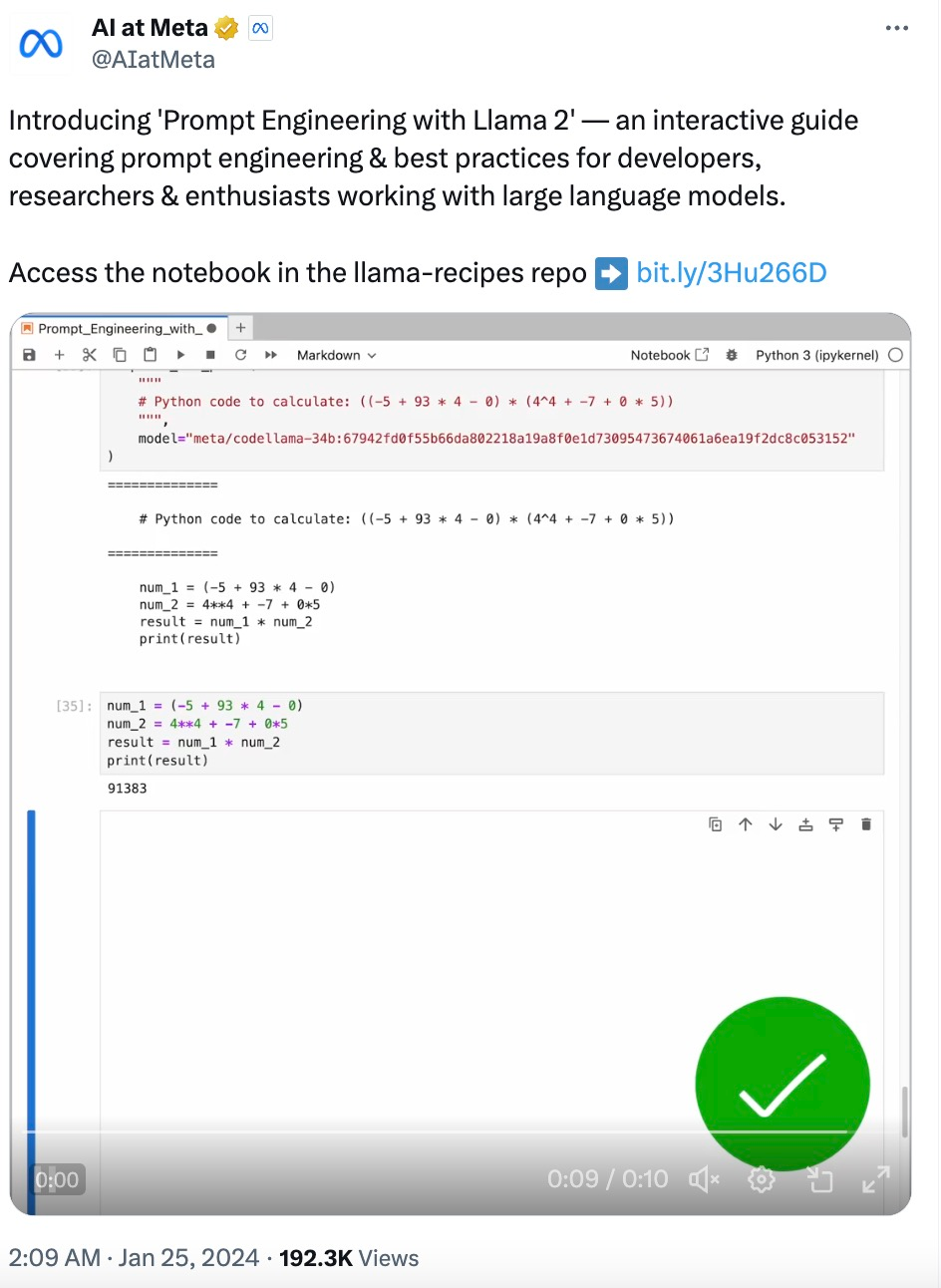
LLM 本质上不擅长执行计算,例如:
complete_and_print ("""Calculate the answer to the following math problem:((-5 + 93 * 4 - 0) * (4^4 + -7 + 0 * 5))""")# Gives incorrect answers like 92448, 92648, 95463Gao et al. (2022) 提出「程序辅助语言模型(Program-aided Language Models,PAL)」的概念。虽然 LLM 不擅长算术,但它们非常擅长代码生成。PAL 通过指示 LLM 编写代码来解决计算任务。
complete_and_print ("""# Python code to calculate: ((-5 + 93 * 4 - 0) * (4^4 + -7 + 0 * 5))""",model="meta/codellama-34b:67942fd0f55b66da802218a19a8f0e1d73095473674061a6ea19f2dc8c053152")# The following code was generated by Code Llama 34B:num1 = (-5 + 93 * 4 - 0)num2 = (4**4 + -7 + 0 * 5)answer = num1 * num2print (answer)
The above is the detailed content of Meta's official Prompt project guide: Llama 2 is more efficient when used this way. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Open source! Beyond ZoeDepth! DepthFM: Fast and accurate monocular depth estimation!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
Open source! Beyond ZoeDepth! DepthFM: Fast and accurate monocular depth estimation!
Apr 03, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
0.What does this article do? We propose DepthFM: a versatile and fast state-of-the-art generative monocular depth estimation model. In addition to traditional depth estimation tasks, DepthFM also demonstrates state-of-the-art capabilities in downstream tasks such as depth inpainting. DepthFM is efficient and can synthesize depth maps within a few inference steps. Let’s read about this work together ~ 1. Paper information title: DepthFM: FastMonocularDepthEstimationwithFlowMatching Author: MingGui, JohannesS.Fischer, UlrichPrestel, PingchuanMa, Dmytr
 The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Imagine an artificial intelligence model that not only has the ability to surpass traditional computing, but also achieves more efficient performance at a lower cost. This is not science fiction, DeepSeek-V2[1], the world’s most powerful open source MoE model is here. DeepSeek-V2 is a powerful mixture of experts (MoE) language model with the characteristics of economical training and efficient inference. It consists of 236B parameters, 21B of which are used to activate each marker. Compared with DeepSeek67B, DeepSeek-V2 has stronger performance, while saving 42.5% of training costs, reducing KV cache by 93.3%, and increasing the maximum generation throughput to 5.76 times. DeepSeek is a company exploring general artificial intelligence
 AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI is indeed changing mathematics. Recently, Tao Zhexuan, who has been paying close attention to this issue, forwarded the latest issue of "Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society" (Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society). Focusing on the topic "Will machines change mathematics?", many mathematicians expressed their opinions. The whole process was full of sparks, hardcore and exciting. The author has a strong lineup, including Fields Medal winner Akshay Venkatesh, Chinese mathematician Zheng Lejun, NYU computer scientist Ernest Davis and many other well-known scholars in the industry. The world of AI has changed dramatically. You know, many of these articles were submitted a year ago.
 Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Boston Dynamics Atlas officially enters the era of electric robots! Yesterday, the hydraulic Atlas just "tearfully" withdrew from the stage of history. Today, Boston Dynamics announced that the electric Atlas is on the job. It seems that in the field of commercial humanoid robots, Boston Dynamics is determined to compete with Tesla. After the new video was released, it had already been viewed by more than one million people in just ten hours. The old people leave and new roles appear. This is a historical necessity. There is no doubt that this year is the explosive year of humanoid robots. Netizens commented: The advancement of robots has made this year's opening ceremony look like a human, and the degree of freedom is far greater than that of humans. But is this really not a horror movie? At the beginning of the video, Atlas is lying calmly on the ground, seemingly on his back. What follows is jaw-dropping
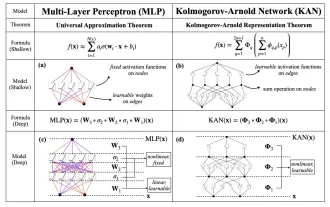 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 The vitality of super intelligence awakens! But with the arrival of self-updating AI, mothers no longer have to worry about data bottlenecks
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
The vitality of super intelligence awakens! But with the arrival of self-updating AI, mothers no longer have to worry about data bottlenecks
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
I cry to death. The world is madly building big models. The data on the Internet is not enough. It is not enough at all. The training model looks like "The Hunger Games", and AI researchers around the world are worrying about how to feed these data voracious eaters. This problem is particularly prominent in multi-modal tasks. At a time when nothing could be done, a start-up team from the Department of Renmin University of China used its own new model to become the first in China to make "model-generated data feed itself" a reality. Moreover, it is a two-pronged approach on the understanding side and the generation side. Both sides can generate high-quality, multi-modal new data and provide data feedback to the model itself. What is a model? Awaker 1.0, a large multi-modal model that just appeared on the Zhongguancun Forum. Who is the team? Sophon engine. Founded by Gao Yizhao, a doctoral student at Renmin University’s Hillhouse School of Artificial Intelligence.
 Kuaishou version of Sora 'Ke Ling' is open for testing: generates over 120s video, understands physics better, and can accurately model complex movements
Jun 11, 2024 am 09:51 AM
Kuaishou version of Sora 'Ke Ling' is open for testing: generates over 120s video, understands physics better, and can accurately model complex movements
Jun 11, 2024 am 09:51 AM
What? Is Zootopia brought into reality by domestic AI? Exposed together with the video is a new large-scale domestic video generation model called "Keling". Sora uses a similar technical route and combines a number of self-developed technological innovations to produce videos that not only have large and reasonable movements, but also simulate the characteristics of the physical world and have strong conceptual combination capabilities and imagination. According to the data, Keling supports the generation of ultra-long videos of up to 2 minutes at 30fps, with resolutions up to 1080p, and supports multiple aspect ratios. Another important point is that Keling is not a demo or video result demonstration released by the laboratory, but a product-level application launched by Kuaishou, a leading player in the short video field. Moreover, the main focus is to be pragmatic, not to write blank checks, and to go online as soon as it is released. The large model of Ke Ling is already available in Kuaiying.
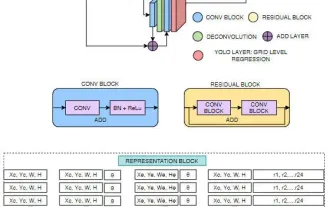 FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
Target detection is a relatively mature problem in autonomous driving systems, among which pedestrian detection is one of the earliest algorithms to be deployed. Very comprehensive research has been carried out in most papers. However, distance perception using fisheye cameras for surround view is relatively less studied. Due to large radial distortion, standard bounding box representation is difficult to implement in fisheye cameras. To alleviate the above description, we explore extended bounding box, ellipse, and general polygon designs into polar/angular representations and define an instance segmentation mIOU metric to analyze these representations. The proposed model fisheyeDetNet with polygonal shape outperforms other models and simultaneously achieves 49.5% mAP on the Valeo fisheye camera dataset for autonomous driving



