 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Five common types of Kafka partition strategies and analysis of their characteristics
Five common types of Kafka partition strategies and analysis of their characteristics
Five common types of Kafka partition strategies and analysis of their characteristics

Five common types of Kafka partition strategies and their characteristics
Kafka partition strategy determines how messages are distributed across different partitions to achieve load balancing and high availability. Kafka supports five common partitioning strategies, which are:
- Round-robin : This is the simplest partitioning strategy, which evenly distributes messages to on all partitions. The advantage of this strategy is that it is simple and easy to use, but the disadvantage is that it may cause some partitions to be overloaded and other partitions to be underloaded.
- Random strategy (Random): This strategy randomly distributes messages to all partitions. The advantage of this strategy is that it can avoid the uneven load problem that may occur in the polling strategy, but the disadvantage is that it may cause some partitions to be overloaded and other partitions to be underloaded.
- Consistent Hashing Strategy : This strategy distributes messages to partitions so that messages with the same key are always distributed to the same partition. The advantage of this strategy is that it guarantees that messages with the same key are always stored on the same partition, but the disadvantage is that it may cause some partitions to be overloaded and other partitions to be underloaded.
- Key Partitioning strategy (Key Partitioning) : This strategy distributes messages to partitions so that messages with the same key are always distributed to the same partition. The advantage of this strategy is that it guarantees that messages with the same key are always stored on the same partition, but the disadvantage is that it may cause some partitions to be overloaded and other partitions to be underloaded.
- Range Partitioning Strategy (Range Partitioning): This strategy distributes messages to partitions so that messages with keys in the same range are always distributed to the same partition. The advantage of this strategy is that it guarantees that messages with the same range of keys are always stored on the same partition, but the disadvantage is that it may cause some partitions to be overloaded and other partitions to be underloaded.
Considerations for choosing a partitioning strategy
When choosing a partitioning strategy, you need to consider the following factors:
- Type of message:If the messages have the same key, you can use a consistent hashing strategy or a key partitioning strategy. If the messages do not have the same key, you can use a round-robin strategy or a random strategy.
- Number of partitions: The number of partitions should match the size of the cluster. If the number of partitions is too small, it may result in some partitions being overloaded and other partitions being underloaded. If there are too many partitions, it may cause excessive partition management overhead.
- Load balancing: The partitioning strategy should be able to achieve load balancing to avoid some partitions being overloaded and other partitions being underloaded.
- High availability: The partitioning strategy should be able to ensure high availability of messages to avoid message loss caused by partition failure.
Conclusion
Kafka partitioning strategy determines how messages are distributed across different partitions to achieve load balancing and high availability. Kafka supports five common partitioning strategies, namely polling strategy, random strategy, consistent hashing strategy, key partitioning strategy and range partitioning strategy. When choosing a partitioning strategy, you need to consider factors such as message type, number of partitions, load balancing, and high availability.
The above is the detailed content of Five common types of Kafka partition strategies and analysis of their characteristics. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
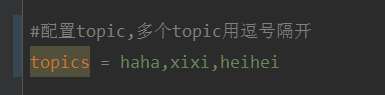 How to dynamically specify multiple topics with @KafkaListener in springboot+kafka
May 20, 2023 pm 08:58 PM
How to dynamically specify multiple topics with @KafkaListener in springboot+kafka
May 20, 2023 pm 08:58 PM
Explain that this project is a springboot+kafak integration project, so it uses the kafak consumption annotation @KafkaListener in springboot. First, configure multiple topics separated by commas in application.properties. Method: Use Spring’s SpEl expression to configure topics as: @KafkaListener(topics="#{’${topics}’.split(’,’)}") to run the program. The console printing effect is as follows
 How to implement real-time stock analysis using PHP and Kafka
Jun 28, 2023 am 10:04 AM
How to implement real-time stock analysis using PHP and Kafka
Jun 28, 2023 am 10:04 AM
With the development of the Internet and technology, digital investment has become a topic of increasing concern. Many investors continue to explore and study investment strategies, hoping to obtain a higher return on investment. In stock trading, real-time stock analysis is very important for decision-making, and the use of Kafka real-time message queue and PHP technology is an efficient and practical means. 1. Introduction to Kafka Kafka is a high-throughput distributed publish and subscribe messaging system developed by LinkedIn. The main features of Kafka are
 How SpringBoot integrates Kafka configuration tool class
May 12, 2023 pm 09:58 PM
How SpringBoot integrates Kafka configuration tool class
May 12, 2023 pm 09:58 PM
spring-kafka is based on the integration of the java version of kafkaclient and spring. It provides KafkaTemplate, which encapsulates various methods for easy operation. It encapsulates apache's kafka-client, and there is no need to import the client to depend on the org.springframework.kafkaspring-kafkaYML configuration. kafka:#bootstrap-servers:server1:9092,server2:9093#kafka development address,#producer configuration producer:#serialization and deserialization class key provided by Kafka
 Comparative analysis of kafka visualization tools: How to choose the most appropriate tool?
Jan 05, 2024 pm 12:15 PM
Comparative analysis of kafka visualization tools: How to choose the most appropriate tool?
Jan 05, 2024 pm 12:15 PM
How to choose the right Kafka visualization tool? Comparative analysis of five tools Introduction: Kafka is a high-performance, high-throughput distributed message queue system that is widely used in the field of big data. With the popularity of Kafka, more and more enterprises and developers need a visual tool to easily monitor and manage Kafka clusters. This article will introduce five commonly used Kafka visualization tools and compare their features and functions to help readers choose the tool that suits their needs. 1. KafkaManager
 Five selections of visualization tools for exploring Kafka
Feb 01, 2024 am 08:03 AM
Five selections of visualization tools for exploring Kafka
Feb 01, 2024 am 08:03 AM
Five options for Kafka visualization tools ApacheKafka is a distributed stream processing platform capable of processing large amounts of real-time data. It is widely used to build real-time data pipelines, message queues, and event-driven applications. Kafka's visualization tools can help users monitor and manage Kafka clusters and better understand Kafka data flows. The following is an introduction to five popular Kafka visualization tools: ConfluentControlCenterConfluent
 How to install Apache Kafka on Rocky Linux?
Mar 01, 2024 pm 10:37 PM
How to install Apache Kafka on Rocky Linux?
Mar 01, 2024 pm 10:37 PM
To install ApacheKafka on RockyLinux, you can follow the following steps: Update system: First, make sure your RockyLinux system is up to date, execute the following command to update the system package: sudoyumupdate Install Java: ApacheKafka depends on Java, so you need to install JavaDevelopmentKit (JDK) first ). OpenJDK can be installed through the following command: sudoyuminstalljava-1.8.0-openjdk-devel Download and decompress: Visit the ApacheKafka official website () to download the latest binary package. Choose a stable version
 The practice of go-zero and Kafka+Avro: building a high-performance interactive data processing system
Jun 23, 2023 am 09:04 AM
The practice of go-zero and Kafka+Avro: building a high-performance interactive data processing system
Jun 23, 2023 am 09:04 AM
In recent years, with the rise of big data and active open source communities, more and more enterprises have begun to look for high-performance interactive data processing systems to meet the growing data needs. In this wave of technology upgrades, go-zero and Kafka+Avro are being paid attention to and adopted by more and more enterprises. go-zero is a microservice framework developed based on the Golang language. It has the characteristics of high performance, ease of use, easy expansion, and easy maintenance. It is designed to help enterprises quickly build efficient microservice application systems. its rapid growth
 In-depth understanding of the underlying implementation mechanism of Kafka message queue
Feb 01, 2024 am 08:15 AM
In-depth understanding of the underlying implementation mechanism of Kafka message queue
Feb 01, 2024 am 08:15 AM
Overview of the underlying implementation principles of Kafka message queue Kafka is a distributed, scalable message queue system that can handle large amounts of data and has high throughput and low latency. Kafka was originally developed by LinkedIn and is now a top-level project of the Apache Software Foundation. Architecture Kafka is a distributed system consisting of multiple servers. Each server is called a node, and each node is an independent process. Nodes are connected through a network to form a cluster. K





