 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 An 8-year masterpiece of NTU Zhou Zhihua's team! The 'learningware' system solves the problem of machine learning reuse, and 'model fusion' emerges a new paradigm of scientific research
An 8-year masterpiece of NTU Zhou Zhihua's team! The 'learningware' system solves the problem of machine learning reuse, and 'model fusion' emerges a new paradigm of scientific research
An 8-year masterpiece of NTU Zhou Zhihua's team! The 'learningware' system solves the problem of machine learning reuse, and 'model fusion' emerges a new paradigm of scientific research
HuggingFace is the most popular machine learning open source community, with 300,000 different machine learning models and 100,000 available applications.
What would it look like if the 300,000 models on HuggingFace could be freely combined to complete new learning tasks together?
In fact, in 2016, when HuggingFace came out, Professor Zhou Zhihua of Nanjing University proposed the concept of “Learnware” and drew such a blueprint.
Recently, the team of Professor Zhou Zhihua of Nanjing University launched such a platform-Beimingwu.
Address: https://bmwu.cloud/
Beimingwu not only provides researchers and users with the opportunity to upload their own models, but also Model matching and collaborative fusion can be performed according to user needs to efficiently handle learning tasks.

Paper address: https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.14427
Beimingwu System warehouse: https://www.gitlink.org.cn/beimingwu/beimingwu
Scientific research toolkit warehouse: https://www.gitlink.org.cn/beimingwu/learnware
The biggest feature of this platform is the introduction of the Learnware system, which has achieved a breakthrough in model adaptive matching and collaboration capabilities based on user needs.
Learningware consists of a machine learning model and a specification describing the model, that is, "Learningware = Model Specification".
The specification of the learning software consists of two parts: "semantic specification" and "statistical specification":
- The semantic specification determines the type of the model through text and functions are described;
- Statistical rules use various machine learning technologies to describe the statistical information contained in the model.
The specification of the learningware describes the capabilities of the model so that the model can be fully recognized and reused in the future without the user knowing anything about the learningware in advance to meet user needs. .
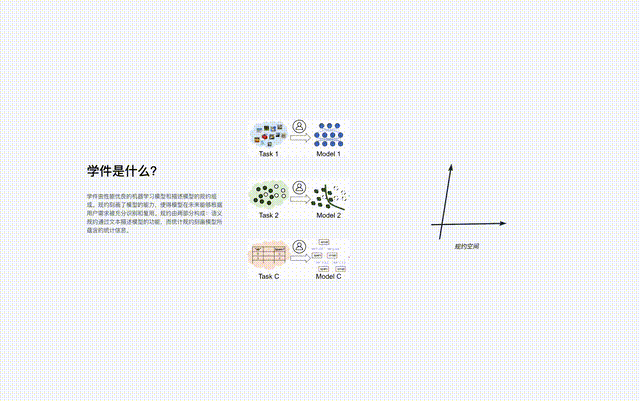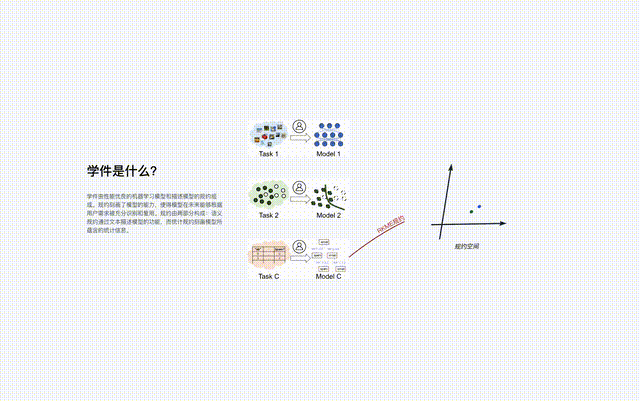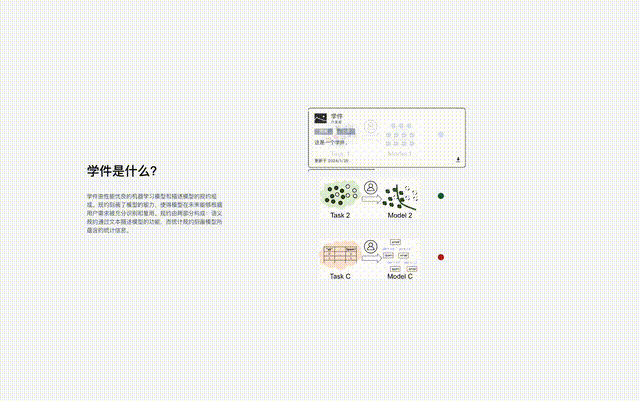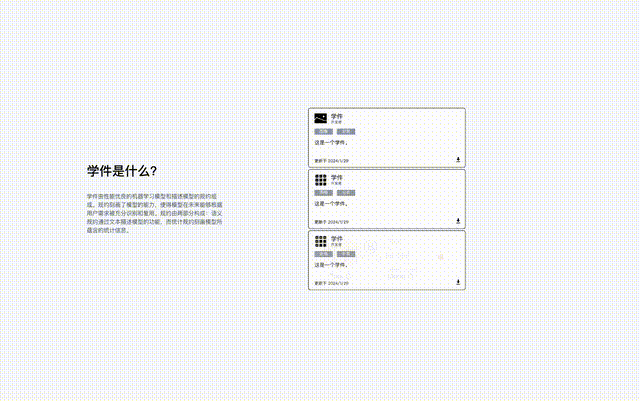
The protocol is the core component of the learningware base system, which connects all the learningware processes in the system, including learningware uploading, organization, Search, deploy and reuse.
Just like Yanziwu in "Dragon Babu" is composed of many small islands, the regulations in Beimingwu are also like small islands.
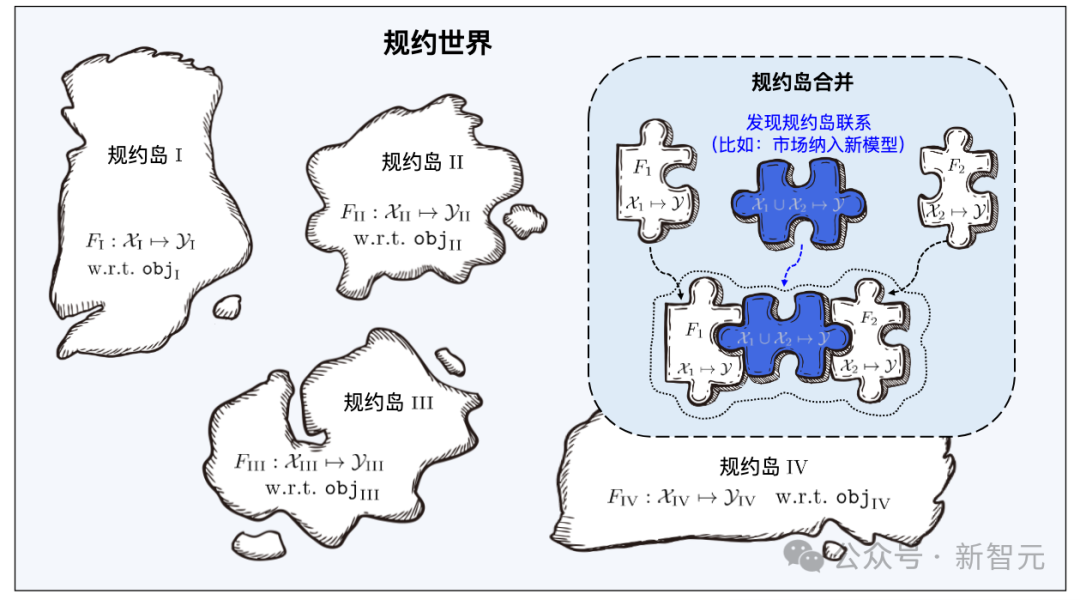
Learnware from different feature/marker spaces constitutes numerous protocol islands, and all protocol islands together constitute the protocol in the learnware base system world. In the protocol world, if the connections between different islands can be discovered and established, then the corresponding protocol islands will be able to be merged.
Under the learningware paradigm, developers around the world can share models to the learningware base system. The system helps users efficiently solve machine learning tasks by effectively searching and reusing learningware. No need to build a machine learning model from scratch.
Beimingwu is the first systematic open source implementation of academicware, providing a preliminary scientific research platform for academicware-related research.
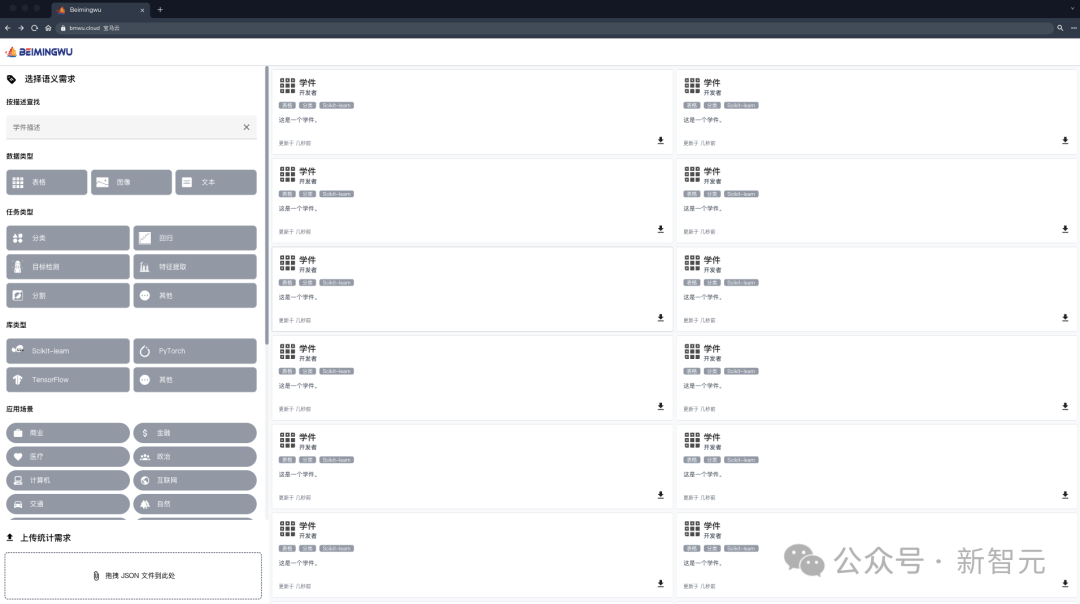
Developers who are willing to share can freely submit models, and the Learning Warehouse assists in generating specifications to form learning software and store them in the Learning Warehouse. In this process, there is no need to disclose your training data to the learning dock.
Future users can submit their requirements to the Learning Warehouse, and with the assistance of the Learning Warehouse, they can search and reuse learning materials to complete their own machine learning tasks, and users do not need to submit to the Learning Warehouse. The dock leaked its own data.
And in the future, after there are millions of learning software in the learning dock, "emergence" behavior may occur: machine learning tasks for which no model has been specially developed in the past may be solved through Solved by reusing several existing learning software.
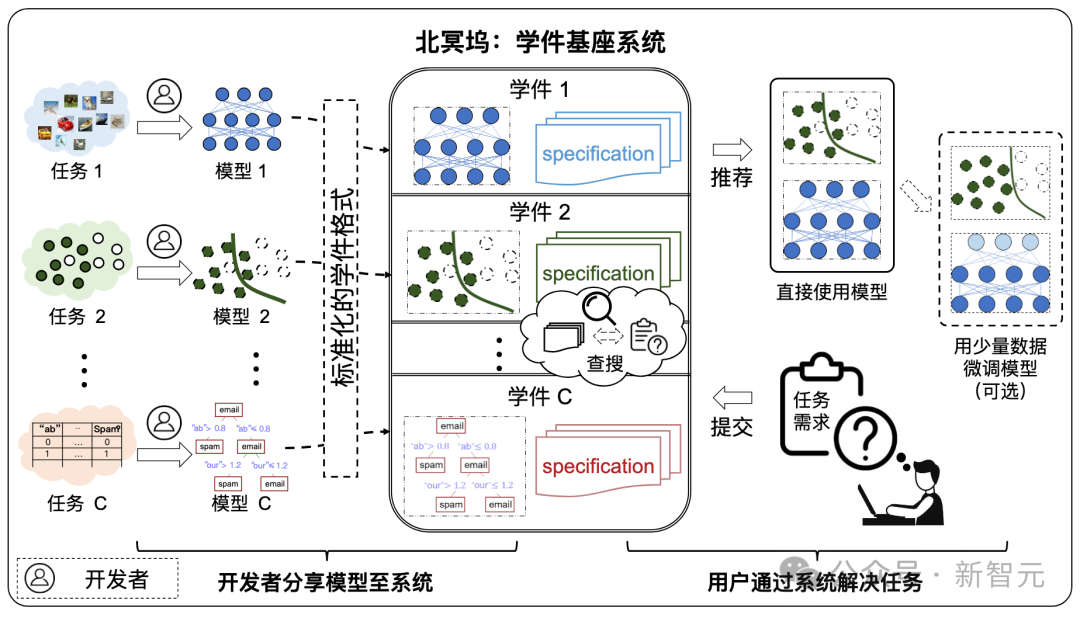
Learningware Base System
Machine learning has achieved great success in many fields, but it still faces many problems, such as the need for a large amount of training data and Superior training techniques, difficulties with continuous learning, risk of catastrophic forgetting, and leakage of data privacy/ownership, etc.
Although each of the above problems has corresponding research, because the problems are coupled to each other, solving one of the problems may cause other problems to become more serious.
The learning base system hopes to solve many of the above problems at the same time through an overall framework:
- Lack of training data/skills: even for lack of Ordinary users with smaller training skills or smaller amounts of data can also obtain powerful machine learning models because users can obtain high-performing learningware from the learningware base system and further adjust or improve it, rather than building the model from scratch themselves. .
- Continuous learning: As learning software with excellent performance trained on various tasks is continuously submitted, the knowledge in the learning software base system will continue to be enriched, thereby naturally realizing continuous and lifelong learning. .
- Catastrophic forgetting: Once a learning piece is received, it will always be accommodated in the learning base system, unless all aspects of its functions can be replaced by other learning pieces. Therefore, old knowledge in the learning base system is always retained and never forgotten.
- Data privacy/ownership: Developers only submit models without sharing private data, so data privacy/ownership can be well protected. Although the possibility of reverse engineering the model cannot be completely ruled out, the risk of privacy leakage with the learning base system is very small compared to many other privacy protection schemes.
The composition of the learning base system
As shown in the figure below, the system workflow is divided into the following two stages:
- Submission stage: Developers spontaneously submit various learning software to the learning software base system, and the system will perform quality inspection and further organization on these learning software.
- Deployment stage: When the user submits task requirements, the learningware base system will recommend learningware that is helpful to the user's task according to the learningware specification and guide the user to deploy and reuse it.
Protocol World
Protocol is the core component of the learning base system, connecting the system in series Regarding the entire process of learning software, including learning software uploading, organization, search, deployment and reuse.
Learning materials from different feature/marker spaces constitute numerous protocol islands, and all protocol islands together constitute the protocol world in the learning component base system. In the protocol world, if the connections between different islands can be discovered and established, then the corresponding protocol islands will be able to be merged.
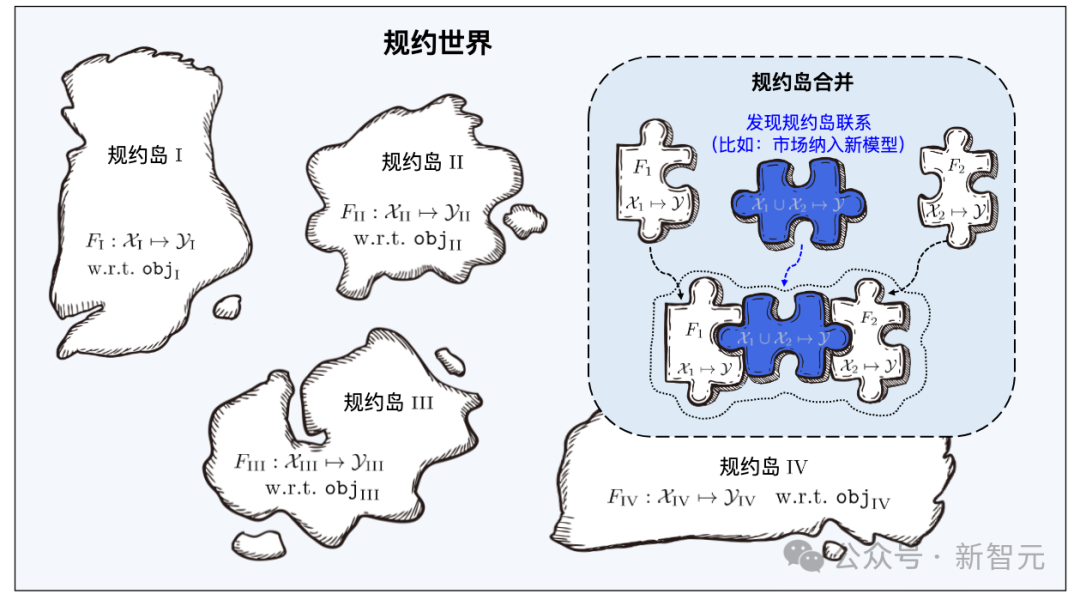
When the learning base system searches, it first locates the specific protocol island through the semantic specifications in the user requirements, and then uses the user requirements to The statistical protocol in the protocol accurately identifies the learning artifacts on the protocol island. The merging of different protocol islands means that the corresponding learning software can be used for tasks in different feature/marker spaces, that is, it can be reused for tasks beyond its original purpose.
Learningware Paradigm builds a unified specification space by making full use of the capabilities of machine learning models shared by the community, and efficiently solves machine learning tasks for new users in a unified manner. As the number of learning pieces increases, by effectively organizing the learning piece structure, the overall ability of the learning piece base system to solve tasks will be significantly enhanced.
The architecture of Beimingwu
As shown in the figure below, the system architecture of Beimingwu contains four levels, from the learning software storage layer As for the user interaction layer, the learningware paradigm is systematically implemented from the bottom up for the first time. The specific functions of the four levels are as follows:
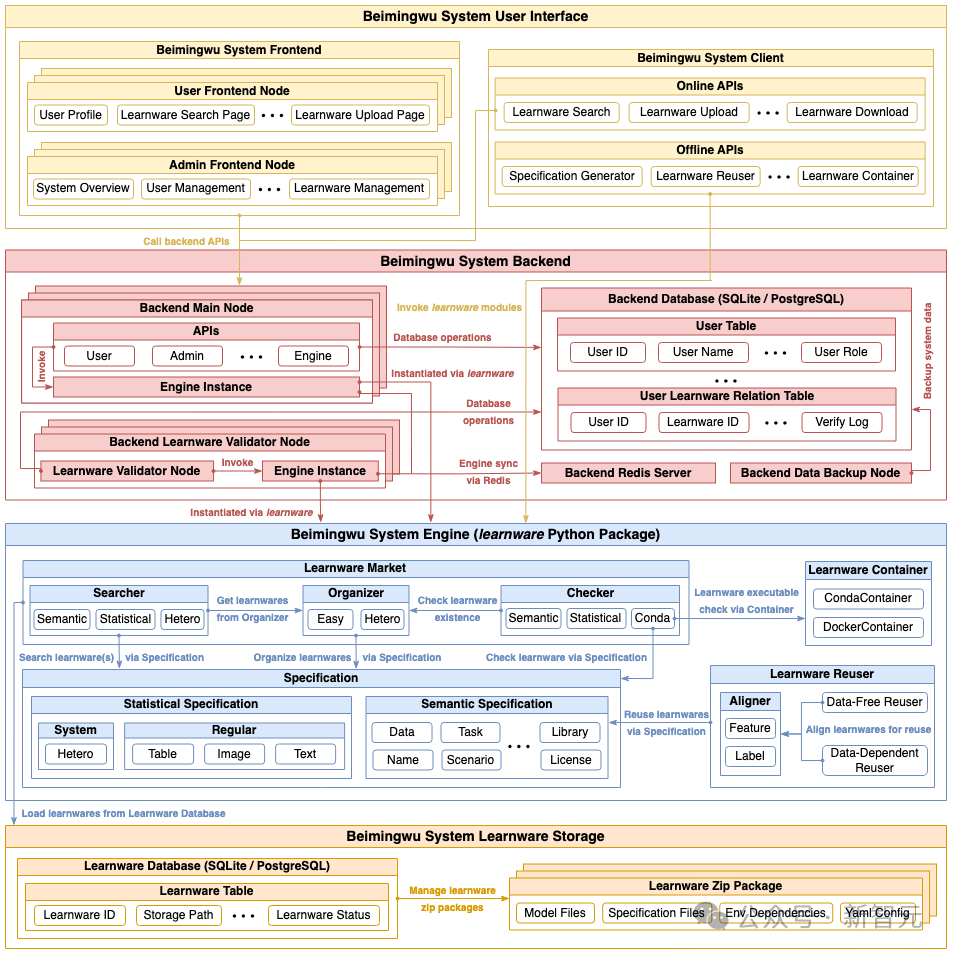
- Learningware storage layer: manages learningware stored in zip package format, and provides access to relevant information through the learningware database;
- System engine layer: includes the learningware paradigm All processes, including learningware uploading, detection, organization, search, deployment and reuse, are run independently of the backend and frontend in the form of a learnware Python package, providing a rich algorithm interface for learningware-related tasks and scientific research exploration;
- System back-end layer: realizes the industrial-grade deployment of Beimingwu, provides stable system online services, and supports user interaction between the front-end and the client by providing a rich back-end API;
- User interaction layer: Implements web-based front-end and command-line-based client, providing rich and convenient ways for user interaction.
Experimental Evaluation
In the paper, the research team also constructed various types of basic experimental scenarios to evaluate tables, images and text data A benchmark algorithm for specification generation, learning artifact identification and reuse.
Tabular Data Experiment
On various tabular data sets, the team first evaluated the learning software system Performance in identifying and reusing learning artifacts that share the same feature space as user tasks.
Furthermore, since form tasks usually come from different feature spaces, the research team also evaluated the recognition and reuse of learning pieces from different feature spaces.
Homogeneous case
In the homogeneous case, the 53 stores in the PFS dataset act as 53 independent user.
Each store utilizes its own test data as user task data and adopts a unified feature engineering approach. These users can then search the base system for homogeneous learning items that share the same feature space as their tasks.
When the user has no labeled data or the amount of labeled data is limited, the team compared different benchmark algorithms, and the average loss for all users is shown in the figure below. The left table shows that the data-free approach is much better than randomly selecting and deploying a learnware from the market; the right chart shows that when the user has limited training data, identifying and reusing single or multiple learnware is better than user-trained models. Better performance.
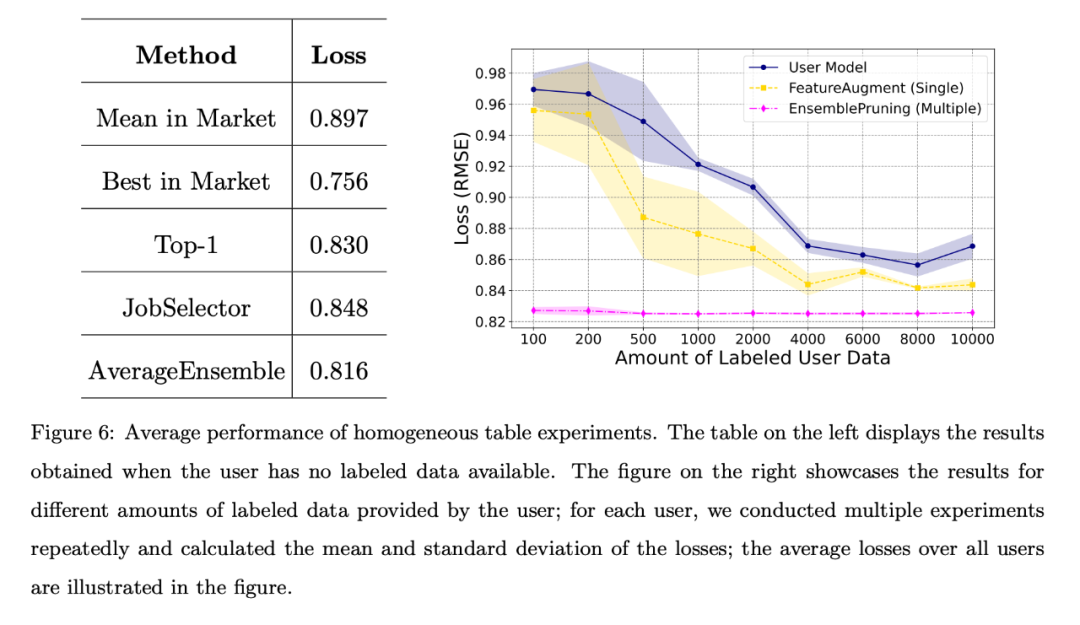
#The left table shows that the data-free approach is much better than randomly selecting and deploying a piece of learning from the market; the right table shows that when the user When training data is limited, identifying and reusing single or multiple learning pieces has better performance than user-trained models.
Heterogeneous cases
Heterogeneous cases can be further divided into for different feature engineering and different task scenarios.
Different feature engineering scenarios:
The results shown on the left in the figure below show that even if the user lacks annotation data, the learning software in the system It can show strong performance, especially the AverageEnsemble method that reuses multiple learning pieces.
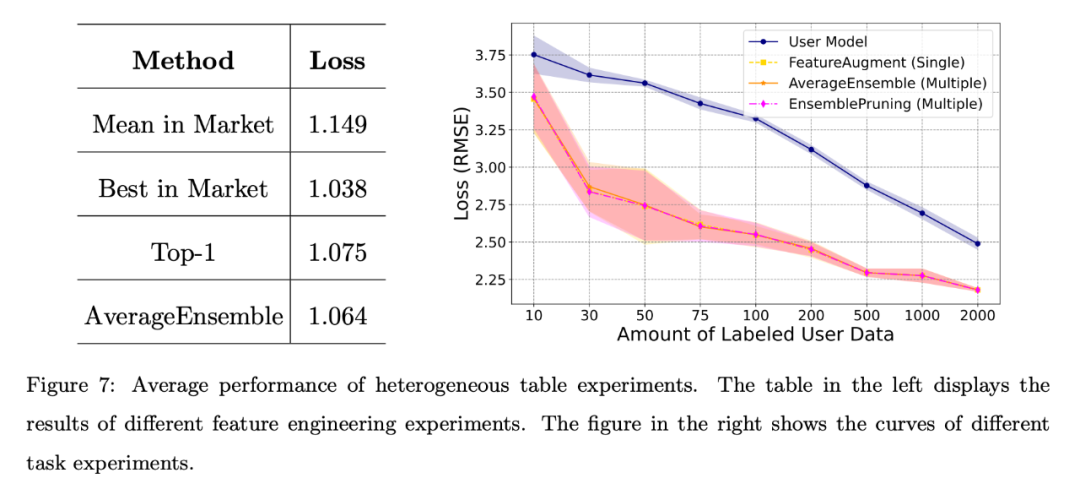
Different task scenarios:
The right picture above shows the user self-training model and several Loss curves for learningware reuse methods.
Obviously, experimental verification of heterogeneous learning pieces is beneficial when the amount of user annotated data is limited, and helps to better align with the user's feature space.
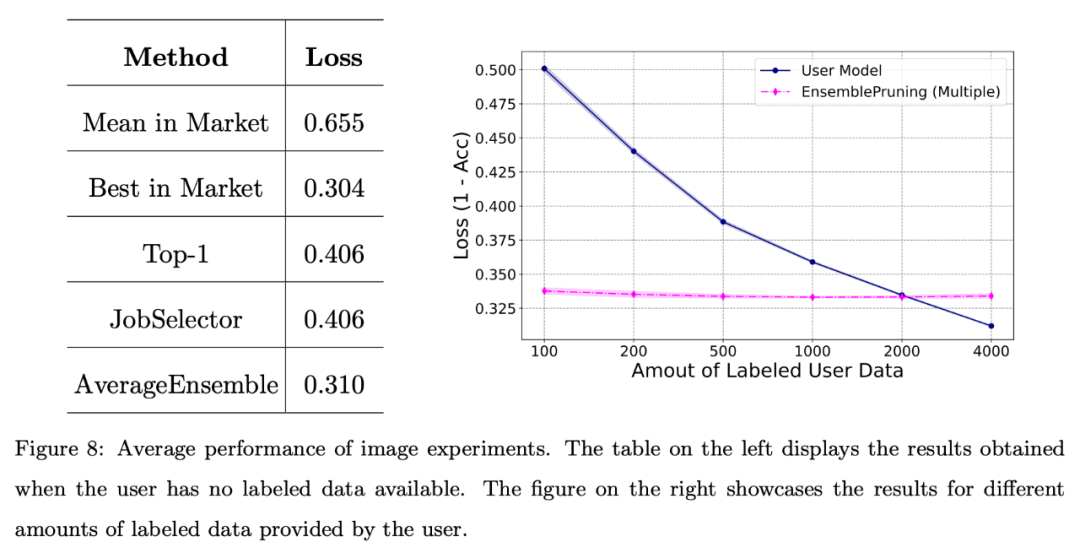
Image and text data experiments
In addition, the research team conducted basic testing of the system on image data sets Evaluate.
The figure below shows that leveraging a learning base system can yield good performance when users face scarcity of annotated data or only have a limited amount of data (fewer than 2000 instances).
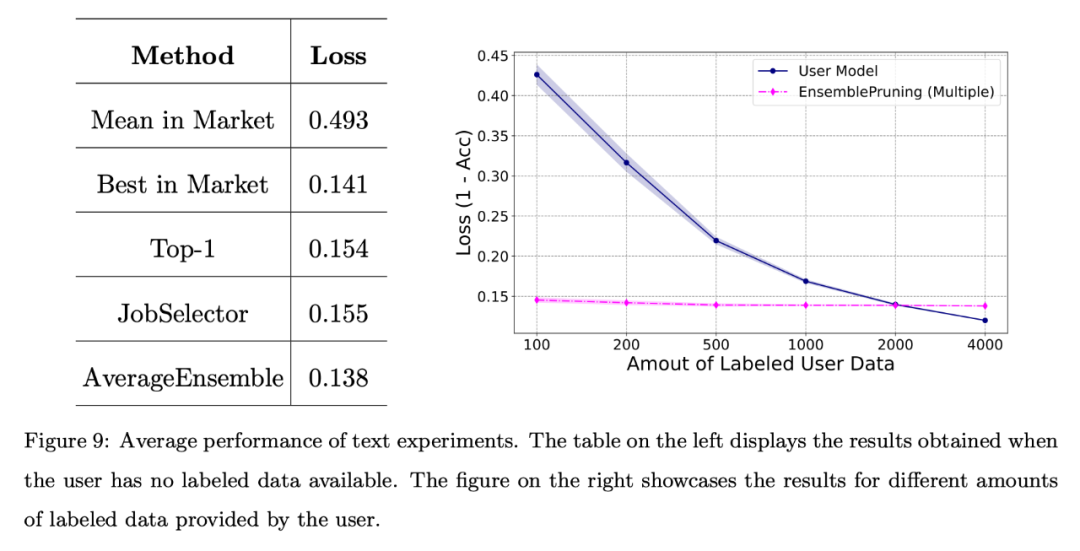
The team also conducted a basic evaluation of the system on a benchmark text dataset. Feature space alignment via a unified feature extractor.
As shown in the figure below, even when no annotation data is provided, the performance obtained through learningware identification and reuse is comparable to the best learningware in the system.
In addition, using the learning base system can reduce approximately 2,000 samples compared to training the model from scratch.
The above is the detailed content of An 8-year masterpiece of NTU Zhou Zhihua's team! The 'learningware' system solves the problem of machine learning reuse, and 'model fusion' emerges a new paradigm of scientific research. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1379
1379
 52
52
 Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Configuring a Debian mail server's firewall is an important step in ensuring server security. The following are several commonly used firewall configuration methods, including the use of iptables and firewalld. Use iptables to configure firewall to install iptables (if not already installed): sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstalliptablesView current iptables rules: sudoiptables-L configuration
 How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
How to set the Debian Apache log level
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:33 AM
This article describes how to adjust the logging level of the ApacheWeb server in the Debian system. By modifying the configuration file, you can control the verbose level of log information recorded by Apache. Method 1: Modify the main configuration file to locate the configuration file: The configuration file of Apache2.x is usually located in the /etc/apache2/ directory. The file name may be apache2.conf or httpd.conf, depending on your installation method. Edit configuration file: Open configuration file with root permissions using a text editor (such as nano): sudonano/etc/apache2/apache2.conf
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information
 Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
The steps to install an SSL certificate on the Debian mail server are as follows: 1. Install the OpenSSL toolkit First, make sure that the OpenSSL toolkit is already installed on your system. If not installed, you can use the following command to install: sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallopenssl2. Generate private key and certificate request Next, use OpenSSL to generate a 2048-bit RSA private key and a certificate request (CSR): openss
 How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
In Debian systems, the readdir function is used to read directory contents, but the order in which it returns is not predefined. To sort files in a directory, you need to read all files first, and then sort them using the qsort function. The following code demonstrates how to sort directory files using readdir and qsort in Debian system: #include#include#include#include#include//Custom comparison function, used for qsortintcompare(constvoid*a,constvoid*b){returnstrcmp(*(
 How to perform digital signature verification with Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How to perform digital signature verification with Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Using OpenSSL for digital signature verification on Debian systems, you can follow these steps: Preparation to install OpenSSL: Make sure your Debian system has OpenSSL installed. If not installed, you can use the following command to install it: sudoaptupdatesudoaptininstallopenssl to obtain the public key: digital signature verification requires the signer's public key. Typically, the public key will be provided in the form of a file, such as public_key.pe
 How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
In Debian systems, OpenSSL is an important library for encryption, decryption and certificate management. To prevent a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM), the following measures can be taken: Use HTTPS: Ensure that all network requests use the HTTPS protocol instead of HTTP. HTTPS uses TLS (Transport Layer Security Protocol) to encrypt communication data to ensure that the data is not stolen or tampered during transmission. Verify server certificate: Manually verify the server certificate on the client to ensure it is trustworthy. The server can be manually verified through the delegate method of URLSession



