A Practical Guide to Improving Website Performance

How to optimize website performance: a practical guide
In today's digital age, websites have become a window for businesses and individuals to showcase themselves. As users have higher and higher requirements for website speed and performance, website performance optimization work has become crucial. A website with good performance can provide users with a better experience, improve user satisfaction, and also help the website achieve better results in search rankings. This article will introduce you to some practical guidelines to help you optimize website performance.
- Test website performance
Before starting optimization work, you first need to test the performance of the website. This can be achieved through the use of various tools and techniques. For example, you can use website performance testing tools such as Google PageSpeed Insights and Pingdom Tools to evaluate your website's speed and performance. These tools can provide some powerful metrics for measuring website performance and giving suggestions for improvements.
- Compressed files and images
Using compressed files and images in a website is one of the important measures to improve website performance. By compressing files and images, you can reduce your website's loading time. Compression tools such as Gzip can be used to compress CSS, JavaScript and HTML files. Also, use appropriate image formats and compression tools to optimize the images on your website.
- Utilize browser caching
Browser caching allows the website to load faster when the user visits again. By setting appropriate cache headers in server responses, browsers can cache some static resources, such as images, CSS, and JavaScript files, to reduce network requests. This reduces the load on the server and makes the website more responsive.
- Reduce HTTP requests
HTTP requests are requests made when loading a web page, including CSS, JavaScript, images, etc. Reducing HTTP requests can significantly improve website performance. You can reduce the number of requests by merging, compressing, and inlining files. In addition, using CSS sprites and lazy loading of CSS and JavaScript are also effective methods.
- Optimizing database queries
For websites that use databases, optimizing database queries is also the key to improving performance. By using the correct indexes, optimizing query statements and avoiding unnecessary queries, you can reduce the time of database operations. In addition, the use of caching techniques, such as caching query results and using cache servers, can also improve database performance.
- Using a CDN
A content delivery network (CDN) is a technology that caches website content on servers around the world, thereby providing faster speeds. By using a CDN, websites can better distribute static resources, reduce latency and network load, and improve website performance.
- Remove unnecessary plug-ins and scripts
Using too many plug-ins and scripts in the website will cause the page to load slowly. Therefore, it is recommended to use only necessary plug-ins and scripts and remove unnecessary functions and code. Also, make sure to use the latest versions of plugins and scripts to ensure their performance is improved.
- Use caching and load balancing
Caching and load balancing are effective means to improve website performance. By using caching technology, the static content of the website can be cached on the cache server, thereby reducing the load on the back-end server and improving the response speed of the website. In addition, by using load balancing technology, traffic can be evenly distributed to multiple servers to improve website availability and performance.
Although website performance optimization is a complex process, by taking some simple steps, you can significantly improve your website performance. This article provides practical guidance that can serve as a starting point for you to begin your website performance optimization efforts. I hope this article can help you build a fast and high-performance website that provides a better user experience.
The above is the detailed content of A Practical Guide to Improving Website Performance. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What is the architecture and working principle of Spring Data JPA?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
What is the architecture and working principle of Spring Data JPA?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
SpringDataJPA is based on the JPA architecture and interacts with the database through mapping, ORM and transaction management. Its repository provides CRUD operations, and derived queries simplify database access. Additionally, it uses lazy loading to only retrieve data when necessary, thus improving performance.
 What is the original meaning of dynamic linking and static linking in Linux?
Feb 05, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
What is the original meaning of dynamic linking and static linking in Linux?
Feb 05, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
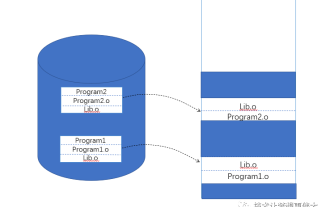
As usual, let’s ask a few questions: Why dynamic linking? How to do dynamic linking? What is address-independent code technology? What is delayed binding technology? How to do explicit linking while the program is running? Why dynamic linking? The emergence of dynamic linking is to solve some shortcomings of static linking: saving memory and disk space: As shown in the figure below, Program1 and Program2 contain two modules, Program1.o and Program2.o respectively, and they both require the Lib.o module. In the case of static linking, both target files use the Lib.o module, so they have copies in the executable files Program1 and program2 output by the link and run at the same time.
 What to do if the html image is too large
Apr 05, 2024 pm 12:24 PM
What to do if the html image is too large
Apr 05, 2024 pm 12:24 PM
Here are some ways to optimize HTML images that are too large: Optimize image file size: Use a compression tool or image editing software. Use media queries: Dynamically resize images based on device. Implement lazy loading: only load the image when it enters the visible area. Use a CDN: Distribute images to multiple servers. Use image placeholder: Display a placeholder image while the image is loading. Use thumbnails: Displays a smaller version of the image and loads the full-size image on click.
 Decoding Laravel performance bottlenecks: Optimization techniques fully revealed!
Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
Decoding Laravel performance bottlenecks: Optimization techniques fully revealed!
Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
Decoding Laravel performance bottlenecks: Optimization techniques fully revealed! Laravel, as a popular PHP framework, provides developers with rich functions and a convenient development experience. However, as the size of the project increases and the number of visits increases, we may face the challenge of performance bottlenecks. This article will delve into Laravel performance optimization techniques to help developers discover and solve potential performance problems. 1. Database query optimization using Eloquent delayed loading When using Eloquent to query the database, avoid
 Java JPA performance optimization tips: make your application fly
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
Java JPA performance optimization tips: make your application fly
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
Article keywords: JavaJPA performance optimization ORM entity management JavaJPA (JavaPersistance API) is an object-relational mapping (ORM) framework that allows you to use Java objects to operate data in the database. JPA provides a unified API for interacting with databases, allowing you to use the same code to access different databases. In addition, JPA also supports features such as lazy loading, caching, and dirty data detection, which can improve application performance. However, if used incorrectly, JPA performance can become a bottleneck for your application. The following are some common performance problems: N+1 query problem: When you use JPQL queries in your application, you may encounter N+1 query problems. In this kind of
 How does Hibernate optimize database query performance?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
How does Hibernate optimize database query performance?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Tips for optimizing Hibernate query performance include: using lazy loading to defer loading of collections and associated objects; using batch processing to combine update, delete, or insert operations; using second-level cache to store frequently queried objects in memory; using HQL outer connections , retrieve entities and their related entities; optimize query parameters to avoid SELECTN+1 query mode; use cursors to retrieve massive data in blocks; use indexes to improve the performance of specific queries.
 How to prevent iframe loading event
Feb 19, 2024 am 08:02 AM
How to prevent iframe loading event
Feb 19, 2024 am 08:02 AM
How to prevent iframe loading events In web development, we often use iframe tags to embed other web pages or content. By default, when the browser loads an iframe, the loading event is triggered. However, in some cases we may want to delay the loading of an iframe, or prevent the loading event entirely. In this article, we'll explore how to achieve this through code examples. 1. Delay loading of iframe If you want to delay loading of iframe, we can use
 What are the disadvantages of Hibernate ORM framework?
Apr 18, 2024 am 08:30 AM
What are the disadvantages of Hibernate ORM framework?
Apr 18, 2024 am 08:30 AM
The HibernateORM framework has the following shortcomings: 1. Large memory consumption because it caches query results and entity objects; 2. High complexity, requiring in-depth understanding of the architecture and configuration; 3. Delayed loading delays, leading to unexpected delays; 4. Performance bottlenecks, in May occur when a large number of entities are loaded or updated at the same time; 5. Vendor-specific implementation, resulting in differences between databases.




