Detailed explanation of Linux program compilation process
Computer programming languages are usually divided into three categories: machine language, assembly language and high-level language. High-level languages need to be translated into machine language before they can be executed. There are two ways of translation, one is compiled and the other is interpreted.
So we basically divide high-level languages into two categories, one is compiled language, such as C, C, Java, and the other is interpreted language, such as Python, Ruby, MATLAB, JavaScript.
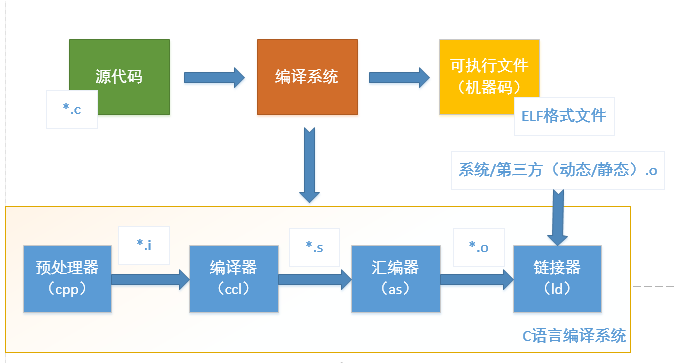
This article will introduce the process of converting high-level programs written in C/C language into binary codes that can be executed by the processor, including four steps:
- Preprocessing
- Compilation
- Assembly
- Linking
GCC tool chain introduction
The commonly referred to as GCC is the abbreviation of GUN Compiler Collection, which is a commonly used compilation tool on Linux systems. GCC tool chain software includes GCC, Binutils, C runtime library, etc.
GCC
GCC (GNU C Compiler) is a compilation tool. This article will introduce the process of converting a program written in C/C language into a binary code that can be executed by the processor, which is completed by the compiler.
Binutils
A set of binary program processing tools, including: addr2line, ar, objcopy, objdump, as, ld, ldd, readelf, size, etc. This set of tools is indispensable for development and debugging. Their respective introductions are as follows:
- addr2line: used to convert the program address into its corresponding program source file and corresponding code line, and also obtain the corresponding function. This tool will help the debugger locate the corresponding source code location during debugging.
- as: Mainly used for assembly, please refer to the following article for detailed introduction to assembly.
- ld: Mainly used for links. For details about links, please see the following article.
- ar: Mainly used to create static libraries. In order to make it easier for beginners to understand, the concepts of dynamic libraries and static libraries are introduced here:
- If you want to generate multiple .o object files into a library file, there are two types of libraries, one is a static library and the other is a dynamic library.
- In Windows, static libraries are files with the .lib suffix, and shared libraries are files with the .dll suffix. In Linux, static libraries are files with the .a suffix, and shared libraries are files with the .so suffix.
- The difference between static libraries and dynamic libraries lies in the time when the code is loaded. The code of the static library has been loaded into the executable program during the compilation process, so it is larger in size. The code of the shared library is loaded into memory when the executable program is running, and is only simply referenced during the compilation process, so the code size is smaller. In Linux systems, you can use the ldd command to view the shared libraries that an executable program depends on.
- If there are multiple programs in a system that need to run at the same time and there are shared libraries between these programs, then using a dynamic library will save more memory.
- ldd: can be used to view the shared libraries that an executable program depends on.
- objcopy: Translate an object file into another format, such as converting .bin to .elf, or converting .elf to .bin, etc.
- objdump: Its main function is disassembly. For a detailed introduction to disassembly, see the following article.
- readelf: Displays information about ELF files, see later for more information.
- size: List the size and total size of each part of the executable file, code segment, data segment, total size, etc. Please see the following article for specific usage examples of using size.
C runtime library
The C language standard mainly consists of two parts: one part describes the syntax of C, and the other part describes the C standard library. The C standard library defines a set of standard header files. Each header file contains some related functions, variables, type declarations and macro definitions. For example, the common printf function is a C standard library function, and its prototype is defined in the stdio header file.
C语言标准仅仅定义了C标准库函数原型,并没有提供实现。因此,C语言编译器通常需要一个C运行时库(C Run Time Libray,CRT)的支持。C运行时库又常简称为C运行库。与C语言类似,C++也定义了自己的标准,同时提供相关支持库,称为C++运行时库。
准备工作
由于GCC工具链主要是在Linux环境中进行使用,因此本文也将以Linux系统作为工作环境。为了能够演示编译的整个过程,本节先准备一个C语言编写的简单Hello程序作为示例,其源代码如下所示:
#include
//此程序很简单,仅仅打印一个Hello World的字符串。
int main(void)
{
printf("Hello World! \n");
return 0;
}
“
编译过程
1.预处理
预处理的过程主要包括以下过程:
- 将所有的#define删除,并且展开所有的宏定义,并且处理所有的条件预编译指令,比如#if #ifdef #elif #else #endif等。
- 处理#include预编译指令,将被包含的文件插入到该预编译指令的位置。
- 删除所有注释“//”和“/* */”。
- 添加行号和文件标识,以便编译时产生调试用的行号及编译错误警告行号。
- 保留所有的#pragma编译器指令,后续编译过程需要使用它们。
使用gcc进行预处理的命令如下:
$ gcc -E hello.c -o hello.i // 将源文件hello.c文件预处理生成hello.i // GCC的选项-E使GCC在进行完预处理后即停止
hello.i文件可以作为普通文本文件打开进行查看,其代码片段如下所示:
// hello.i代码片段
extern void funlockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 942 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 2 "hello.c" 2
# 3 "hello.c"
int
main(void)
{
printf("Hello World!" "\n");
return 0;
}
2.编译
编译过程就是对预处理完的文件进行一系列的词法分析,语法分析,语义分析及优化后生成相应的汇编代码。
使用gcc进行编译的命令如下:
$ gcc -S hello.i -o hello.s // 将预处理生成的hello.i文件编译生成汇编程序hello.s // GCC的选项-S使GCC在执行完编译后停止,生成汇编程序
上述命令生成的汇编程序hello.s的代码片段如下所示,其全部为汇编代码。
// hello.s代码片段 main: .LFB0: .cfi_startproc pushq %rbp .cfi_def_cfa_offset 16 .cfi_offset 6, -16 movq %rsp, %rbp .cfi_def_cfa_register 6 movl $.LC0, %edi call puts movl $0, %eax popq %rbp .cfi_def_cfa 7, 8 ret .cfi_endproc
3.汇编
汇编过程调用对汇编代码进行处理,生成处理器能识别的指令,保存在后缀为.o的目标文件中。由于每一个汇编语句几乎都对应一条处理器指令,因此,汇编相对于编译过程比较简单,通过调用Binutils中的汇编器as根据汇编指令和处理器指令的对照表一一翻译即可。
当程序由多个源代码文件构成时,每个文件都要先完成汇编工作,生成.o目标文件后,才能进入下一步的链接工作。注意:目标文件已经是最终程序的某一部分了,但是在链接之前还不能执行。
使用gcc进行汇编的命令如下:
$ gcc -c hello.s -o hello.o // 将编译生成的hello.s文件汇编生成目标文件hello.o // GCC的选项-c使GCC在执行完汇编后停止,生成目标文件 //或者直接调用as进行汇编 $ as -c hello.s -o hello.o //使用Binutils中的as将hello.s文件汇编生成目标文件
注意:hello.o目标文件为ELF(Executable and Linkable Format)格式的可重定向文件。
4.链接
链接也分为静态链接和动态链接,其要点如下:
- 静态链接是指在编译阶段直接把静态库加入到可执行文件中去,这样可执行文件会比较大。链接器将函数的代码从其所在地(不同的目标文件或静态链接库中)拷贝到最终的可执行程序中。为创建可执行文件,链接器必须要完成的主要任务是:符号解析(把目标文件中符号的定义和引用联系起来)和重定位(把符号定义和内存地址对应起来然后修改所有对符号的引用)。
- 动态链接则是指链接阶段仅仅只加入一些描述信息,而程序执行时再从系统中把相应动态库加载到内存中去。
- 在Linux系统中,gcc编译链接时的动态库搜索路径的顺序通常为:首先从gcc命令的参数-L指定的路径寻找;再从环境变量LIBRARY_PATH指定的路径寻址;再从默认路径/lib、/usr/lib、/usr/local/lib寻找。
- 在Linux系统中,执行二进制文件时的动态库搜索路径的顺序通常为:首先搜索编译目标代码时指定的动态库搜索路径;再从环境变量LD_LIBRARY_PATH指定的路径寻址;再从配置文件/etc/ld.so.conf中指定的动态库搜索路径;再从默认路径/lib、/usr/lib寻找。
- 在Linux系统中,可以用ldd命令查看一个可执行程序依赖的共享库。
由于链接动态库和静态库的路径可能有重合,所以如果在路径中有同名的静态库文件和动态库文件,比如libtest.a和libtest.so,gcc链接时默认优先选择动态库,会链接libtest.so,如果要让gcc选择链接libtest.a则可以指定gcc选项-static,该选项会强制使用静态库进行链接。以Hello World为例:
- 如果使用命令“gcc hello.c -o hello”则会使用动态库进行链接,生成的ELF可执行文件的大小(使用Binutils的size命令查看)和链接的动态库(使用Binutils的ldd命令查看)如下所示:
$ gcc hello.c -o hello $ size hello //使用size查看大小 text data bss dec hex filename 1183 552 8 1743 6cf hello $ ldd hello //可以看出该可执行文件链接了很多其他动态库,主要是Linux的glibc动态库 linux-vdso.so.1 => (0x00007fffefd7c000) libc.so.6 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 (0x00007fadcdd82000) /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007fadce14c000)
如果使用命令“gcc -static hello.c -o hello”则会使用静态库进行链接,生成的ELF可执行文件的大小(使用Binutils的size命令查看)和链接的动态库(使用Binutils的ldd命令查看)如下所示:
$ gcc -static hello.c -o hello $ size hello //使用size查看大小 text data bss dec hex filename 823726 7284 6360 837370 cc6fa hello //可以看出text的代码尺寸变得极大 $ ldd hello not a dynamic executable //说明没有链接动态库
链接器链接后生成的最终文件为ELF格式可执行文件,一个ELF可执行文件通常被链接为不同的段,常见的段譬如.text、.data、.rodata、.bss等段。
分析ELF文件
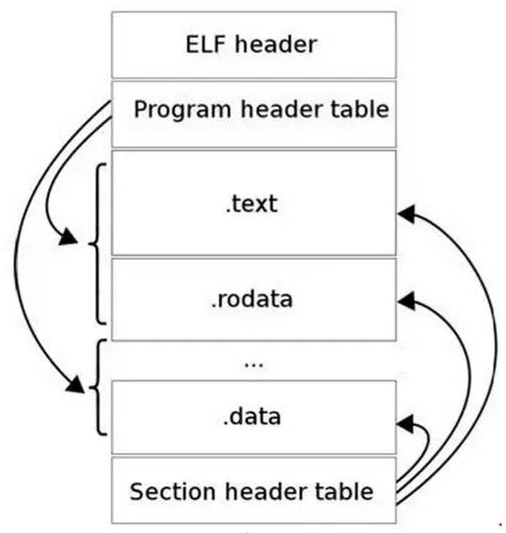
1.ELF文件的段
ELF文件格式如下图所示,位于ELF Header和Section Header Table之间的都是段(Section)。一个典型的ELF文件包含下面几个段:
- .text:已编译程序的指令代码段。
- .rodata:ro代表read only,即只读数据(譬如常数const)。
- .data:已初始化的C程序全局变量和静态局部变量。
- .bss:未初始化的C程序全局变量和静态局部变量。
- .debug:调试符号表,调试器用此段的信息帮助调试。
可以使用readelf -S查看其各个section的信息如下
$ readelf -S hello There are 31 section headers, starting at offset 0x19d8: Section Headers: [Nr] Name Type Address Offset Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align [ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 00000000 0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 0 …… [11] .init PROGBITS 00000000004003c8 000003c8 000000000000001a 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 4 …… [14] .text PROGBITS 0000000000400430 00000430 0000000000000182 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 16 [15] .fini PROGBITS 00000000004005b4 000005b4 ……
2.反汇编ELF
由于ELF文件无法被当做普通文本文件打开,如果希望直接查看一个ELF文件包含的指令和数据,需要使用反汇编的方法。
使用objdump -D对其进行反汇编如下:
$ objdump -D hello …… 0000000000400526 : // main标签的PC地址 //PC地址:指令编码 指令的汇编格式 400526: 55 push %rbp 400527: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp 40052a: bf c4 05 40 00 mov $0x4005c4,%edi 40052f: e8 cc fe ff ff callq 400400 400534: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax 400539: 5d pop %rbp 40053a: c3 retq 40053b: 0f 1f 44 00 00 nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
使用objdump -S将其反汇编并且将其C语言源代码混合显示出来:
$ gcc -o hello -g hello.c //要加上-g选项
$ objdump -S hello
……
0000000000400526 :
#include
int
main(void)
{
400526: 55 push %rbp
400527: 48 89 e5 mov %rsp,%rbp
printf("Hello World!" "\n");
40052a: bf c4 05 40 00 mov $0x4005c4,%edi
40052f: e8 cc fe ff ff callq 400400
return 0;
400534: b8 00 00 00 00 mov $0x0,%eax
}
400539: 5d pop %rbp
40053a: c3 retq
40053b: 0f 1f 44 00 00 nopl 0x0(%rax,%rax,1)
……
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Linux program compilation process. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
DeepSeek is a powerful intelligent search and analysis tool that provides two access methods: web version and official website. The web version is convenient and efficient, and can be used without installation; the official website provides comprehensive product information, download resources and support services. Whether individuals or corporate users, they can easily obtain and analyze massive data through DeepSeek to improve work efficiency, assist decision-making and promote innovation.
 How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
There are many ways to install DeepSeek, including: compile from source (for experienced developers) using precompiled packages (for Windows users) using Docker containers (for most convenient, no need to worry about compatibility) No matter which method you choose, Please read the official documents carefully and prepare them fully to avoid unnecessary trouble.
 BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet is a cryptocurrency exchange that provides a variety of trading services including spot trading, contract trading and derivatives. Founded in 2018, the exchange is headquartered in Singapore and is committed to providing users with a safe and reliable trading platform. BITGet offers a variety of trading pairs, including BTC/USDT, ETH/USDT and XRP/USDT. Additionally, the exchange has a reputation for security and liquidity and offers a variety of features such as premium order types, leveraged trading and 24/7 customer support.
 Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi OKX, the world's leading digital asset exchange, has now launched an official installation package to provide a safe and convenient trading experience. The OKX installation package of Ouyi does not need to be accessed through a browser. It can directly install independent applications on the device, creating a stable and efficient trading platform for users. The installation process is simple and easy to understand. Users only need to download the latest version of the installation package and follow the prompts to complete the installation step by step.
 Get the gate.io installation package for free
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Get the gate.io installation package for free
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Gate.io is a popular cryptocurrency exchange that users can use by downloading its installation package and installing it on their devices. The steps to obtain the installation package are as follows: Visit the official website of Gate.io, click "Download", select the corresponding operating system (Windows, Mac or Linux), and download the installation package to your computer. It is recommended to temporarily disable antivirus software or firewall during installation to ensure smooth installation. After completion, the user needs to create a Gate.io account to start using it.
 Ouyi Exchange Download Official Portal
Feb 21, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Ouyi Exchange Download Official Portal
Feb 21, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Ouyi, also known as OKX, is a world-leading cryptocurrency trading platform. The article provides a download portal for Ouyi's official installation package, which facilitates users to install Ouyi client on different devices. This installation package supports Windows, Mac, Android and iOS systems. Users can choose the corresponding version to download according to their device type. After the installation is completed, users can register or log in to the Ouyi account, start trading cryptocurrencies and enjoy other services provided by the platform.
 gate.io official website registration installation package link
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
gate.io official website registration installation package link
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
Gate.io is a highly acclaimed cryptocurrency trading platform known for its extensive token selection, low transaction fees and a user-friendly interface. With its advanced security features and excellent customer service, Gate.io provides traders with a reliable and convenient cryptocurrency trading environment. If you want to join Gate.io, please click the link provided to download the official registration installation package to start your cryptocurrency trading journey.
 How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set the permissions of unixsocket after the system restarts. Every time the system restarts, we need to execute the following command to modify the permissions of unixsocket: sudo...






