Why the default page size of Linux system is 4KB
As we all know, Linux manages memory in units of pages. Whether it is loading data from disk into memory or writing data from memory back to disk, the operating system will operate in units of pages, which also means that if we only write one byte of data to disk , the operating system also needs to flush all the data in the entire page to the disk.
It is worth noting that in Linux, we can either use normal-sized memory pages for operations or use huge memory pages (Huge Page), although the default size of memory pages on most processors is 4KB. But some processors will use 8KB, 16KB or 64KB as the default page size. In addition to normal memory page sizes, different processors support different huge page sizes. For example, on an x86 processor we can use memory pages of 2MB size.
4KB memory pages have become a historical relic. This page size was widely adopted starting in the 1980s and still remains today. Although today's hardware is richer than in the past, we are still stuck with the 4KB memory page size passed down from the past. Normally, we can clearly see the specifications of the memory module when installing the memory, as shown in the figure below:

Figure 1 – Random Access Memory
Today, 4KB memory page size may not be the best choice. 8KB or 16KB may be a better choice, but this is a trade-off made in the past under specific scenarios. In this article, we should not be too obsessed with the number 4KB. We should pay more attention to the several factors that determine this result, so that when we encounter similar scenarios, we can consider the best choice from these aspects. In this article The article will introduce the following two factors that affect the memory page size, they are:
Too small page size will bring larger page table entries to increase the TLB (Translation lookaside buffer) search speed and additional overhead during addressing;
Excessive page size will waste memory space, cause memory fragmentation, and reduce memory utilization;
In the last century, the above two factors were fully considered when designing the memory page size, and finally 4KB memory pages were selected as the most common page size of the operating system. Next, we will introduce in detail the impact of the above on the performance of the operating system. Influence.
Page table entry
We have introduced virtual memory in Linux in the article Why Linux Needs Virtual Memory. What each process can see is an independent virtual memory space. Virtual memory space is only a logical concept. The process still needs to access virtual memory. Memory corresponds to physical memory, and the conversion from virtual memory to physical memory requires the use of page tables held by each process.
In order to store the mapped data of 128 TiB virtual memory in the 64-bit operating system, Linux introduced a four-layer page table to assist virtual address translation in 2.6.10, and a five-layer page table structure was introduced in 4.11. In the future, more layers of page table structures may be introduced to support 64-bit virtual addresses.
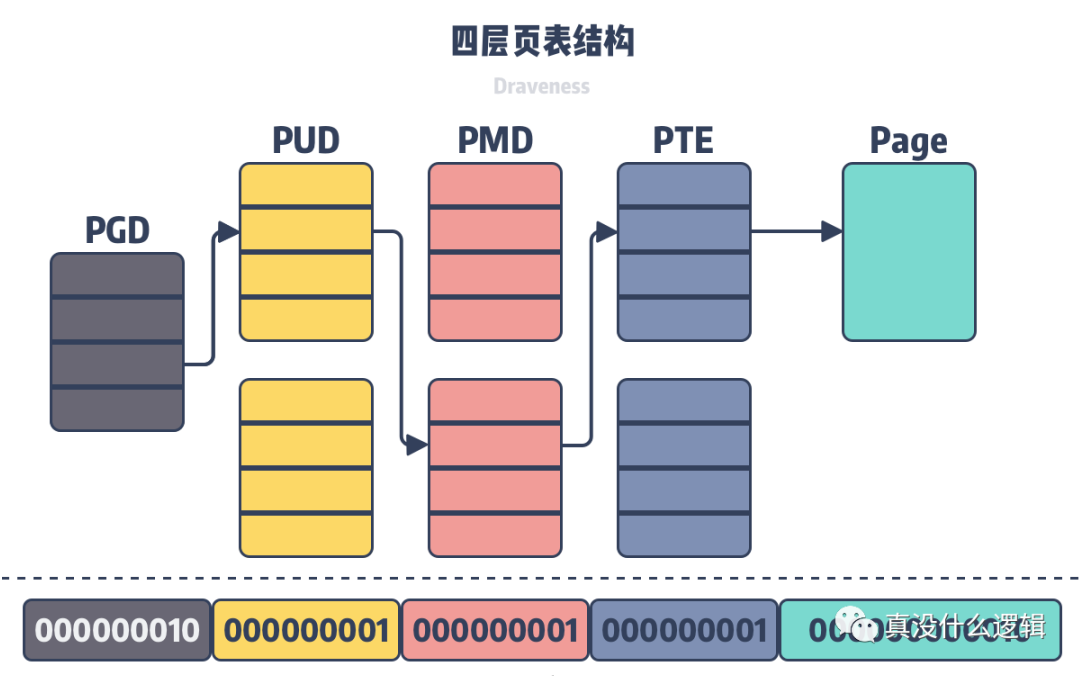
Figure 2 – Four-layer page table structure
In the four-layer page table structure shown in the figure above, the operating system will use the lowest 12 bits as the page offset, and the remaining 36 bits will be divided into four groups to represent the current level in the previous layer. Index, all virtual addresses can use the above-mentioned multi-layer page table to find the corresponding physical address.
Because the size of the virtual address space of the operating system is certain, the entire virtual address space is evenly divided into N memory pages of the same size, so the size of the memory page will ultimately determine the level of page table entries in each process. Structure and specific number, the smaller the virtual page size, the more page table entries and virtual pages there are in a single process.
PagesCount=VirtualMemory ÷ PageSize
Because the current virtual page size is 4096 bytes, the 12 bits at the end of the virtual address can represent the address in the virtual page. If the size of the virtual page is reduced to 512 bytes, then the original four-level page table structure or five-level page table structure The layered page table structure will become five or six layers, which will not only increase the additional overhead of memory access, but also increase the memory size occupied by the page table entries in each process.
Fragmentation
Because the memory mapping device works at the memory page level, the operating system believes that the smallest unit of memory allocation is the virtual page. Even if the user program only applies for 1 byte of memory, the operating system will apply for a virtual page for it, as shown in the figure below. If the size of the memory page is 24KB, then applying for 1 byte of memory will waste ~99.9939% of the space. .
Figure 3 – Fragmentation of large memory
As the memory page size increases, memory fragmentation will become more and more serious. Small memory pages will reduce memory fragmentation in the memory space and improve memory utilization. In the last century, memory resources were not as abundant as they are today. In most cases, memory is not a resource that limits the running of programs. Most online services require more CPUs, not more memory. However, memory was actually a scarce resource in the last century, so improving the utilization of scarce resources is something we have to consider:
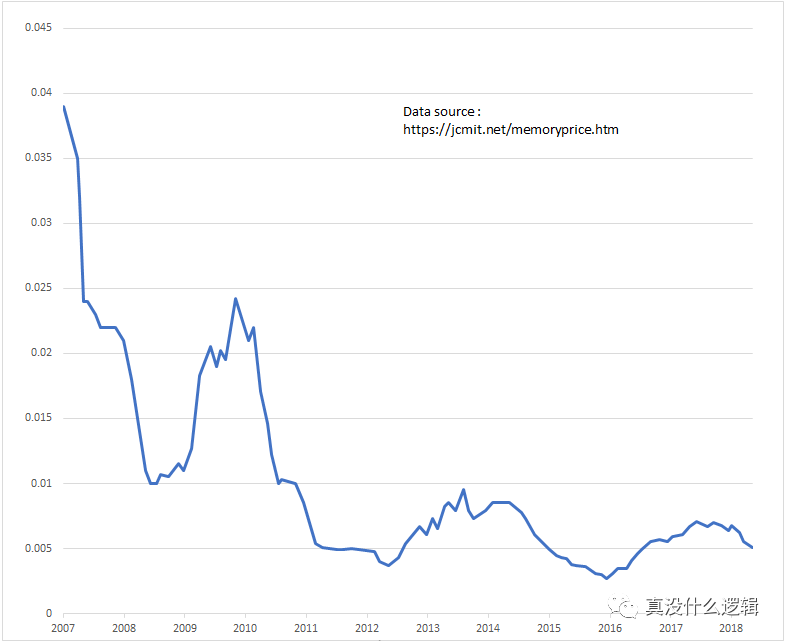
Figure 4 – Price of memory
Memory sticks in the 1980s and 1990s were only 512KB or 2MB, and the price was ridiculously expensive. However, memory of several GB is very common today, so although memory utilization is still very important, the price of memory Today, with significant reductions, fragmented memory is no longer a key problem that needs to be solved.
In addition to memory utilization, larger memory pages will also increase the additional overhead of memory copying. Because of the copy-on-write mechanism on Linux, when multiple processes share the same memory, when one of the processes Modifying the shared virtual memory will trigger the copy of the memory page. At this time, the smaller the memory page of the operating system, the smaller the additional overhead caused by copy-on-write.
Summarize
As we mentioned above, 4KB memory page is the default setting decided in the last century. From today's perspective, this is probably the wrong choice. Arm64, ia64 and other architectures can already support it. Memory pages of 8KB, 16KB and other sizes. As the price of memory becomes lower and lower and the system memory becomes larger and larger, larger memory may be a better choice for the operating system. Let’s review the two Factors that determine memory page size:
- Too small a page size will lead to larger page table entries, which will increase the TLB (Translation lookaside buffer) search speed and additional overhead during addressing, but will also reduce memory fragmentation in the program and improve memory utilization;
- Excessive page size will waste memory space, cause memory fragmentation, and reduce memory utilization, but it can reduce page table entries in the process and TLB addressing time;
Finally, let’s look at some relatively open related questions. Interested readers can think carefully about the following questions:
What are the differences and connections between sectors, blocks and pages in Linux?
How is the block size determined in Linux? What are the common sizes?
The above is the detailed content of Why the default page size of Linux system is 4KB. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
CentOS installation steps: Download the ISO image and burn bootable media; boot and select the installation source; select the language and keyboard layout; configure the network; partition the hard disk; set the system clock; create the root user; select the software package; start the installation; restart and boot from the hard disk after the installation is completed.
 Centos options after stopping maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
Centos options after stopping maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
CentOS has been discontinued, alternatives include: 1. Rocky Linux (best compatibility); 2. AlmaLinux (compatible with CentOS); 3. Ubuntu Server (configuration required); 4. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (commercial version, paid license); 5. Oracle Linux (compatible with CentOS and RHEL). When migrating, considerations are: compatibility, availability, support, cost, and community support.
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Troubleshooting steps for failed Docker image build: Check Dockerfile syntax and dependency version. Check if the build context contains the required source code and dependencies. View the build log for error details. Use the --target option to build a hierarchical phase to identify failure points. Make sure to use the latest version of Docker engine. Build the image with --t [image-name]:debug mode to debug the problem. Check disk space and make sure it is sufficient. Disable SELinux to prevent interference with the build process. Ask community platforms for help, provide Dockerfiles and build log descriptions for more specific suggestions.
 What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
After CentOS is stopped, users can take the following measures to deal with it: Select a compatible distribution: such as AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, and CentOS Stream. Migrate to commercial distributions: such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Oracle Linux. Upgrade to CentOS 9 Stream: Rolling distribution, providing the latest technology. Select other Linux distributions: such as Ubuntu, Debian. Evaluate other options such as containers, virtual machines, or cloud platforms.
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)




