A simple Go simulation - concurrency issues

php Editor Shinichi brings you a simple but interesting Go simulation game called "Concurrency Problem". This game takes concurrent programming as its theme, allowing players to experience the charm of concurrent programming in a virtual world. In the game, players need to write code to handle the simultaneous execution of multiple tasks and test their concurrent programming abilities. The game interface is concise and clear, and the operation is simple, suitable for beginners to get started, and it also provides multiple difficulty and challenge modes for players to choose from. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, you can enjoy the fun of concurrent programming in this simulation game.
Question content
I am a student from Poland and this semester I started a concurrent programming course (Go, Ada and some theoretical and CSP languages in the future). To be honest, Golang looks interesting but I'm a bit confused. The bottom line is that in my experience I would call myself a below average programmer. Basically, my task is to create a simulation, which I will describe like this:
-
There is an n*m grid
-
Travelers can be generated randomly, up to k travelers, each traveler has a unique ID (1, 2, 3, etc., up to k)
-
At a random moment, if the space is free (I'm sure the free space is 0), the traveler can move up, left, right or down on the grid
-
There is also a camera that sometimes prints the current state of the mesh as well as recent movements (not implemented yet)
-
Unofficially, I've heard that I should use channels, whatever that means
My idea is to create a structure with the id and coordinates of each traveler and send their id to a channel that represents willingness to move, and then I will randomly choose the direction of movement.
I'm a little confused about concurrency - not only if and where should I use wgs and mutexes, but also if for example if I do go func(){} should the loop be inside or outside. I would be very happy to appreciate any tips, help or fixes/ideas to fix my code because currently, as you guessed, it is not working properly (e.g. when the camera prints the grid, sometimes there are more than k travelers , where multiple travelers share the same number and sometimes they seem to disappear). Hope everyone has a great day and I'd really appreciate any help :)
package main;
import(
"fmt"
"os"
"strconv"
"math/rand"
//"sync"
"time"
)
type traveler struct{
id int;
x int;
y int;
}
func main(){
//command line
n, err := strconv.Atoi(os.Args[1]);
m, err := strconv.Atoi(os.Args[2]);
k, err := strconv.Atoi(os.Args[3]);
if err != nil{
panic(err)
return
}
//board
var grid [][]int;
grid = make([][]int, n)
for i:=0; i<n; i++{
grid[i] = make([]int, m)
}
//array of travelers, channel for moves and id
travelers := make([]traveler, k)
no_of_travelers := 0;
move := make(chan int, k);
id := 1;
//var wg sync.WaitGroup
go camera(grid);
go func() {
for i:=0; i<len(travelers); i++ {
if no_of_travelers<k{
travelers[i] = spawnTraveler(&id,grid);
no_of_travelers++;
}
}
}()
go func() {
for{
a:= rand.Intn(k);
sendMoveTraveler(&travelers[a], move);
}
}()
receiveMoveTraveler(travelers, move, grid);
}
func spawnTraveler(id *int, grid [][]int) traveler{
x:=-1;
y:=-1;
for{
x = rand.Intn(len(grid));
y = rand.Intn(len(grid));
if(grid[x][y]==0){
break;
}
}
t := traveler{id: *id, x: x, y:y};
grid[x][y] = *id;
*id++;
return t;
}
func sendMoveTraveler(t *traveler, move chan int){
move <- t.id
}
func receiveMoveTraveler(travelers []traveler, move chan int, grid [][]int){
for{
id := <- move
for i:=0; i<len(travelers); i++{
if travelers[i].id == id{
direction := rand.Intn(4); //1-left 2-up 3-right 4-down
switch direction {
case 0:
if travelers[i].x>0 && grid[travelers[i].x-1][travelers[i].y] == 0{
grid[travelers[i].x-1][travelers[i].y] = grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y];
grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y] = 0;
travelers[i].x = travelers[i].x-1;
travelers[i].y = travelers[i].y;
}
case 1:
if travelers[i].y>0 && grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y-1] == 0{
grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y-1] = grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y];
grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y] = 0;
travelers[i].x = travelers[i].x;
travelers[i].y = travelers[i].y-1;
}
case 2:
if travelers[i].x<len(grid)-1 && grid[travelers[i].x+1][travelers[i].y] == 0{
grid[travelers[i].x+1][travelers[i].y] = grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y];
grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y] = 0;
travelers[i].x = travelers[i].x+1;
travelers[i].y = travelers[i].y;
}
case 3:
if travelers[i].y<len(grid)-1 && grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y+1] == 0{
grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y+1] = grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y];
grid[travelers[i].x][travelers[i].y] = 0;
travelers[i].x = travelers[i].x;
travelers[i].y = travelers[i].y+1;
}
}
//fmt.Println("Ściagnalem ruch", travelers[i].id);
}
}
}
}
func camera(grid [][]int){
for{
for i:=0; i<len(grid); i++{
for j:=0; j<len(grid); j++{
if grid[i][j]!= 0{
fmt.Printf("%02d ", grid[i][j]);
} else{
fmt.Printf("-- ");
}
}
fmt.Println();
}
fmt.Println();
time.Sleep(time.Second * 3);
}
}I'm a little overwhelmed by all the ideas - wgs, mutexes, atoms, etc.
Solution
- If you want to process work simultaneously (for example, taking a camera snapshot and moving a traveler can happen at the same time), goroutines are lightweight threads.
- Channels are used to transfer data between Go routines.
- Mutexes are used to allow goroutines to add locks on shared data for exclusive data access to avoid race conditions.
That being said:
- Running the camera snapshot in one goroutine while having the traveler move around in another goroutine looks good. Spawning the Goroutine is not necessary, you only need to do it once, so you can execute it in the main Goroutine.
- In your case, the channel brings no benefit. You have a Goroutine that generates a message and sends it over a channel to another Goroutine that will do the movement. You can do all of this sequentially in a single goroutine and avoid unnecessary complexity. Channels are useful for different use cases, but here it is redundant.
- Since you have two goroutines accessing shared memory (the grid), you need a mutex to avoid race conditions. Whenever one of these runs, it must "lock", do its work, and then "unlock". Another goroutine will block at the lock step until the first goroutine that acquired the lock unlocks. You can further optimize it using read/write locks (only the camera needs a read lock, while the mobile coroutine needs a read/write lock)
- If you want more randomness, you can create a goroutine for each traveler.
The above is the detailed content of A simple Go simulation - concurrency issues. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What does dao mean in java
Apr 21, 2024 am 02:08 AM
What does dao mean in java
Apr 21, 2024 am 02:08 AM
DAO (Data Access Object) in Java is used to separate application code and persistence layer, its advantages include: Separation: Independent from application logic, making it easier to modify it. Encapsulation: Hide database access details and simplify interaction with the database. Scalability: Easily expandable to support new databases or persistence technologies. With DAOs, applications can call methods to perform database operations such as create, read, update, and delete entities without directly dealing with database details.
 What grade does i7-13620h belong to?
Apr 15, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
What grade does i7-13620h belong to?
Apr 15, 2024 pm 04:30 PM
I believe you have seen that among the latest products announced by Mechanic, there is the latest model i7-13620h. So, what everyone wants to know is, what grade does i7-13620h belong to? i7-13620h is a high-performance processor, belonging to the mid-to-high-end range. It uses Intel's process technology, has 6 P-Core and 8 E-Core, a total of 14 cores and 20 threads, with a main frequency of 2.6GHz, a maximum core frequency of 5.0GHz, and is equipped with 96 sets of EU cores Xe core display. i7-13620h has a large cache capacity, including level three cache (L3Cache), which can provide faster data access speed and accelerate the processor's data processing and calculation. believe you
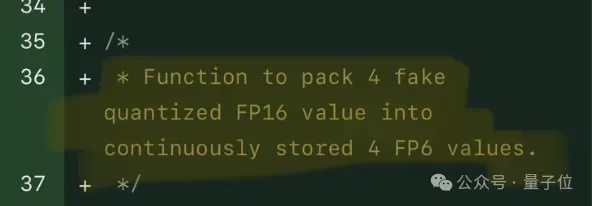 Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
Single card running Llama 70B is faster than dual card, Microsoft forced FP6 into A100 | Open source
Apr 29, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
FP8 and lower floating point quantification precision are no longer the "patent" of H100! Lao Huang wanted everyone to use INT8/INT4, and the Microsoft DeepSpeed team started running FP6 on A100 without official support from NVIDIA. Test results show that the new method TC-FPx's FP6 quantization on A100 is close to or occasionally faster than INT4, and has higher accuracy than the latter. On top of this, there is also end-to-end large model support, which has been open sourced and integrated into deep learning inference frameworks such as DeepSpeed. This result also has an immediate effect on accelerating large models - under this framework, using a single card to run Llama, the throughput is 2.65 times higher than that of dual cards. one
 What does schema mean in mysql
May 01, 2024 pm 08:33 PM
What does schema mean in mysql
May 01, 2024 pm 08:33 PM
Schema in MySQL is a logical structure used to organize and manage database objects (such as tables, views) to ensure data consistency, data access control and simplify database design. The functions of Schema include: 1. Data organization; 2. Data consistency; 3. Data access control; 4. Database design.
 How to remove the write protection of a USB flash drive? Several simple and effective methods can help you do it
May 02, 2024 am 09:04 AM
How to remove the write protection of a USB flash drive? Several simple and effective methods can help you do it
May 02, 2024 am 09:04 AM
U disk is one of the commonly used storage devices in our daily work and life, but sometimes we encounter situations where the U disk is write-protected and cannot write data. This article will introduce several simple and effective methods to help you quickly remove the write protection of the USB flash drive and restore the normal use of the USB flash drive. Tool materials: System version: Windows1020H2, macOS BigSur11.2.3 Brand model: SanDisk UltraFlair USB3.0 flash drive, Kingston DataTraveler100G3USB3.0 flash drive Software version: DiskGenius5.4.2.1239, ChipGenius4.19.1225 1. Check the physical write protection switch of the USB flash drive on some USB flash drives Designed with
 What is the API interface for?
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:51 PM
What is the API interface for?
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:51 PM
An API interface is a specification for interaction between software components and is used to implement communication and data exchange between different applications or systems. The API interface acts as a "translator", converting the developer's instructions into computer language so that the applications can work together. Its advantages include convenient data sharing, simplified development, improved performance, enhanced security, improved productivity and interoperability.
 How to fix the problem that the server system cannot be entered?
Apr 16, 2024 pm 12:54 PM
How to fix the problem that the server system cannot be entered?
Apr 16, 2024 pm 12:54 PM
Guidelines for fixing server system inaccessibility include: checking for hardware issues (power supply, cables, fans); checking network connections (IP address, gateway settings); checking BIOS settings (boot order, date and time); repairing the operating system (using safe mode) , system repair tools); check security software (disable antivirus software, firewall); check for application problems (uninstall, adjust settings); contact technical support (provide details).
 Redis cache implementation principle
Apr 19, 2024 pm 10:36 PM
Redis cache implementation principle
Apr 19, 2024 pm 10:36 PM
The Redis caching mechanism is implemented through key-value storage, memory storage, expiration policies, data structures, replication, and persistence. It follows the steps of obtaining data, cache hit, cache miss, writing to cache, and updating cache to provide fast data access and high-performance caching services.






