Simplify your daily tasks with Linux command line tools
Linux provides many command line tools to simplify your daily tasks. One such tool is the wc command.
wc is your go-to command when you need to know the number of words in a file or how many files there are in a specific directory. But that's not all the wc command can do. Read on to learn what the wc command is and how to use it effectively on Linux.
The wc command prints out the number of lines, words, characters, or bytes in a file or output. Here's how to use it to your advantage.
What is the wc command?
The wc command is the abbreviation of word count. It is a command line tool that counts the number of words, lines, characters and bytes in the output. It comes pre-installed on every Unix and Linux-based operating system, so you don't need to install it manually.
wc command syntax
To use wc, you need to specify a file or text output and the command options to use. The basic syntax of the wc command is:
wc [OPTION] [FILE]
There are many options available for use with the command, all of which we will discuss later. For command line help on the wc command, check its man page by running the following command:
man wc
“
How to use wc command
For this example, create a file: linuxmi.txt. In this file, paste the following text:
Beautiful is better than ugly. Explicit is better than implicit. Simple is better than complex. Complex is better than complicated. Flat is better than nested. Sparse is better than dense. Readability counts. Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules. Although practicality beats purity. Errors should never pass silently. Unless explicitly silenced. In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess. There should be one– and preferably only one –obvious way to do it.[a] Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch. Now is better than never. Although never is often better than right now.[b] If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea. If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea. Namespaces are one honking great idea – let's do more of those!
“
This is the Zen of Python, a set of 19 guiding principles written by Tim Peters for writing simple, elegant, and concise Python code.
If you use the cat command to create the file, leave a blank line before pasting the text.
Use default wc command
By default, when you use the wc command on a file or output, it prints out the number of lines, words, and bytes present in the output.
Try using linuxmi.txt by executing the following command in the terminal:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ wc linuxmi.txt
result:
19 137 830 linuxmi.txt
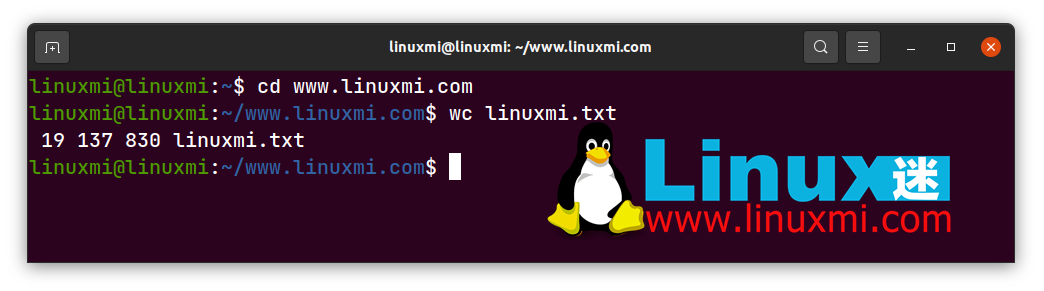
You will see that it outputs four columns containing the number of lines, the number of words, the number of bytes, and the file name.
Print the number of lines present in the file
To count the number of lines present in a file or output, use the -l or –lines option. The syntax is as follows:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ wc -l linuxmi.txt
result:
19 linuxmi.txt
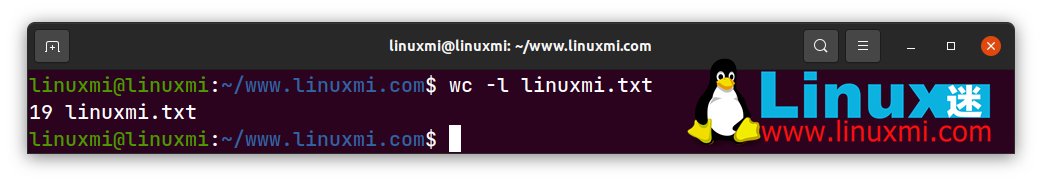
It shows that there are 19 lines in the file and also prints out the name of the text file.
Print the number of words in the file
To count the number of words in a file, use the -w or –words option. Try it:
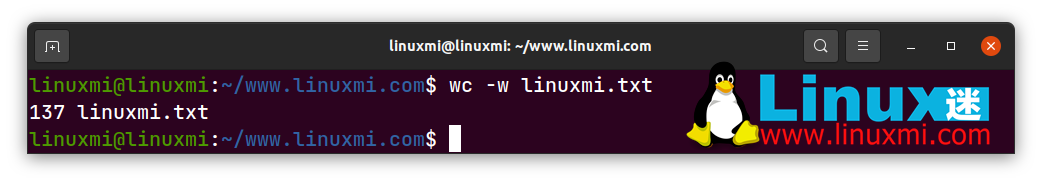
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ wc -w linuxmi.txt
result:
137 linuxmi.txt
Display number of bytes
You can use the wc command with the -c or -****-bytes option to determine the exact number of bytes in the file. Execute the following command to try it out:
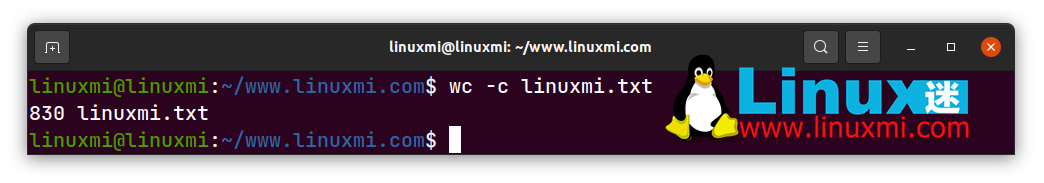
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ wc -c linuxmi.txt
result:
830 linuxmi.txt
打印文件中的字符数
要打印出文件中的字符数,请使用 -m 或 –chars 选项。语法如下所示:
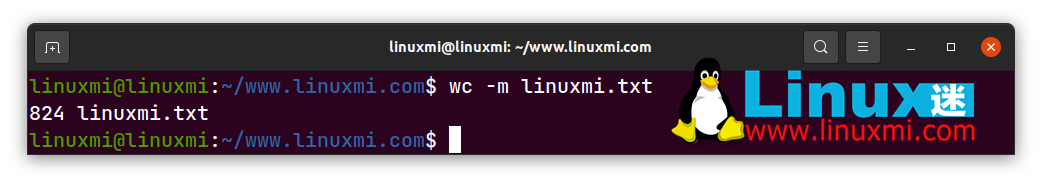
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ wc -m linuxmi.txt
结果:
824 linuxmi.txt
打印最长行的长度
如果需要知道文件中最长行的长度(该行中的字符数),请将 -L 或 –max 行长度选项与 wc 命令配合使用。它看起来像这样:
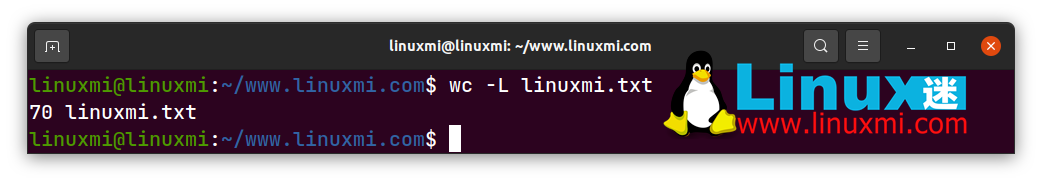
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ wc -l linuxmi.txt
结果:
70 linuxmi.txt
对多个文件使用 wc 命令
您可以将 wc 命令用于多个文件或输入。为此,您需要再创建两个文件。第一个文件是 zimu**.txt,其中包含字母表的列表,而第二个文件是shuzi.txt**,包含从 1 到 10 的数字列表。
或者,您可以使用任意两个文本文件。让我们来试试吧:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ wc linuxmi.txt zimu.txt shuzi.txt
结果如下图:

前三行包含每个文件的行数、字数和字节数,最后一行包含每列的总和。
将 wc 命令与其他 Linux 命令一起使用
您可以通过管道命令将 wc 与其他命令一起使用。管道符号将一个命令的输出作为输入重定向到另一个命令。
计算目录中的文件或文件夹数
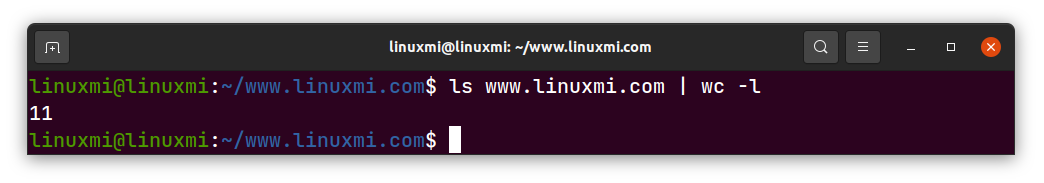
为此,您可以使用 ls 命令列出目录中的文件数,然后将输入通过管道传输到 wc 命令中。例如,要打印某一目录上的文件数,请执行以下命令:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ ls www.linuxmi.com | wc -l
计算系统上正在运行的进程数
进程是您的计算机正在处理或当前正在运行的任务或程序。执行命令或打开应用程序时,该应用程序将注册为进程。
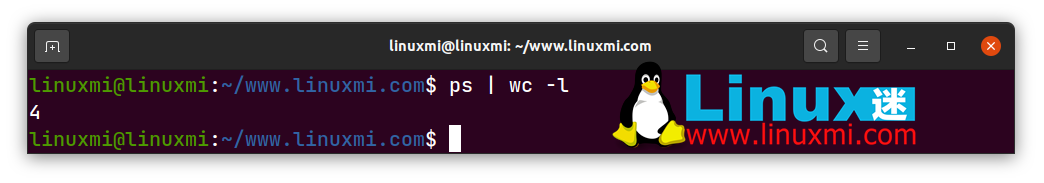
要计算进程数,请使用带有 wc 的 ps 命令。在这里,尝试一下:
linuxmi@linuxmi:~/www.linuxmi.com$ ps | wc -l
使用 wc 尝试其他 Linux 命令
Linux 上有很多可用的命令,它们具有非常独特的功能,并使整体 Linux 体验无缝衔接。您只需要知道它们是什么以及如何使用它们!现在就开始你的 Linux 命令之旅吧!
The above is the detailed content of Simplify your daily tasks with Linux command line tools. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to solve permission issues when using python --version command in Linux terminal?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:36 AM
How to solve permission issues when using python --version command in Linux terminal?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:36 AM
Using python in Linux terminal...
 Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Multithreading in the language can greatly improve program efficiency. There are four main ways to implement multithreading in C language: Create independent processes: Create multiple independently running processes, each process has its own memory space. Pseudo-multithreading: Create multiple execution streams in a process that share the same memory space and execute alternately. Multi-threaded library: Use multi-threaded libraries such as pthreads to create and manage threads, providing rich thread operation functions. Coroutine: A lightweight multi-threaded implementation that divides tasks into small subtasks and executes them in turn.
 How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
To open a web.xml file, you can use the following methods: Use a text editor (such as Notepad or TextEdit) to edit commands using an integrated development environment (such as Eclipse or NetBeans) (Windows: notepad web.xml; Mac/Linux: open -a TextEdit web.xml)
 Can the Python interpreter be deleted in Linux system?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:00 AM
Can the Python interpreter be deleted in Linux system?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:00 AM
Regarding the problem of removing the Python interpreter that comes with Linux systems, many Linux distributions will preinstall the Python interpreter when installed, and it does not use the package manager...
 What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.
 How is Debian Hadoop compatibility
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:42 AM
How is Debian Hadoop compatibility
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:42 AM
DebianLinux is known for its stability and security and is widely used in server, development and desktop environments. While there is currently a lack of official instructions on direct compatibility with Debian and Hadoop, this article will guide you on how to deploy Hadoop on your Debian system. Debian system requirements: Before starting Hadoop configuration, please make sure that your Debian system meets the minimum operating requirements of Hadoop, which includes installing the necessary Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and Hadoop packages. Hadoop deployment steps: Download and unzip Hadoop: Download the Hadoop version you need from the official ApacheHadoop website and solve it
 Do I need to install an Oracle client when connecting to an Oracle database using Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:48 PM
Do I need to install an Oracle client when connecting to an Oracle database using Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:48 PM
Do I need to install an Oracle client when connecting to an Oracle database using Go? When developing in Go, connecting to Oracle databases is a common requirement...
 Is Debian Strings compatible with multiple browsers
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:30 AM
Is Debian Strings compatible with multiple browsers
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:30 AM
"DebianStrings" is not a standard term, and its specific meaning is still unclear. This article cannot directly comment on its browser compatibility. However, if "DebianStrings" refers to a web application running on a Debian system, its browser compatibility depends on the technical architecture of the application itself. Most modern web applications are committed to cross-browser compatibility. This relies on following web standards and using well-compatible front-end technologies (such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and back-end technologies (such as PHP, Python, Node.js, etc.). To ensure that the application is compatible with multiple browsers, developers often need to conduct cross-browser testing and use responsiveness




