Mastering Linux File Time: From Getting Started to Practical Combat
File time is an important concept in Linux systems. It not only records the creation, modification and access time of files, but also helps us with file management, backup and recovery. For Linux system administrators, understanding file time-related knowledge is essential.
Three times of the file
I believe everyone is already familiar with the windows operating system. When we create a file under the windows system, the system will also establish relevant parameters for the file to describe the file, as shown in the figure:
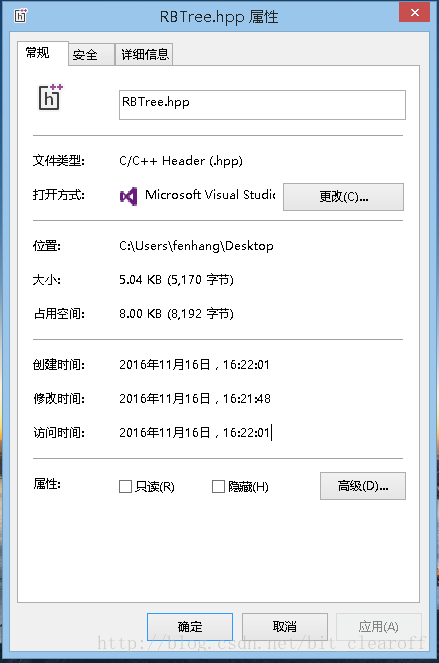
These parameters include the file size, file type, location, and the creation, modification, and access times of the three files. So let's see if there are similar parameters under the Linux system?
Under Linux, we can use the stat file name to view the relevant parameters of the file. The specific parameters are explained as follows:
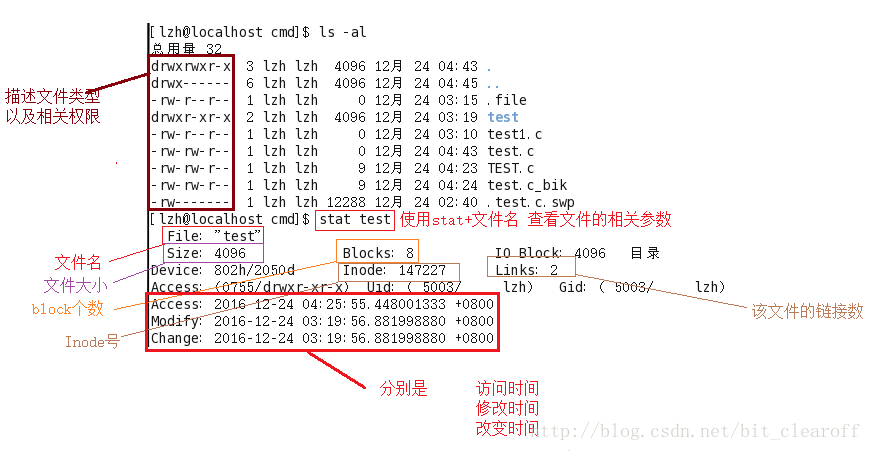
In the file system in Linux, we found that in addition to the file size, file name, file time, etc., there is also more information about the Inode number and block. This is mainly related to the composition of the Linux file system. A file under Linux has an Inode number, and an Inode number corresponds to at least one block. Bolck is a structure for accessing file content. The number of file blocks is related to the size of the file, and under the Linux system, the size of the block is stable. Today we mainly introduce the three times under the Linux system. They are
Access Time, Modify Time, Change Time.
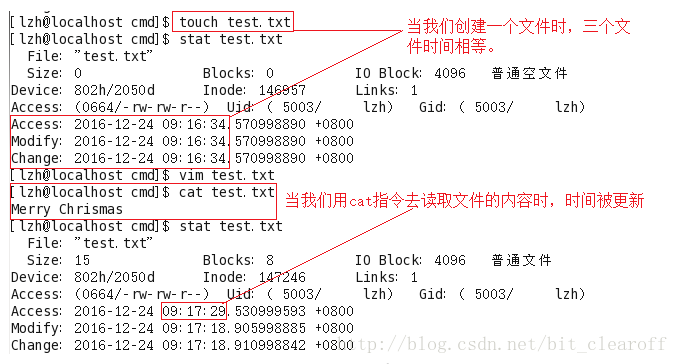
atime
atime is the abbreviation of Access Time. It is called access time in the Linux file system. When the content of the file is accessed, this time will be updated. For example, we use cat, more, less and other commands to view the file. content, the access time of the file will be updated, as shown below:
mtime
mtime is the abbreviation of Modification Time. It means that when the "content data" is modified, the Linux system will update this time. For example: we use echo, vim and other instructions to write data to the file
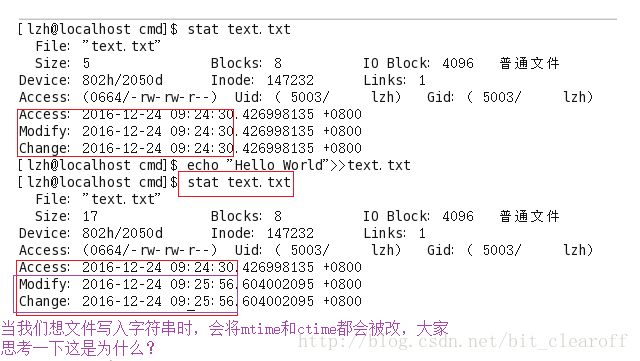
In the picture above, when we use the echo command to write a string to the test.txt file, we find that mtime and the ctime we are going to mention below have been changed. Let us first enter the following Use ctime to see why such a result is produced!
ctime
ctime is the status time in the Linux system, which is the status time. When the status of the file, that is, the attributes of the file, is changed, this time will be changed, such as links (number of links) and size (size of the file) in the file system. , file permissions, blocks (the number of blocks in the file); when these parameters are changed, Linux will change the time parameter corresponding to the file.
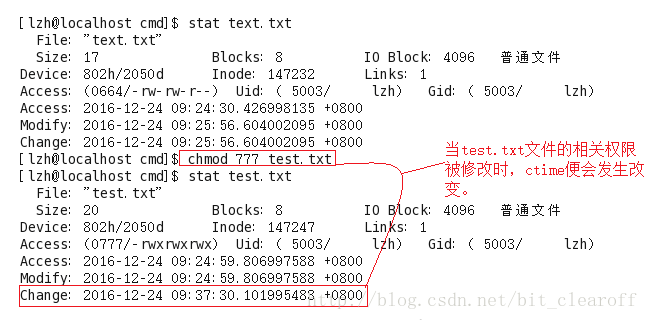
Now you may understand why the ctime of the file was also changed when the mtime of the file was modified. Because when the content of the file is modified, the size of the file will definitely change, so The file's status time is updated as the file's contents are modified. So if the mtime of the file is modified, the ctime of the file will also be changed.
Other ways to view file time
1.ls -l –time=xx time file name;
This query method displays the mtime of the file by default.
2.ls -lx file name
In this query method
cctime
uatime
ls -lc filename lists the ctime (last modified time) of the file
ls -lu filename lists the atime (last access time) of the file
ls -l filename lists the mtime (last modification time) of the file
Summarize
In short, the file time in the Linux system is very important information, which can help us better manage and maintain files. Through the introduction of this article, we can clearly understand the concept, types and usage of file time. Mastering these skills is very helpful for better working and learning in the Linux field.
The above is the detailed content of Mastering Linux File Time: From Getting Started to Practical Combat. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 How to solve permission issues when using python --version command in Linux terminal?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:36 AM
How to solve permission issues when using python --version command in Linux terminal?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:36 AM
Using python in Linux terminal...
 Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Multithreading in the language can greatly improve program efficiency. There are four main ways to implement multithreading in C language: Create independent processes: Create multiple independently running processes, each process has its own memory space. Pseudo-multithreading: Create multiple execution streams in a process that share the same memory space and execute alternately. Multi-threaded library: Use multi-threaded libraries such as pthreads to create and manage threads, providing rich thread operation functions. Coroutine: A lightweight multi-threaded implementation that divides tasks into small subtasks and executes them in turn.
 How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
To open a web.xml file, you can use the following methods: Use a text editor (such as Notepad or TextEdit) to edit commands using an integrated development environment (such as Eclipse or NetBeans) (Windows: notepad web.xml; Mac/Linux: open -a TextEdit web.xml)
 Can the Python interpreter be deleted in Linux system?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:00 AM
Can the Python interpreter be deleted in Linux system?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:00 AM
Regarding the problem of removing the Python interpreter that comes with Linux systems, many Linux distributions will preinstall the Python interpreter when installed, and it does not use the package manager...
 What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.
 How is Debian Hadoop compatibility
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:42 AM
How is Debian Hadoop compatibility
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:42 AM
DebianLinux is known for its stability and security and is widely used in server, development and desktop environments. While there is currently a lack of official instructions on direct compatibility with Debian and Hadoop, this article will guide you on how to deploy Hadoop on your Debian system. Debian system requirements: Before starting Hadoop configuration, please make sure that your Debian system meets the minimum operating requirements of Hadoop, which includes installing the necessary Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and Hadoop packages. Hadoop deployment steps: Download and unzip Hadoop: Download the Hadoop version you need from the official ApacheHadoop website and solve it
 Do I need to install an Oracle client when connecting to an Oracle database using Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:48 PM
Do I need to install an Oracle client when connecting to an Oracle database using Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:48 PM
Do I need to install an Oracle client when connecting to an Oracle database using Go? When developing in Go, connecting to Oracle databases is a common requirement...
 Is Debian Strings compatible with multiple browsers
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:30 AM
Is Debian Strings compatible with multiple browsers
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:30 AM
"DebianStrings" is not a standard term, and its specific meaning is still unclear. This article cannot directly comment on its browser compatibility. However, if "DebianStrings" refers to a web application running on a Debian system, its browser compatibility depends on the technical architecture of the application itself. Most modern web applications are committed to cross-browser compatibility. This relies on following web standards and using well-compatible front-end technologies (such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and back-end technologies (such as PHP, Python, Node.js, etc.). To ensure that the application is compatible with multiple browsers, developers often need to conduct cross-browser testing and use responsiveness




