
Have you ever wondered how to write drivers for your hardware devices in Linux? Have you ever wondered how to adapt your driver to different hardware platforms and configurations in Linux? Have you ever thought about how to enable your driver to implement some advanced functions in Linux systems, such as hot-plugging, power management, device sharing, etc.? If you are interested in these issues, then this article will introduce you to an effective method to achieve these goals-Linux device driver devicetree. Devicetree is a data structure used to describe hardware devices. It allows you to pass the information and attributes of hardware devices to the kernel in a simple and unified way, thereby realizing device identification and driver. Devicetree is also a mechanism for achieving hardware independence. It allows you to separate the configuration and management of hardware devices from the driver code in a flexible and portable way, thereby achieving multi-platform support. Devicetree is also a framework for implementing advanced functions. It allows you to define and use the interfaces and protocols of various hardware devices in a standard and universal way, thereby realizing functions such as hot plugging, power management, and device sharing. . This article will introduce the application and role of devicetree in Linux device drivers in detail from the basic concepts, grammatical rules, writing methods, compilation process, loading method, etc. of devicetree, and help you master this useful and powerful method.
Devicetree (device tree) is a tree model used to describe system hardware information, which is designed to unify the kernel. The devicetree information is passed to the kernel through the bootloader, and then the kernel initializes the corresponding board-level driver based on these device descriptions to achieve the purpose of sharing one kernel across multiple platforms.
Devicetree is mainly designed to describe board-level hardware information of non-pluggable (non-dynamic) devices. It consists of a hierarchical tree structure of nodes describing device information. The content contained in each node is represented by a property/value pair. Except for the root node, every node has a parent. as the picture shows: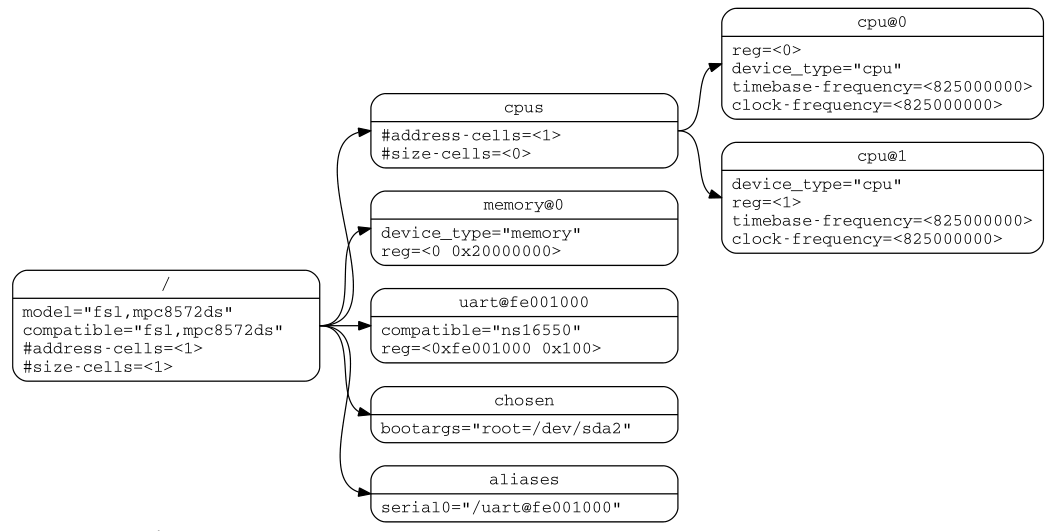
Except for the root node name, which is represented by '/', the other nodes are named by node-name@unit-address, and must be unique at the same level.
node-name
表示节点名,由1-31个字符组成。如非必须,推荐使用以下通用的node-name: cpu、memory、memory-controller、gpio、serial、watchdog、flash、compact-flash、 rtc、interrupt-controller、dma-controller、ethernet、ethernet-phy、timer、 mdio、spi、i2c、usb、can、keyboard、ide、disk、display、sound、atm、cache- controller、crypto、fdc、isa、mouse、nvram、parallel、pc-card、pci、pcie、sata、 scsi、vme。
unit-address
表示这个节点所在的bus类型。它必须和节点中reg属性的第一个地址一致。如果这个节点没有 reg属性,则不需“@unit-address”。
represents the full path of a node. For example:
/node-name-1/node-name-2/node-name-N
The main content contained in each node is the attribute information of the device described, which consists of name and value:
Property Names
1-31个字符,可包含字母、数字、及‘,’,‘.’,‘_’,‘+’,‘?’,‘#’。
Property Values
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| empty | The attribute value is empty, used to represent true-false information |
| u32/u64 | 32/64-bit big-endian unsigned integer, please add | when expressing it.
| string,stringlist | null-terminated string or list thereof |
compatible
Value type: Description: 表示兼容的设备类型,内核据此选择合适的驱动程序。由多个字符串组成,从左到由列出 这个设备兼容的驱动(from most specific to most general)。 推荐的格式为:“制造商名,具体型号”。 Example: compatible = "fsl,mpc8641-uart", "ns16550"; 内核先搜索支持“fsl,mpc8641-uart”的驱动,如未找到,则搜索支持更通用的“ns16550” 设备类型的驱动。
model
Value type: Description: 表明设备型号。 推荐的格式为:“制造商名,具体型号”。 Example: model = "fsl,MPC8349EMITX";
phandle
Value type:
Description:
用一个树内唯一的数字标识所在的这个节点,其他节点可以直接通过这个数字标识来引用
这个节点。
Example:
pic@10000000 {
phandle = ;
interrupt-controller;
};
interrupt-parent = ;
status
Value type: Description: 表示设备的可用状态: "okay" -> 设备可用 "disabled" -> 目前不可用,但以后可能会可用 "fail" -> 不可用。出现严重问题,得修一下 "fail-sss" -> 不可用。出现严重问题,得修一下。sss指明错误类型。
#address-cells and #size-cells
Value type:
Description:
在拥有子节点的节点中使用,来描述它的字节点的地址分配问题。即分别表示子节点中使
用多少个u32大小的cell来编码reg属性中的address域和size域。
这两个属性不会继承,必须明确指出。如未指出,默认#address-cells=2,#size-
cells=1。
Example:
soc {
#address-cells = ;
#size-cells = ;
serial {
reg = ;
};
};
reg
Value type: encoded as an arbitraty number of (address, length) pairs. Description: 描述该设备在parent bus定义的地址空间中的地址资源分配。 Example: reg = ; a 32-byte block at offset 0x3000 and a 256-byte block at offset 0xFE00。
virtual-reg
Value type: Description: 表示映射到reg第一个物理地址对应的effective address。使bootloader能够提供给内 核它所建立的virtual-to-physical mappings。
ranges
Value type: or encoded as an arbitrary number of (child-bus-address,parent-bus-
address, length) triplets.
Description:
提供了子地址空间与父地址空间的映射关系,如果值为空则父子地址相等,无需转换。
Example:
soc {
compatible = "simple-bus";
#address-cells = ;
#size-cells = ;
ranges = ;
serial {
compatible = "ns16550";
reg = ;
};
};
将子节点serial的0x0地址映射到父节点soc的0xe0000000,映射长度为0x100000。此时
reg的实际物理地址就为0xe0004600。
dma-ranges
Value type: or encoded as an arbitrary number of (child-bus-address,parent-bus-address, length) triplets. Description: 提供了dma地址的映射方法。
描述中断的属性有4个:
interrupt-controller
一个空的属性用来指示这个节点设备是接收中断信号的控制器。
#interrupt-cells
这是上面所说中断控制器中的一个属性,用来描述需要用多少个cell来描述这个中断控制器的 interrupt specifier(类似#address-cells和#size-cells)。
interrupt-parent
常出现在根节点的一个属性,它的属性值是指向interrupt-controller的一个phandle。可从 parent继承。
interrupts
包含interrupt specifiers列表,每一个specifier表示一个中断输出信号。
Example
/ {
interrupt-parent = ;
intc: interrupt-controller@10140000 {
compatible = "arm,pl190";
reg = ;
interrupt-controller;
#interrupt-cells = ;
};
serial@101f0000 {
interrupts = ;
};
};
所有的设备树都必须有一个root节点,且root节点下必须包含一个cpus节点和至少一个memory节点。
root node
root节点须包含 #address-cells、#size-cells、model、compatible等属性。
/cpus node
是cpu子节点的父节点容器。须包含 #address-cells、#size-cells属性。
/cpus/cpu* node
是描述系统cpu的节点。
/memory node
描述系统物理内存的layout。须包含reg节点。
Example:
假如一个64位系统有如下两块物理内存:
- RAM: starting address 0x0, length 0x80000000 (2GB)
- RAM: starting address 0x100000000, length 0x100000000 (4GB)
则我们可以有下面两种描述方法(#address-cells = and #size-cells =):
Example #1
memory@0 {
reg = ;
};
Example #2
memory@0 {
reg = ;
};
memory@100000000 {
reg = ;
};
/chosen node
根节点下的一个子节点,不是描述设备而是描述运行时参数。常用来给内核传递bootargs:
chosen {
bootargs = "root=/dev/nfs rw nfsroot=192.168.1.1 console=ttyS0,115200";
};
/aliases node
由1-31个字母、数字或下划线组成的设备节点full path的别名。它的值是节点的全路径,因此最终会被编码成字符串。
aliases {
serial0 = "/simple-bus@fe000000/serial@llc500";
}
更多具体设备具体类别的描述信息:内核源代码/Documentation/devicetree/bindings。
DTS是描述devicetree的源文本文件,它通过内核中的DTC(Devicetree Compiler)编译后生成相应平台可烧写的二进制DTB。
DTB又称Flattened Devicetree(FDT),在内存中的结构如下图所示: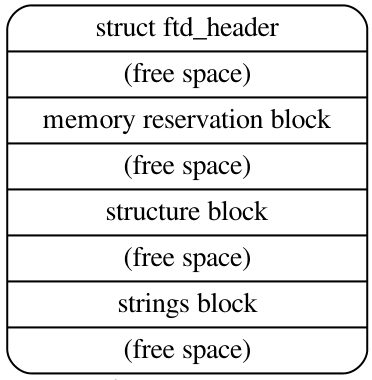
大端字节序结构体:
struct fdt_header {
uint32_t magic; /* contain the value 0xd00dfeed (big-endian) */
uint32_t totalsize; /* the total size of the devicetree data structure */
uint32_t off_dt_struct; /* offset in bytes of the structure block */
uint32_t off_dt_strings; /* offset in bytes of the strings block */
uint32_t off_mem_rsvmap; /* offset in bytes of the memory reservation block */
uint32_t version; /* the version of the devicetree data structure */
uint32_t last_comp_version; /* the lowest version used is backwards compatible */
uint32_t boot_cpuid_phys; /* the physical ID of the system’s boot CPU */
uint32_t size_dt_strings; /* the length in bytes of the strings block */
uint32_t size_dt_struct; /* the length in bytes of the structure block */
};
Purpose
为系统保留一些特殊用途的memory。这些保留内存不会进入内存管理系统。
Format
struct fdt_reserve_entry {
uint64_t address;
uint64_t size;
};
Devicetree结构体存放的位置。由一行行“token+内容”片段线性组成。
| token | Description |
|---|---|
| FDT_BEGIN_NODE (0x00000001) | 节点起始,其后内容为节点名 |
| FDT_END_NODE (0x00000002) | 节点结束 |
| FDT_PROP (0x00000003) | 描述属性 |
| FDT_NOP (0x00000004) | nothing,devicetree解析器忽略它 |
| FDT_END (0x00000009) | block结束 |
[label:] node-name[@unit-address] {
[properties definitions]
[child nodes]
};
Version 1 DTS files have the overall layout:
/dts-v1/; /* dts 版本1 */
[memory reservations] /* DTB中内存保留表的入口 */
/ {
[property definitions]
[child nodes]
};
通过本文,我们了解了devicetree在Linux设备驱动中的应用和作用,学习了如何编写、编译、加载、修改和调试devicetree。我们发现,devicetree是一种非常适合嵌入式系统开发的方法,它可以让我们方便地描述和管理硬件设备,实现硬件无关性和高级功能。当然,devicetree也有一些注意事项和限制,比如需要遵循语法规范、需要注意兼容性问题、需要注意内存占用和性能影响等。因此,在使用devicetree时,我们需要有一定的硬件知识和经验,以及良好的编程习惯和调试技巧。希望本文能够为你提供一个入门级的指导,让你对devicetree有一个初步的认识和理解。如果你想深入学习devicetree,建议你参考更多的资料和示例,以及自己动手实践和探索。
The above is the detailed content of Linux device driver devicetree: an efficient method to describe and manage hardware devices. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




