Enable KVM Nested Virtualization on RHEL 8 / Rocky Linux 8
In this article, we will show you how to enable nested virtualization in KVM on RHEL 8 / Rocky Linux 8.
Nested virtualization in KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) is a feature that allows you to run virtual machines within other virtual machines. This means you can create a virtual environment within a virtual machine and run another virtual machine within it.
Nested virtualization is particularly useful for test and development scenarios where you may want to create multiple virtual machines with different configurations or operating systems without the need for separate physical hardware. For example, you can use nested virtualization to test the compatibility of applications running on multiple operating system versions.
prerequisites
- Preinstall KVM on RHEL 8 / Rocky Linux 8
- Have Sudo or Root access
I assume you have already configured a KVM virtualizer. If you are unfamiliar with how to install and configure a KVM virtualization program, please refer to the following article:
- How to install and configure KVM on RHEL 8 / CentOS 8
Without further ado, let’s get into the practical steps.
Enable KVM nested virtualization
Verify that your KVM host has nested virtualization enabled.
For Intel processor-based machines, run the following cat command:
[root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested N [root@kvm-hypervisor ~]#
For AMD processor-based machines, run the following command:
[root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# cat /sys/module/kvm_amd/parameters/nested N [root@kvm-hypervisor ~]#
In the above output, "N" means nested virtualization is not enabled. If the output we get is "Y", it means nested virtualization is enabled on your host.
Now to enable nested virtualization, create a file called "/etc/modprobe.d/kvm-nested.conf" with the following content:
[root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# vi /etc/modprobe.d/kvm-nested.conf options kvm-intel nested=1 options kvm-intel enable_shadow_vmcs=1 options kvm-intel enable_apicv=1 options kvm-intel ept=1
Save and exit the file.
Next, please remove the kvm_intel module and add the same module using the modprobe command. Before removing the module, make sure the virtual machine is shut down, otherwise we will receive the following error message: "modprobe: FATAL: Module kvm_intel is in use".
[root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# modprobe -r kvm_intel [root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# modprobe -a kvm_intel [root@kvm-hypervisor ~]#
Now to verify that the nested virtualization feature is enabled, run the following command:
[root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested Y [root@kvm-hypervisor ~]#
For AMD-based systems, run the following command:
[root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# rmmod kvm-amd [root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# echo 'options kvm-amd nested=1'>>/etc/modprobe.d/dist.conf [root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# modprobe kvm-amd
Testing KVM Nested Virtualization
Suppose we have a virtual machine named "director" in the KVM virtualizer and I have enabled nested virtualization in it. Before testing, make sure the CPU mode of the virtual machine is "host-model" or "host-passthrough". You can use the Virt-Manager GUI or the virsh edit command to check the CPU mode of the virtual machine.
# virsh edit director
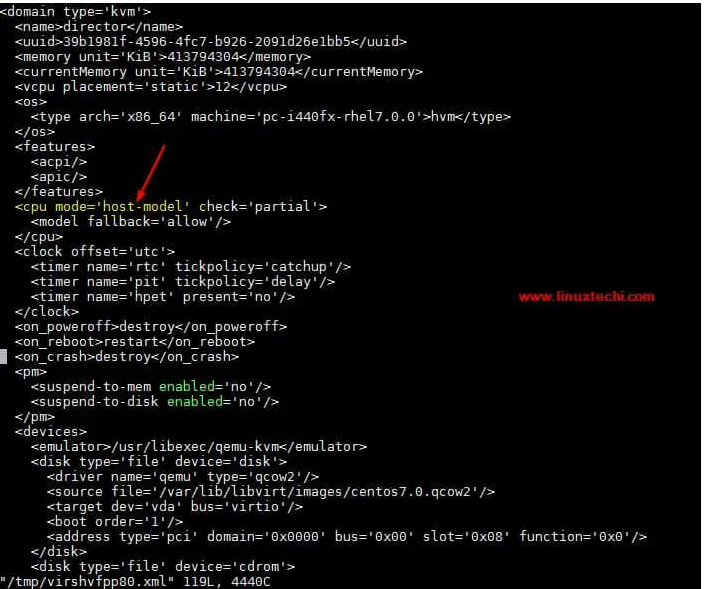
For new virtual machines that you want to use nested virtualization, check the "Copy host CPU configuration" option under CPU settings in virt-manager.
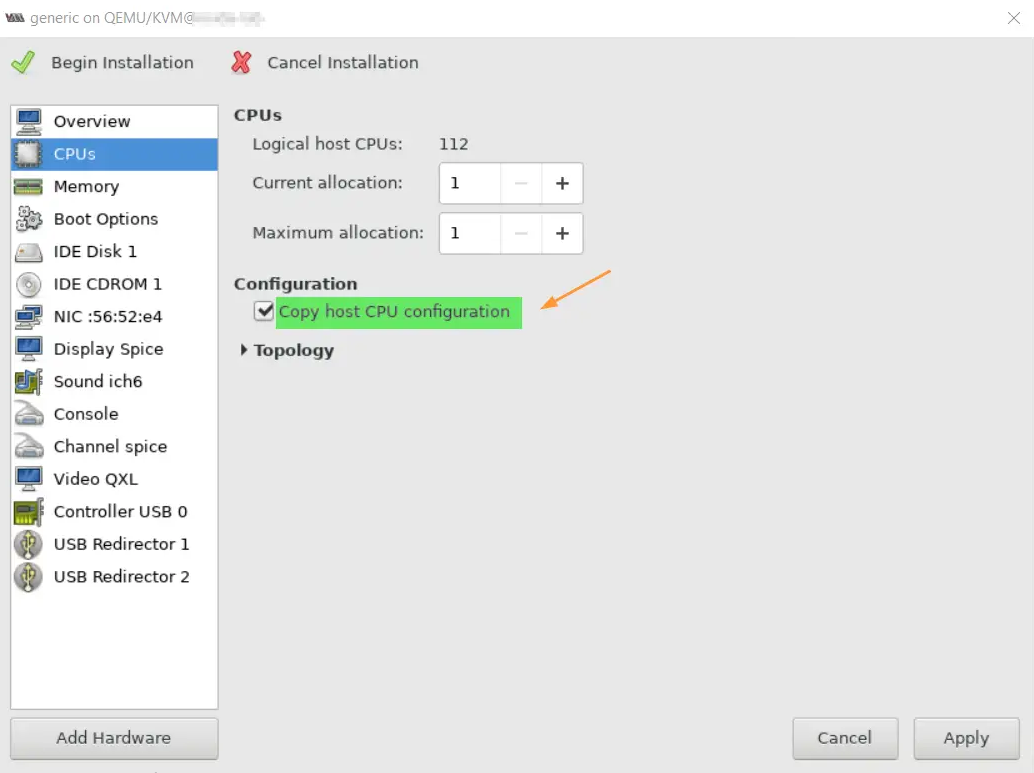
Now log in to the director VM and run the lscpu and lsmod commands.
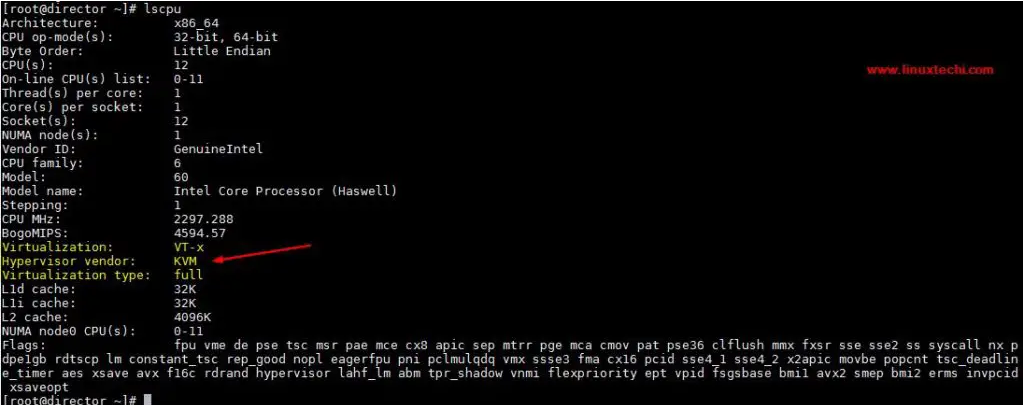
[root@kvm-hypervisor ~]# ssh 192.168.126.1 -l root root@192.168.126.1's password: Last login: Sun Dec 10 07:05:59 2017 from 192.168.126.254 [root@director ~]# lsmod | grep kvm kvm_intel 170200 0 kvm 566604 1 kvm_intel irqbypass 13503 1 kvm [root@director ~]# [root@director ~]# lscpu
让我们尝试在 director vm 中创建虚拟机,可以使用 virt-manager GUI 或 virt-install 命令。在我的测试中,我使用了 virt-install 命令。
[root@director ~]# virt-install -n Nested-VM --description "Test Nested VM" \ --os-type=Linux --os-variant=rhel7 --ram=2048 --vcpus=2 --disk \ path=/var/lib/libvirt/images/nestedvm.img,bus=virtio,size=10 --graphics \ none --location /var/lib/libvirt/images/CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1511.iso\ --extra-args console=ttyS0 Starting install... Retrieving file .treeinfo... | 1.1 kB 00:00:00 Retrieving file vmlinuz... | 4.9 MB 00:00:00 Retrieving file initrd.img... | 37 MB 00:00:00 Allocating 'nestedvm.img' | 10 GB 00:00:00 Connected to domain Nested-VM Escape character is ^] [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpuset [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpu [ 0.000000] Initializing cgroup subsys cpuacct [ 0.000000] Linux version 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 ………………………………………………
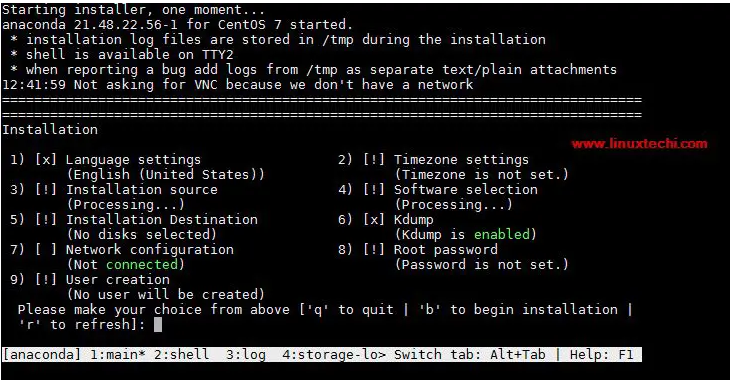
这证实了嵌套虚拟化已成功启用,因为我们能够在虚拟机中创建虚拟机。
The above is the detailed content of Enable KVM Nested Virtualization on RHEL 8 / Rocky Linux 8. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
CentOS installation steps: Download the ISO image and burn bootable media; boot and select the installation source; select the language and keyboard layout; configure the network; partition the hard disk; set the system clock; create the root user; select the software package; start the installation; restart and boot from the hard disk after the installation is completed.
 Centos options after stopping maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
Centos options after stopping maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:51 PM
CentOS has been discontinued, alternatives include: 1. Rocky Linux (best compatibility); 2. AlmaLinux (compatible with CentOS); 3. Ubuntu Server (configuration required); 4. Red Hat Enterprise Linux (commercial version, paid license); 5. Oracle Linux (compatible with CentOS and RHEL). When migrating, considerations are: compatibility, availability, support, cost, and community support.
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
After CentOS is stopped, users can take the following measures to deal with it: Select a compatible distribution: such as AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, and CentOS Stream. Migrate to commercial distributions: such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Oracle Linux. Upgrade to CentOS 9 Stream: Rolling distribution, providing the latest technology. Select other Linux distributions: such as Ubuntu, Debian. Evaluate other options such as containers, virtual machines, or cloud platforms.
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 What underlying technologies does Docker use?
Apr 15, 2025 am 07:09 AM
What underlying technologies does Docker use?
Apr 15, 2025 am 07:09 AM
Docker uses container engines, mirror formats, storage drivers, network models, container orchestration tools, operating system virtualization, and container registry to support its containerization capabilities, providing lightweight, portable and automated application deployment and management.




