How to set up Linux and Windows dual boot on the same machine using UEFI
Want to install both Linux and Windows systems on the same computer and perform dual boot? This is a great option, but how to properly configure the system to achieve this can be intimidating to many people. This article will provide you with a quick explanation to help you understand the importance of UEFI in setting up Linux and Windows dual boot and how to overcome some of the problems you may encounter during installation.
Here's a quick explanation for setting up Linux and Windows dual-boot on the same machine, using Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI).
Rather than give you a step-by-step guide on how to configure your system for dual boot, I will highlight a few important points. As an example, I'll mention the laptop I bought new a few months ago. I started by installing Ubuntu Linux to the entire hard drive, which destroyed the pre-installed Windows 10 environment. After a few months, I decided to install a different Linux distribution, Fedora Linux, and also decided to install Windows 10 again alongside it in a dual-boot configuration. I will highlight some extremely important practical facts. let's start!
firmware
Dual boot is not just a software issue. Or maybe it's a software issue, since it requires changing your firmware to tell your machine how to start the boot process. There are some important things to keep in mind regarding firmware.
UEFI vs BIOS
Before attempting to install, make sure your firmware configuration is optimal. Most computers sold today have a new type of firmware called Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). UEFI has more or less replaced another firmware type called Basic Input Output System (BIOS). Many people (including many firmware vendors) often refer to the BIOS as Legacy Boot.
I don't need a BIOS, so I chose UEFI mode.
Secure Boot
Another important setting is Secure Boot. This feature will detect if the boot path has been tampered with and prevent unapproved operating systems from booting. For now, I disable this option to ensure I can install Fedora Linux. According to the introduction in the "Features/Secure Boot" section of the Fedora project wiki: Fedora Linux can also work when the secure boot option is enabled. This may be different for other Linux distributions - I plan to revisit this setup in the future.
In short, if you find that you cannot install your Linux operating system when this setting is enabled, then disable Secure Boot and retry the installation again.
Partition the boot drive
If you choose dual boot and both operating systems are on the same drive, then you must split it into multiple partitions. Even if you dual-boot with two different drives, most Linux environments are best split into a few basic partitions for a variety of reasons. Here are some options worth considering.
GPT vs MBR
If you decide to manually partition your boot drive, before doing so, I recommend using the GUID Partition Table (GPT) instead of the old Master Boot Record (MBR). One reason for this change: MBR has two specific limitations that GPT does not:
MBR can have up to 15 partitions, while GPT can have up to 128 partitions.
MBR only supports disks up to 2 TB, while GPT uses 64-bit addresses, which allows it to support disks up to 8 million TB.
If you've purchased a hard drive recently, you probably know that many modern hard drives exceed the 2 TB limit.
EFI system partition
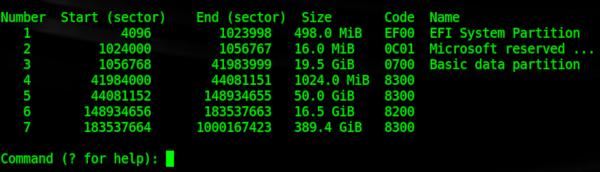
If you are doing a fresh installation or using a new drive, there may not be a partition to start with. In this case, the operating system installer will first create a partition, the EFI System Partition (ESP). If you choose to use a tool such as gdisk to manually partition your drive, you will need to use some parameters to create the partition. Based on the existing ESP, I set it to a size of about 500 MB and assigned it an ef00 (EFI System) partition type. The UEFI specification requires formatting as FAT32/msdos, most likely because this format is supported by a large number of operating systems.
Operating System Installation
After you complete the previous two tasks, you can install your operating system. Although I'm focusing on Windows 10 and Fedora Linux here, the process is very similar when installing other combinations.
Windows 10
I started the Windows 10 installation and created a 20 GB Windows partition. Since I had previously installed Linux on my laptop, the drive already had an ESP, which I chose to keep. I deleted all existing Linux and swap partitions to start a fresh install, and then started my Windows installation. Windows Setup automatically creates another small 16 MB partition called a Microsoft Reserved Partition (MSR). After this is completed, there will still be approximately 400 GB of unallocated space on the 512 GB boot drive.
Next, I continued through the Windows 10 installation process. I then rebooted into Windows to make sure it was working, create my user account, set up Wi-Fi, and complete other necessary tasks when the operating system first boots.
Fedora Linux
Next, I turned my attention to installing Linux. I started the installation process and as the installation progressed to the disk configuration steps I made sure not to change the Windows NTFS and MSR partitions. I also don't change the ESP, but I set its mount point to /boot/efi. Then I created the usual ext4 formatted partitions, / (root partition), /boot and /home. The last partition I created was a Linux swap partition.
I continued through the Linux installation just like I did with Windows and then rebooted. To my delight, the GRand Unified Boot Loader (GRUB) menu provides the option to select Windows or Linux at boot time, which means I don't need to do any additional configuration. I chose Linux and completed the usual steps such as creating my user account.
Summarize
By understanding the importance of UEFI and tips like proper partitioning, configuring boot modes, and disabling Secure Boot, you can install and run multiple operating systems on the same computer. There may be some challenges during the installation process, but if you follow the correct steps and precautions, you will be able to successfully configure Linux and Windows dual boot.
The above is the detailed content of How to set up Linux and Windows dual boot on the same machine using UEFI. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
CentOS installation steps: Download the ISO image and burn bootable media; boot and select the installation source; select the language and keyboard layout; configure the network; partition the hard disk; set the system clock; create the root user; select the software package; start the installation; restart and boot from the hard disk after the installation is completed.
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 How to mount hard disk in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
How to mount hard disk in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
CentOS hard disk mount is divided into the following steps: determine the hard disk device name (/dev/sdX); create a mount point (it is recommended to use /mnt/newdisk); execute the mount command (mount /dev/sdX1 /mnt/newdisk); edit the /etc/fstab file to add a permanent mount configuration; use the umount command to uninstall the device to ensure that no process uses the device.
 What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
After CentOS is stopped, users can take the following measures to deal with it: Select a compatible distribution: such as AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, and CentOS Stream. Migrate to commercial distributions: such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Oracle Linux. Upgrade to CentOS 9 Stream: Rolling distribution, providing the latest technology. Select other Linux distributions: such as Ubuntu, Debian. Evaluate other options such as containers, virtual machines, or cloud platforms.




