How to set up a private Git server on Linux
Git is an open source version control system used by developers around the world. Next, we'll cover how to create your own Git Linux server to host your projects.
A Git server is used to host a project's repository, which contains source code and other core files. While in most cases you can rely on a globally renowned Git hosting service like GitHub, in some cases it is better to host your own personal Git server for added privacy, customizability, and security.
Now, let’s learn how to set up a private Git server on Linux.
Prerequisites for setting up Git server
Before you start setting up your private Git server, you will need to have access to a backup computer or subscribe to a cloud provider. This is important because you will be setting up the backup machine as a Git server and connecting to it from your local machine and performing Git operations.
Although there are no explicit system requirements, 1GB of RAM should be enough to get the Git server running properly. Also, make sure you have a Linux distribution installed and running on your computer.
Step 1: Download and install Git on the Linux server
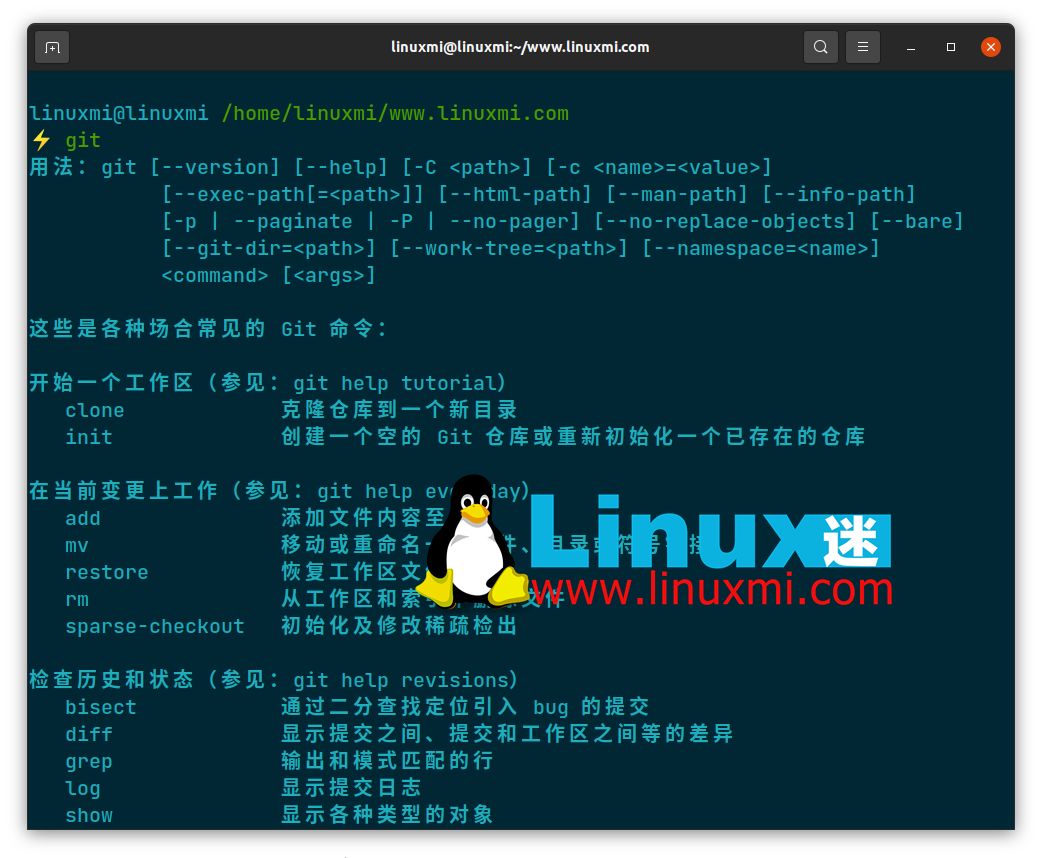
It goes without saying that as a preliminary step, you need to install Git on your Linux server. Launch a terminal and use your Linux distribution’s package manager to install Git:
On Debian/Ubuntu derivatives:
sudo apt install git
Arch-based distributions:
sudo pacman -S git
On CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
sudo dnf install git
“
After installing Git on your system, continue with the following steps to configure your Linux system to host your Git repository as a Git server.
Step 2: Set up a Git user account
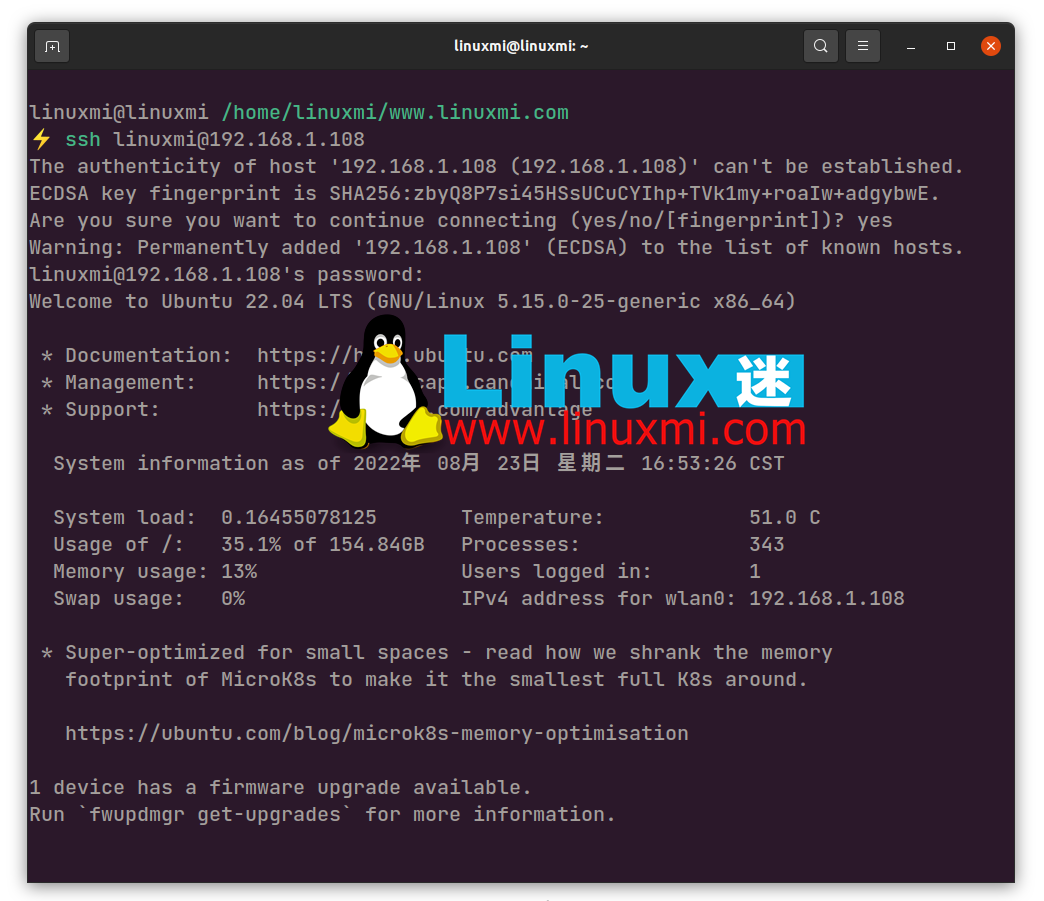
Connect to your Linux server via SSH, RDP or any other remote access protocol. Alternatively, if you are using an alternate machine as a server, turn it on and create a new user account to work with your repository.
ssh username@address sudo useradd git
“
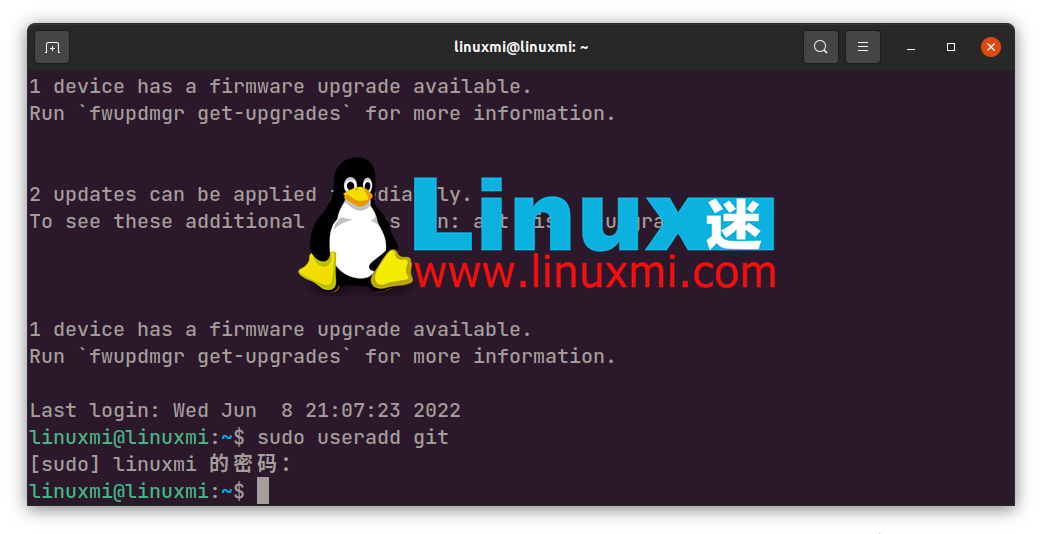
After adding a new user, use the su command to switch to the user:
su git
Create a dedicated git User account is a security protocol that ensures clients connecting to your Git server have limited visibility and access to the resources on the machine. This allows you to collaborate securely on group projects where multiple team members will have access to your server.
Step 3: Create .ssh directory and add authorization key
Creating a **.ssh** directory is necessary to store the public key and other basic data that will determine who can access this Git server. First, log in to the git user account you created earlier, create a .ssh directory, and restrict access to only the git user:
ssh git@address mkdir .ssh chmod 700 .ssh/ touch .ssh/authorized_keys
“
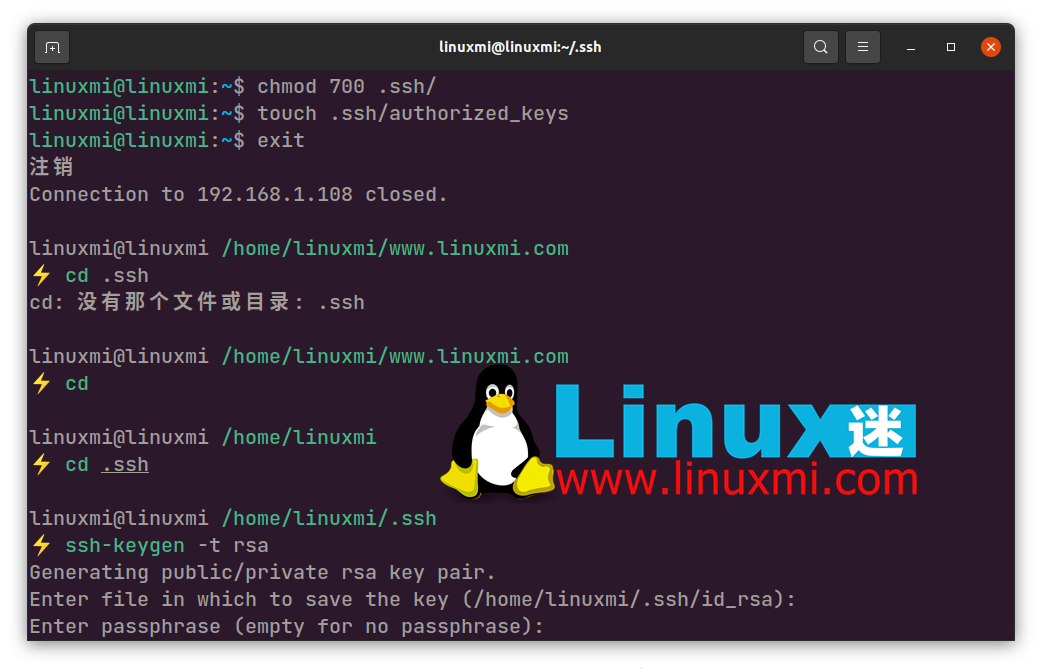
Use the chmod command to protect directory access to ensure that no one but you can change it. Go into the **.ssh directory and use the ****touch** command to create a new file "authorized_keys".
cd .ssh ssh-keygen -t rsa #如果您没有 id_rsa.pub 文件,请使用此命令 cat id_rsa.pub
“
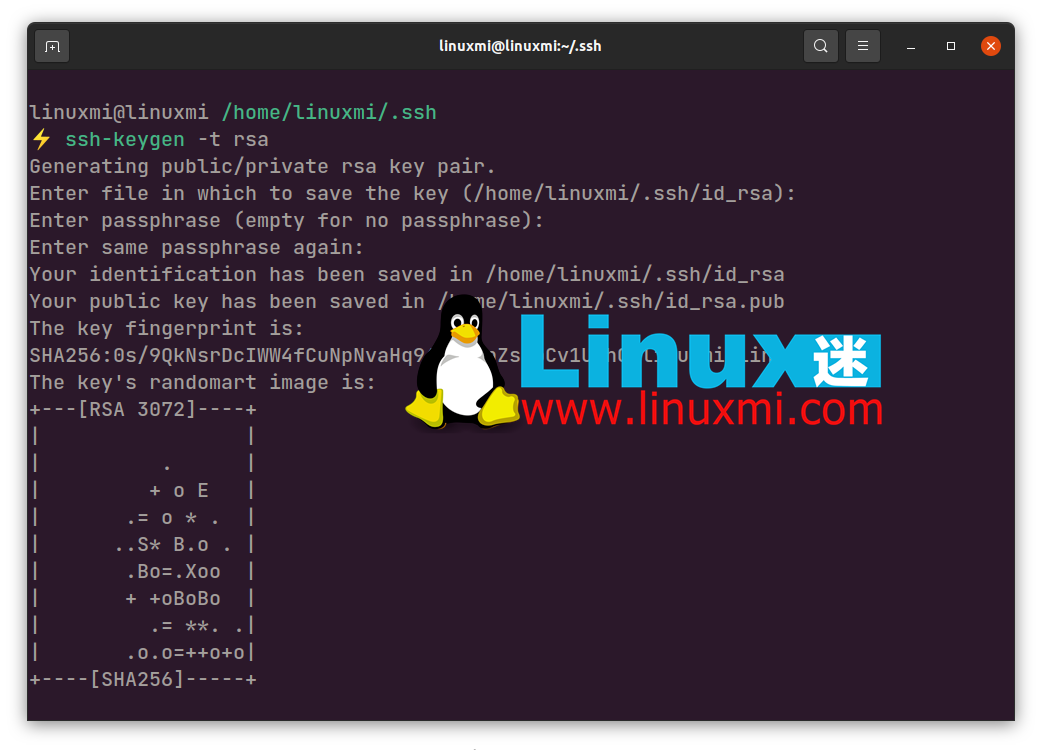
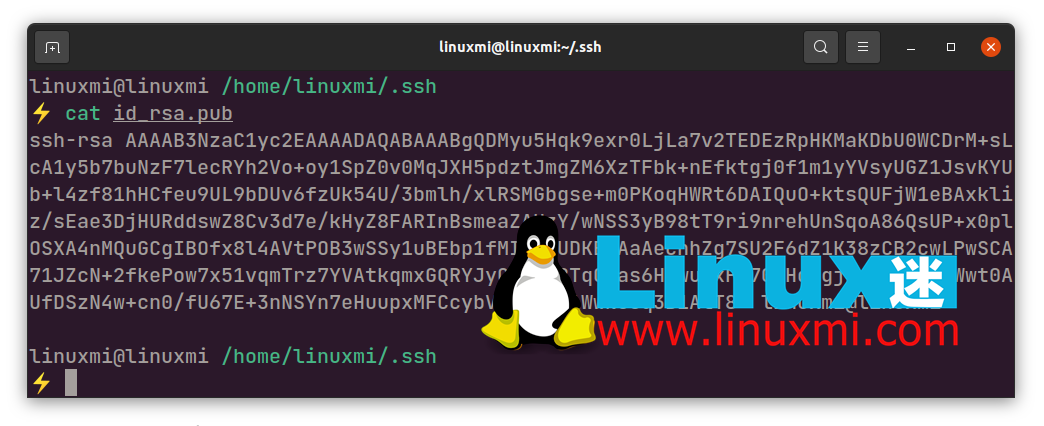
您必须使用您希望授予对 Git 服务器访问权限的客户端的 SSH 公钥来更新此文件。暂停 SSH 会话并使用文本编辑器或cat 命令在本地计算机中打开**.ssh/id_rsa.pub**文件。该文件包含您的公共加密密钥,当将其写入authorized_keys 文件时,您将无需密码即可访问Git 服务器。
cd .sshvi authorized_keys
复制公钥并启动到 Git 服务器的新 SSH 连接。进入**.ssh**目录,使用文本编辑器打开 authorized_keys 文件并粘贴公钥。保存更改并退出。
从那时起,您应该能够在没有任何密码的情况下连接到服务器。对将连接到服务器的每台计算机重复此步骤。
第 4 步:创建一个目录来存储您的所有存储库
访问 Linux 服务器并创建一个目录或使用内置目录作为根目录。请记住,这是存储所有存储库的目录。为了更整洁地组织项目,这是一个很好的做法。
mkdir directory_name
创建目录后,继续本指南的最后一步以完成 Git 服务器的设置。
第 5 步:通过添加新项目启动开发
您现在实际上已经完成了 Git 服务器的设置。现在您只需要通过初始化存储库并将远程源添加到本地计算机来开始开发。使用cd命令进入父目录并创建一个**.git**项目目录:
cd parent_director ymkdir new_project.git
现在,初始化一个裸 git 存储库:
git init --bare
初始化存储库后,是时候在本地计算机上添加远程源了:
git remote add origin name git@address:new_project.git
这就是您在服务器端需要做的所有事情。现在任何经过身份验证的客户端都可以执行常规的 Git 操作,例如推送、拉取、合并、克隆等。要开始新项目,每次创建新项目时都必须重复此步骤。
通过执行 git push 测试其功能:
touch testfile git add testfile git commit -m "test file" git push name master git clone git@address:new_project.git
您的文件将成功推送到远程源。要交叉检查推送操作是否有效,您可以克隆存储库,您应该在存储库中找到测试文件。
Git 服务器的安全提示
随着 Git 服务器的启动和运行,您必须密切注意它的安全状态,因为它是您的个人服务器,维护和保护它免受外部威胁是您的唯一责任。要采用的一些最佳安全实践是:
- 禁用密码登录
- 将默认 shell 更改为 git-shell。这限制了登录用户发出任何非 git 命令
- 为 SSH 使用自定义端口
- 禁用root用户登录
- 定期备份数据
您可以在 Linux 服务器上实施许多此类安全配置和安全措施,以保护其免受攻击者的侵害并防止未经授权的访问。
The above is the detailed content of How to set up a private Git server on Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
DeepSeek is a powerful intelligent search and analysis tool that provides two access methods: web version and official website. The web version is convenient and efficient, and can be used without installation; the official website provides comprehensive product information, download resources and support services. Whether individuals or corporate users, they can easily obtain and analyze massive data through DeepSeek to improve work efficiency, assist decision-making and promote innovation.
 How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
There are many ways to install DeepSeek, including: compile from source (for experienced developers) using precompiled packages (for Windows users) using Docker containers (for most convenient, no need to worry about compatibility) No matter which method you choose, Please read the official documents carefully and prepare them fully to avoid unnecessary trouble.
 Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi OKX, the world's leading digital asset exchange, has now launched an official installation package to provide a safe and convenient trading experience. The OKX installation package of Ouyi does not need to be accessed through a browser. It can directly install independent applications on the device, creating a stable and efficient trading platform for users. The installation process is simple and easy to understand. Users only need to download the latest version of the installation package and follow the prompts to complete the installation step by step.
 BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet is a cryptocurrency exchange that provides a variety of trading services including spot trading, contract trading and derivatives. Founded in 2018, the exchange is headquartered in Singapore and is committed to providing users with a safe and reliable trading platform. BITGet offers a variety of trading pairs, including BTC/USDT, ETH/USDT and XRP/USDT. Additionally, the exchange has a reputation for security and liquidity and offers a variety of features such as premium order types, leveraged trading and 24/7 customer support.
 Get the gate.io installation package for free
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Get the gate.io installation package for free
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Gate.io is a popular cryptocurrency exchange that users can use by downloading its installation package and installing it on their devices. The steps to obtain the installation package are as follows: Visit the official website of Gate.io, click "Download", select the corresponding operating system (Windows, Mac or Linux), and download the installation package to your computer. It is recommended to temporarily disable antivirus software or firewall during installation to ensure smooth installation. After completion, the user needs to create a Gate.io account to start using it.
 Ouyi Exchange Download Official Portal
Feb 21, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Ouyi Exchange Download Official Portal
Feb 21, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Ouyi, also known as OKX, is a world-leading cryptocurrency trading platform. The article provides a download portal for Ouyi's official installation package, which facilitates users to install Ouyi client on different devices. This installation package supports Windows, Mac, Android and iOS systems. Users can choose the corresponding version to download according to their device type. After the installation is completed, users can register or log in to the Ouyi account, start trading cryptocurrencies and enjoy other services provided by the platform.
 How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set the permissions of unixsocket after the system restarts. Every time the system restarts, we need to execute the following command to modify the permissions of unixsocket: sudo...
 Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Causes and solutions for errors when using PECL to install extensions in Docker environment When using Docker environment, we often encounter some headaches...






