
To understand the lsscsi command, first we need to understand what SCSI is and common hard disk interfaces and common hard disk parameters.
SCSI (Small Computer System Interface) is a complete data transfer protocol, which is mainly used to transfer commands, status and block data between the host and storage devices. Among various storage technologies, SCSI technology is the most important pillar.
The SCSI protocol is located between the operating system and external resources. It has a series of functional components. The operating system's I/O operations on external devices (such as disks, tapes, CD-ROMs, printers , etc.) can be implemented through the SCSI protocol. Typically, the SCSI protocol is embedded in the device driver or the host adapter's onboard logic.
Its English name: Integrated Drive Electronics, the common 2.5-inch IDE hard disk interface, its original meaning refers to the hard disk drive that integrates the "hard disk controller" and the "disk body".
IDE represents a type of hard disk, but in actual applications, people are also accustomed to using IDE to refer to the earliest IDE type hard disk ATA-1. This type of interface has been eliminated with the development of interface technology. , and then developed into more types of hard disk interfaces, such as ATA, Ultra ATA, DMA, Ultra DMA and other interfaces, which are all IDE hard disks.
Its characteristics are: low price, strong compatibility, high cost performance, slow data transmission, does not support hot swapping, etc.

SCSI is not an interface specifically designed for hard disks. It is a high-speed data transmission technology widely used on minicomputers.
The SCSI interface has the advantages of wide application range, multi-tasking, large bandwidth, low CPU usage, and hot-swappability. However, the higher price makes it difficult to be as popular as IDE hard drives, so SCSI hard drives are mainly used in medium and , high-end servers and high-end workstations.
Its characteristics are: high transmission rate, good reading and writing performance, can connect multiple devices, and can support hot swapping, but the price is relatively expensive.

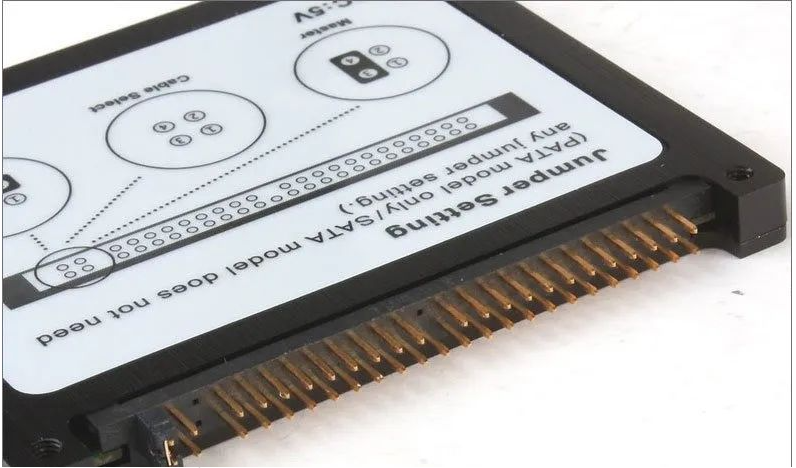
The English name is: Serial Advanced Technology Attachment. Hard drives using the SATA (Serial ATA) port are also called serial hard drives and are the future trend of PC hard drives.
Serial ATA uses a serial connection method. The Serial ATA bus uses an embedded clock signal and has stronger error correction capabilities. Compared with the past, its biggest difference is that it can transmit instructions (not just data). Check and automatically correct errors if found, which greatly improves the reliability of data transmission.
The serial interface also has the advantages of simple structure and support for hot swapping.
lsscsi lists scsi/sata device information, such as hard drives and optical drives.
-bash: lsscsi command not found #Debian apt-get install lsscsi #Ubuntu apt-get install lsscsi #Alpine apk add lsscsi #Arch Linux pacman -S lsscsi #Kali Linux apt-get install lsscsi #CentOS yum install lsscsi #Fedora dnf install lsscsi #Raspbian apt-get install lsscsi #Docker docker run cmd.cat/lsscsi lsscsi
Detailed command description address
https://sg.danny.cz/scsi/lsscsi.html

lsscsi command syntax:
lsscsi [选项] [H:C:T:L]
lsscsi command options:
| Options | meaning |
|---|---|
| -g | Display SCSI common device file name |
| -k | Display kernel name instead of device node name |
| -d | Display the primary and secondary numbers of the device node |
| -H | List the SCSI hosts currently connected to the system instead of the SCSI devices |
| -l | Display additional information for each SCSI device (host) |
| -c | Relative to the output of executing cat /proc/scsi/scsi command |
| -p | Show additional data integrity (protection) information |
| -t | Display transmission information |
| -L | Display additional information in the form of "attribute name=value" |
| -v | Output directory name when information is found |
| -y | Assume that sysfs is mounted at the specified path instead of the default "/sys" |
| -s | Display capacity size. |
| -c | Display the default information with the full name. |
| -d | Display the device primary and secondary device numbers. |
| -g | Display the corresponding sg device name. |
| -H | Display host controller list, -Hl, -Hlv. |
| -l | Display related attributes, -ll,-llll=-L. |
| -v | Display the directory where the device properties are located. |
| -x | Display the lun number in hexadecimal. |
| -p | Output DIF,DIX protection type. |
| -P | Output valid protection mode information. |
| -i | Display udev related attributes |
| -w | Show WWN |
| -t | Display corresponding transmission information (ATA, FC, SBP, ISCSI, SPI, SAS, SATA, USB), -Ht, -tl. (including sas address) |

lsscsi 列出所有 SCSI 设备:
peng@ubuntu:~$ lsscsi [3:0:0:0] cd/dvd NECVMWar VMware SATA CD01 1.00 /dev/sr0 [32:0:0:0] disk VMware, VMware Virtual S 1.0 /dev/sda
lsscsi -L列出所有具有详细属性的 SCSI 设备:
peng@ubuntu:~$ lsscsi -L [3:0:0:0] cd/dvd NECVMWar VMware SATA CD01 1.00 /dev/sr0 device_blocked=0 iocounterbits=32 iodone_cnt=0x229 ioerr_cnt=0x4 iorequest_cnt=0x23a queue_depth=1 queue_type=none scsi_level=6 state=running timeout=30 type=5 [32:0:0:0] disk VMware, VMware Virtual S 1.0 /dev/sda device_blocked=0 iocounterbits=32 iodone_cnt=0x37370 ioerr_cnt=0x3 iorequest_cnt=0x37370 queue_depth=32 queue_type=simple scsi_level=3 state=running timeout=180 type=0
lsscsi -s列出所有具有人类可读磁盘容量的 SCSI 设备:
peng@ubuntu:~$ lsscsi -s [3:0:0:0] cd/dvd NECVMWar VMware SATA CD01 1.00 /dev/sr0 - [32:0:0:0] disk VMware, VMware Virtual S 1.0 /dev/sda 536GB
/proc/scsi/
peng@ubuntu:~$ cd /proc/scsi/ peng@ubuntu:/proc/scsi$ ls device_info mptspi scsi sg peng@ubuntu:/proc/scsi$ cat scsi Attached devices: Host: scsi32 Channel: 00 Id: 00 Lun: 00 Vendor: VMware, Model: VMware Virtual S Rev: 1.0 Type: Direct-Access ANSI SCSI revision: 02 Host: scsi3 Channel: 00 Id: 00 Lun: 00 Vendor: NECVMWar Model: VMware SATA CD01 Rev: 1.00 Type: CD-ROM ANSI SCSI revision: 05
/sys/class/scsi_host
peng@ubuntu:/sys/class/scsi_host$ ls host0 host12 host16 host2 host23 host27 host30 host5 host9 host1 host13 host17 host20 host24 host28 host31 host6 host10 host14 host18 host21 host25 host29 host32 host7 host11 host15 host19 host22 host26 host3 host4 host8
/sys/class/scsi_device
peng@ubuntu:/sys/class/scsi_device$ ls 3:0:0:0 32:0:0:0
/sys/class/scsi_disk
peng@ubuntu:/sys/class/scsi_disk$ ls 32:0:0:0
/sys/class/scsi_generic
peng@ubuntu:/sys/class/scsi_generic$ ls sg0 sg1
/sys/bus/scsi
peng@ubuntu:/sys/bus/scsi$ ls devices drivers drivers_autoprobe drivers_probe uevent peng@ubuntu:/sys/bus/scsi/devices$ ls 3:0:0:0 host11 host16 host20 host25 host3 host5 target3:0:0 32:0:0:0 host12 host17 host21 host26 host30 host6 target32:0:0 host0 host13 host18 host22 host27 host31 host7 host1 host14 host19 host23 host28 host32 host8 host10 host15 host2 host24 host29 host4 host9
其中target3:0:0
对应
host:bus:id:lun
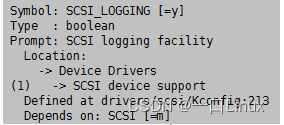
drivers/scsi/Kconfig:213 config SCSI_LOGGING bool "SCSI logging facility" depends on SCSI ---help--- This turns on a logging facility that can be used to debug a number of SCSI related problems. If you say Y here, no logging output will appear by default, but you can enable logging by saying Y to "/proc file system support" and "Sysctl support" below and executing the command echo > /proc/sys/dev/scsi/logging_level where is a four byte value representing the logging type and logging level for each type of logging selected. There are a number of logging types and you can find them in the source at . The logging levels are also described in that file and they determine the verbosity of the logging for each logging type. If you say N here, it may be harder to track down some types of SCSI problems. If you say Y here your kernel will be somewhat larger, but there should be no noticeable performance impact as long as you have logging turned off.
-> drivers\scsi\scsi_logging.h
/* * Note - the initial logging level can be set here to log events at boot time. * After the system is up, you may enable logging via the /proc interface. */ unsigned int scsi_logging_level; #if defined(CONFIG_SCSI_LOGGING) EXPORT_SYMBOL(scsi_logging_level); #endif
scsi_logging_level 被定义成int类型(32bit),该机制使用了30个bit,从低位到高位每3bit为一个logging level从SCSI_LOG_ERROR_SHIFT到SCSI_LOG_IOCTL_SHIFT(SCSI_LOG_XXX_SHIFT为不同level的移位数),每个level使用的bit数都是3,所以 SCSI_LOG_XXX_BITS 均为3
-1 - Enable scsi events to syslog. // 开启所有scsi log 0 - Disable scsi events to syslog. // 关闭所有scsi log
命令:
echo 0/-1 > /proc/sys/dev/scsi/logging_level
The above is the detailed content of Detailed explanation of Linux command lsscsi. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




