
The vastness of Linux means people can always submit unique content. This content will not only benefit their careers but also increase their knowledge. Here we will attempt to do so, and let our readers be the judge of how successfully we do so.
As a supplement to shell scripts, in this article we will interpret Linux Shell-related issues from an interview perspective.
1. How to interrupt script execution before the shell script is successfully executed?
Answer: We need to use the exit command to achieve the above situation. When the exit command is forced to output a non-zero value, the script will report an error and exit. In a Unix shell script, a value of 0 indicates successful execution. Therefore, executing an unquoted exit -1 command before the script terminates will abort the script.
#!/bin/bash echo "Hello" exit -1 echo "bye"
Save the file and execute.
# sh linuxmi.sh Hello linuxmi.sh:行3: exit-1: 未找到命令 bye
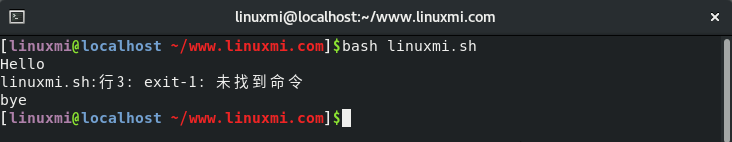
It can be clearly seen from the above script that the script executes fine before the exit -1 command.
2. How to use Linux commands to remove file headers?
Answer: When we need to delete specified lines in a file, the sed command can be used to solve the problem.
This is the correct command to delete the file header (the first line of the file).
# sed '1 d' file.txt
Well, in fact, the -i switch built into the sed command can do this job, so there is no need for a redirection character.
# sed -i '1 d' file.txt
3. How do you check the length of a line in a text file?
Answer: sedThe command can also be used to find a certain line in a text file or check its length.
sed -n 'n p' file.txt can be solved, where n represents the line number, p prints out the matching content (to standard output) , this command is usually used with the -n command line option. So, how to get the length count? Obviously, we need to pipe the output to the wc command for calculation.
# sed –n 'n p' file.txt | wc –c
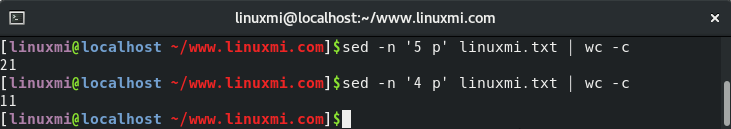
To get the length of the fifth line of the text file ‘linuxmi.txt’, run the following command:
# sed -n '5 p' linuxmi.txt | wc -c
4. Can all non-printing characters be viewed on a Linux system? how did you do it?
Answer: Yes. All non-printing characters can be viewed in Linux. To implement the solution mentioned above, we need the help of the vi editor. How to display non-printing characters in the vi editor?
Open the vi editor.
先按[esc]键,然后按:进入到vi编辑器的命令模式。
最后,从 vi 编辑器的命令界面输入set list命令并执行。
“
注: 这种方式可以查看文本文件中的所有非打印字符,包括 ctrl+m(^M)。
”
5、假如你是一个员工组的团队领导,为xyz公司工作。公司要求你创建一个**dir_xyz目录,让该组成员都能在该目录下创建或访问文件,但是除了文件创建者之外的其他人不能删除文件,你会怎么做?**
解答:这真是个有趣的工作方案。好吧,上面所讲的方案,我们需要通过下面的步骤来实施,这简直就是小菜一碟。
# mkdir dir_xyz # chmod g+wx dir_xyz # chmod +t dir_xyz
第一行命令创建了一个目录(dir_xyz),上面的第二行命令让组(g)具有‘写’和‘执行’的权限,而上面的最后一行命令——权限位最后的‘+t’是‘粘滞位’,它用来替换‘x’,表明在这个目录中,文件只能被它们的拥有者、目录的拥有者或者是超级用户root删除。
6、你能告诉我一个Linux进程经历的各个阶段吗?
解答:一个 Linux 进程在它的一生中,通常经历了四个主要阶段。
这里是Linux进程要经历的四个阶段。
7、Linux中**cut命令怎么用?**
解答:cut是一个很有用的 Linux 命令,当我们要截取文件的指定部分并打印到标准输出,当文本区域以及文件本身很大时,这个命令很有用。
例如,取txt_linuxmi文件的前10列。
# cut -c1-10 txt_linuxmi
要截取该文件中的第二,第五和第七列。
# cut -d;-f2 -f5 -f7 txt_linuxmi
8、**cmp和diff命令的区别是什么?**
解答:cmp和diff命令用来获取相同的东西,但各有侧重。diff命令输出为了使两个文件一样而应该做的修改。而‘cmp’命令则将两个文件逐字节对比,并报告第一个不匹配的项。
9. Can the **echo command be used to replace the ls command? **
Answer: Yes. The 'ls' command can be replaced with the 'echo' command. The ‘ls’ command lists the directory contents. From the perspective of replacing the above command, we can use ‘echo *’. The output of the two commands is exactly the same.
10. You may have heard of inode. Can you briefly describe the inode?
Answer: inode is a data structure used for file identification on Linux. Each file has a separate inode and a unique inode number on Unix systems.
The above is the detailed content of 10 Useful 'Interview Questions and Answers' for Linux Shell Scripting. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




