
There are mainly .zip, .gz, .bz2, .tar.gz and .tar.bz2 compression formats in Linux
.zip format syntax:
Compress the 11.txt file into: 11.zip file: zip 11.zip 11.txt
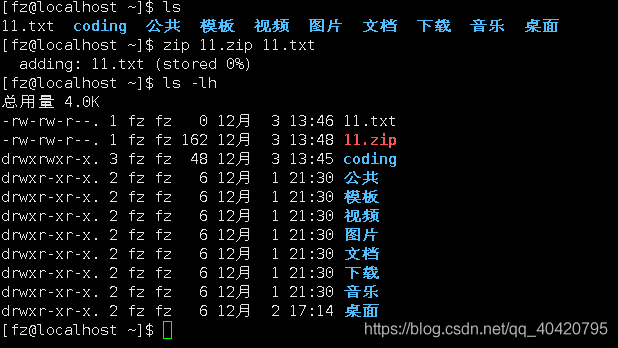
Compress the coding directory into: coding.zip file: zip -r coding.zip coding (As you can see from the picture below, all the contents in the directory will be compressed)
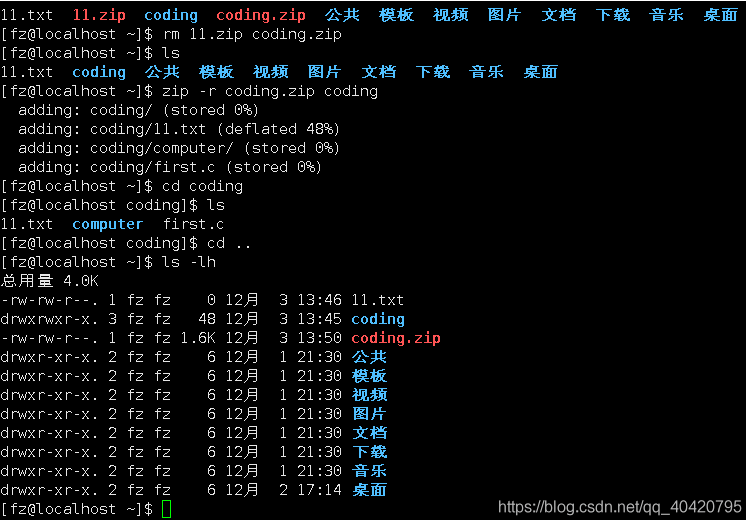
Compress the coding directory into: coding.zip file: zip coding.zip coding (it only compresses coding/, which does not contain the original content of the coding folder)
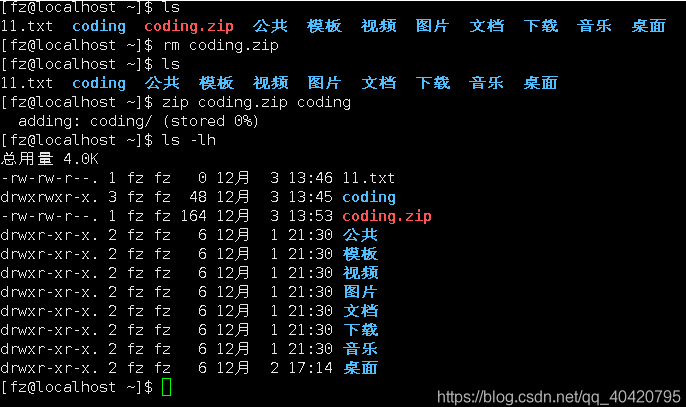
Decompress the coding.zip file (the coding.zip file obtained in the picture above), you can see that all the original first.c and other files are gone

.gz format syntax:
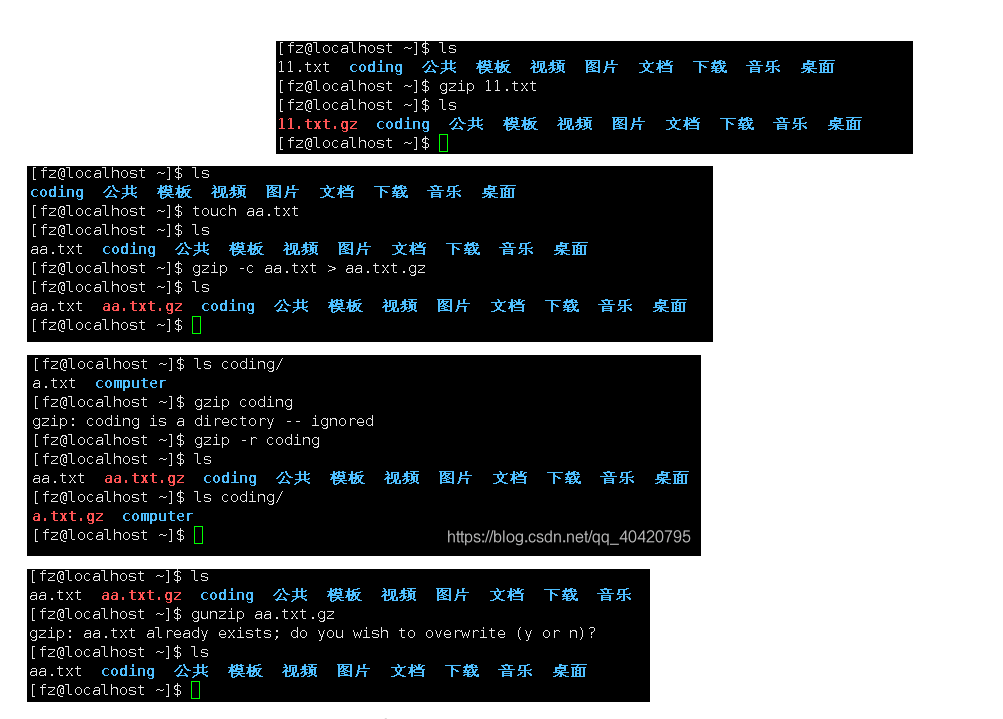
gzip source file #Compress to a compressed file in .gz format, the source file will disappear
gzip -c source file > compressed file #Compress to .gz format, keep the source file. For example: gzip-c cangls>cangls.gz
gzip -r directory #Compress all subfiles in the directory, but the directory cannot be compressed
gunzip compressed file name #unzip compressed file
.bz2 format syntax

In response to the shortcoming that the .gz and .bz2 formats cannot compress directories, Linux can solve this problem by first packaging all the files in a directory through the tar command, and then compressing them into .gz or .bz2 formats.
Packaging command tar
For example:
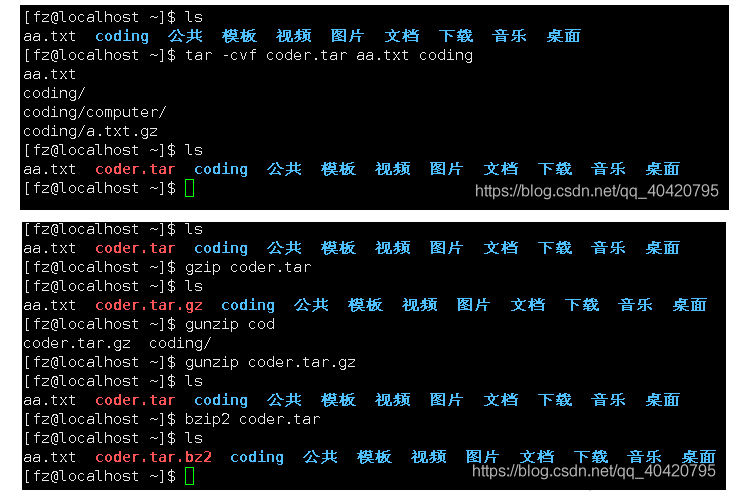
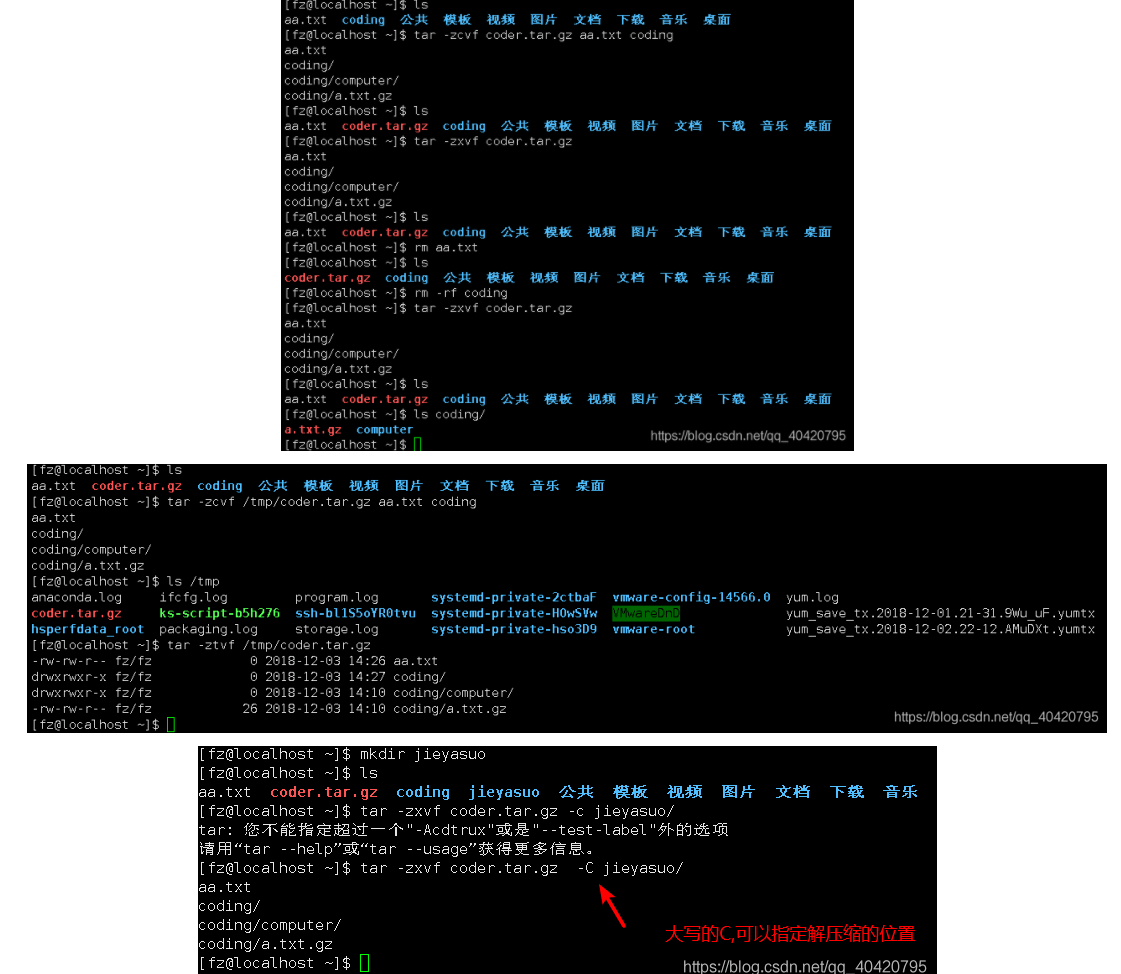
.tar.gz compression format In fact, the .tar.gz format is first packaged into .tar format and then compressed into .gz format
.tar.bz2 compression format
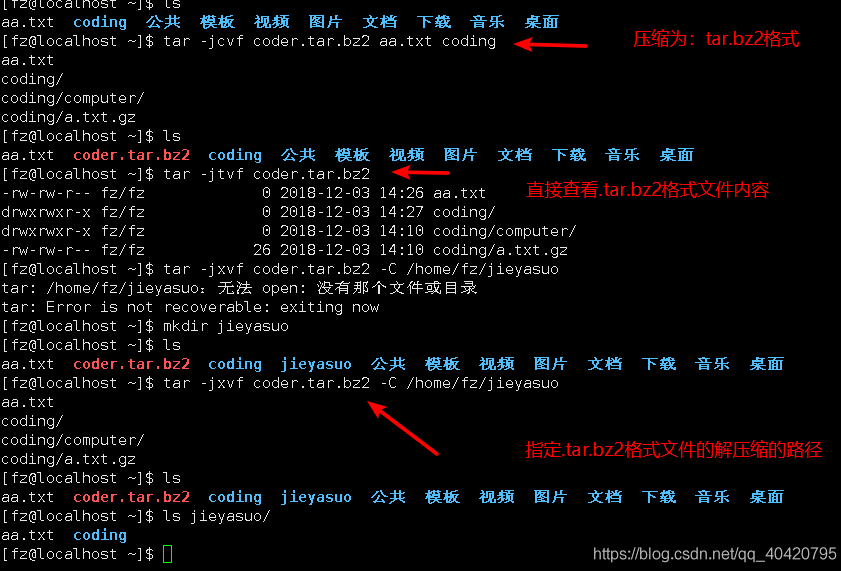
In Linux, .tar.gz and .tar.bz2 are the two most common compressed file formats. From the above practice, we can see that these two file formats can easily compress files. and directory, you can also view the contents contained in the compressed package, so these two formats need to be mastered proficiently. As for the .zip, .gz, and .bz2 formats, it is enough to understand them. No proficiency is required. When using them, just a little bit Impression, just find Du Niang.
The above is the detailed content of Compression command in linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




