Linux command history - easily improve command line efficiency
For Linux enthusiasts and developers, the command line is an extremely important tool. However, in the process of frequent use of the command line, we will inevitably make input errors or forget the commands we have used before. At this point, Linux command history can come in handy. It allows us to easily find and reuse previous commands, greatly improving our work efficiency. Now, let’s explore this powerful tool together!
The basis of history
HISTSIZE Variable value sets the number of commands saved in the history list. By default, this value is 500. These previously issued commands (called the history list) are stored in a history file. Its default location is ~/.bash_history, which is stored in the shell variable HISTFILE.
The ! command is used in this article to introduce commands in the bash history list into the input. This feature makes it easy for users to quickly repeat commands, replace text, manipulate parameters, and fix spelling errors in previous commands.
Command Repeat Example
Here are some examples of what you can do with !.
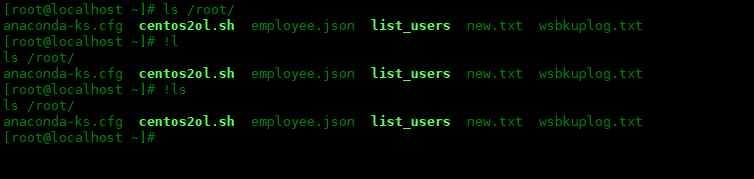
Repeat the last command at the beginning of the matching string
! followed by the first character (or string) that matches the command to be run will repeat an instance of that command:
[root@localhost ~]# ls /root/ anaconda-ks.cfg centos2ol.sh employee.json list_users new.txt wsbkuplog.txt [root@localhost ~]# !l ls /root/ anaconda-ks.cfg centos2ol.sh employee.json list_users new.txt wsbkuplog.txt [root@localhost ~]# !ls ls /root/ anaconda-ks.cfg centos2ol.sh employee.json list_users new.txt wsbkuplog.txt
Repeatly matches the last command anywhere in the string
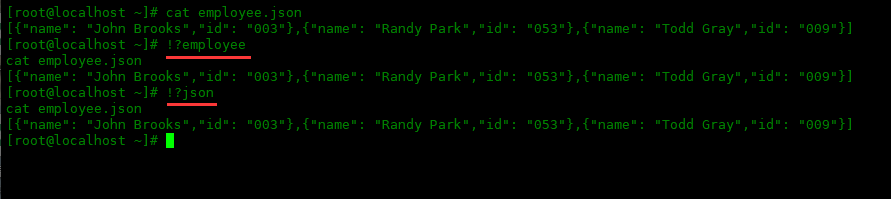
!?The format is the same as above, but Li Shiming’s order does not have to be the beginning of the command:
[root@localhost ~]# cat employee.json
[{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"},{"name": "Randy Park","id": "053"},
{"name": "Todd Gray","id": "009"}]
[root@localhost ~]# !?employee
cat employee.json
[{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"},{"name": "Randy Park","id": "053"},
{"name": "Todd Gray","id": "009"}]
[root@localhost ~]# !?json
cat employee.json
[{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"},{"name": "Randy Park","id": "053"},
{"name": "Todd Gray","id": "009"}]
Repeat the nth command in history
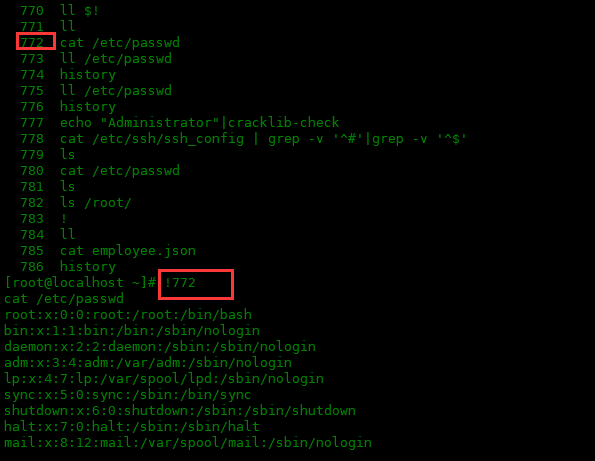
Repeat the nth command in bash history:
[root@localhost ~]# !772
Repeat last command
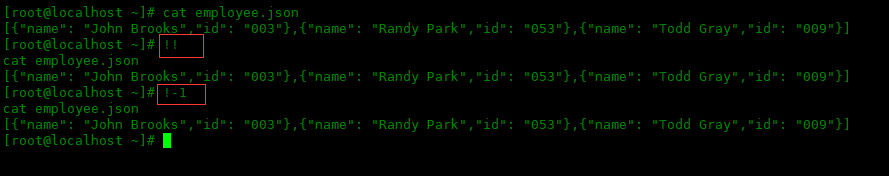
If there's one command I use all the time, it's !!. Repeats the last command in the history list, behaves the same as !-1:
[root@localhost ~]# cat employee.json
[{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"},{"name": "Randy Park","id": "053"},
{"name": "Todd Gray","id": "009"}]
[root@localhost ~]# !!
cat employee.json
[{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"},{"name": "Randy Park","id": "053"},
{"name": "Todd Gray","id": "009"}]
[root@localhost ~]# !-1
cat employee.json
[{"name": "John Brooks","id": "003"},{"name": "Randy Park","id": "053"},
{"name": "Todd Gray","id": "009"}]
[root@localhost ~]#
If you forgot to add sudo to the previous command, you can use it in combination with !!. It can also be used later in conjunction with the pipe character.
$ yum update Loaded plugins: priorities, update-motd, upgrade-helper You need to be root to perform this command. $ sudo !! sudo yum update Loaded plugins: priorities, update-motd, upgrade-helper $ ls dir dir1 dir2 file file1 file2 hello.txt $ !! | grep file ls | grep file file file1 file2
Repeat and replace string
I often enter long commands and then re-enter them with different parameters. Or, I need to reissue a command because there was a typo in my previous command. String substitution allows me to do this without retyping the entire long command. The following is the syntax:
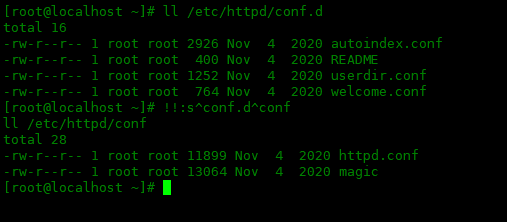
!!:s^oldstring^newstring
^ in the command is the delimiter, and the previous oldstring string is replaced with the following newstring string.
[root@localhost ~]# ll /etc/httpd/conf.d total 16 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 2926 Nov 4 2020 autoindex.conf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 400 Nov 4 2020 README -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 1252 Nov 4 2020 userdir.conf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 764 Nov 4 2020 welcome.conf [root@localhost ~]# !!:s^conf.d^conf ll /etc/httpd/conf total 28 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 11899 Nov 4 2020 httpd.conf -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 13064 Nov 4 2020 magic [root@localhost ~]#
通过本文的学习,我们已经学会了如何使用Linux命令历史记录来提高我们的命令行操作效率。同时,我们还了解了常用的历史命令操作以及如何对历史记录进行配置和管理。希望这篇文章对你在使用Linux命令行时有所帮助,并能够让你更加高效地完成自己的工作。
The above is the detailed content of Linux command history - easily improve command line efficiency. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 How to solve permission issues when using python --version command in Linux terminal?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:36 AM
How to solve permission issues when using python --version command in Linux terminal?
Apr 02, 2025 am 06:36 AM
Using python in Linux terminal...
 How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to open web.xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 06:51 AM
To open a web.xml file, you can use the following methods: Use a text editor (such as Notepad or TextEdit) to edit commands using an integrated development environment (such as Eclipse or NetBeans) (Windows: notepad web.xml; Mac/Linux: open -a TextEdit web.xml)
 Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Four ways to implement multithreading in C language
Apr 03, 2025 pm 03:00 PM
Multithreading in the language can greatly improve program efficiency. There are four main ways to implement multithreading in C language: Create independent processes: Create multiple independently running processes, each process has its own memory space. Pseudo-multithreading: Create multiple execution streams in a process that share the same memory space and execute alternately. Multi-threaded library: Use multi-threaded libraries such as pthreads to create and manage threads, providing rich thread operation functions. Coroutine: A lightweight multi-threaded implementation that divides tasks into small subtasks and executes them in turn.
 Can the Python interpreter be deleted in Linux system?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:00 AM
Can the Python interpreter be deleted in Linux system?
Apr 02, 2025 am 07:00 AM
Regarding the problem of removing the Python interpreter that comes with Linux systems, many Linux distributions will preinstall the Python interpreter when installed, and it does not use the package manager...
 What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
What is the Linux best used for?
Apr 03, 2025 am 12:11 AM
Linux is best used as server management, embedded systems and desktop environments. 1) In server management, Linux is used to host websites, databases, and applications, providing stability and reliability. 2) In embedded systems, Linux is widely used in smart home and automotive electronic systems because of its flexibility and stability. 3) In the desktop environment, Linux provides rich applications and efficient performance.
 How is Debian Hadoop compatibility
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:42 AM
How is Debian Hadoop compatibility
Apr 02, 2025 am 08:42 AM
DebianLinux is known for its stability and security and is widely used in server, development and desktop environments. While there is currently a lack of official instructions on direct compatibility with Debian and Hadoop, this article will guide you on how to deploy Hadoop on your Debian system. Debian system requirements: Before starting Hadoop configuration, please make sure that your Debian system meets the minimum operating requirements of Hadoop, which includes installing the necessary Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and Hadoop packages. Hadoop deployment steps: Download and unzip Hadoop: Download the Hadoop version you need from the official ApacheHadoop website and solve it
 Do I need to install an Oracle client when connecting to an Oracle database using Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:48 PM
Do I need to install an Oracle client when connecting to an Oracle database using Go?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 03:48 PM
Do I need to install an Oracle client when connecting to an Oracle database using Go? When developing in Go, connecting to Oracle databases is a common requirement...
 Unable to log in to mysql as root
Apr 08, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
Unable to log in to mysql as root
Apr 08, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
The main reasons why you cannot log in to MySQL as root are permission problems, configuration file errors, password inconsistent, socket file problems, or firewall interception. The solution includes: check whether the bind-address parameter in the configuration file is configured correctly. Check whether the root user permissions have been modified or deleted and reset. Verify that the password is accurate, including case and special characters. Check socket file permission settings and paths. Check that the firewall blocks connections to the MySQL server.




