Steps and configuration methods for installing udev on CentOS
php editor Youzi will introduce you to the steps and configuration methods of installing udev on CentOS. udev is a device manager used to dynamically create device nodes in Linux systems. Installing udev on CentOS can help us better manage devices and drivers. The steps to install udev are very simple. First, you need to install the udev package through the yum command, and then make relevant settings in the configuration file. Next, we will introduce in detail the steps and configuration methods of installing udev to help you better use the CentOS system.
#udev is a device management tool in the Linux kernel. It is responsible for automatically identifying and configuring hardware devices when the Linux system starts. udev can configure the device according to the attributes and rules of the device. The device allocates a unique device node and loads the corresponding driver as needed. In CentOS, udev is also an important component. It can automatically identify newly added hardware devices and assign device nodes to them.
1. Open the terminal and log in to the CentOS system as the root user.
2. Use the following command to install udev:
```
yum install udev
This will automatically download and install the udev package and its dependencies item.
Configuring udev can be completed by editing the udev configuration file. The udev configuration file is located in the `/etc/udev/` directory and mainly includes the following two files:
1. `udev .conf`: This file contains the global configuration options of udev. You can modify the global configuration of udev by editing this file, such as setting the default device node permissions, setting rules for loading drivers, etc.
2. `rules.d/` directory: This directory contains a series of rule files with the suffix `.rules`. These rule files define how udev identifies and configures the device. You can edit these rule files To modify udev's device identification and configuration rules.
2. Use a text editor to open the `/etc/udev/udev.conf` file:
vi /etc/udev/udev.conf
3. As needed Modify configuration options, such as setting the default device node permissions:
#Default device node permissions
MODE="0666"
This will set the default device node permissions to 0666, that is, all users have read and write permissions.
4. Save the file and exit the editor.
2. Use a text editor to open the rules file in the `/etc/udev/rules.d/` directory, for example `/etc/udev/rules.d/10-local.rules`:
vi /etc/udev/rules.d/10-local.rules
3. Add or modify rules as needed, for example, add a rule to identify and configure a USB device:
# USB Device Rules
SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ATTR{idVendor}=="1234", ATTR{idProduct}=="5678", MODE="0666"
This will set the device node permissions to 0666 when a USB device with idVendor 1234 and idProduct 5678 is plugged in.
2. Use the following command to restart the udev service:
systemctl restart udev
This will make the new udev configuration take effect.
CentOS udev installation and configuration has been completed.
In Linux systems, you can use the `lsusb` command to list all devices connected to the USB bus. This command can help us view the detailed information of the USB device, such as the manufacturer ID and product ID of the device, etc. , use the `lsusb -v` command to display more detailed device information.
The above is the detailed content of Steps and configuration methods for installing udev on CentOS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
Mastering Text Manipulation With the Sed Command
Mar 16, 2025 am 09:48 AM
The Linux command line interface provides a wealth of text processing tools, one of the most powerful tools is the sed command. sed is the abbreviation of Stream EDitor, a multi-functional tool that allows complex processing of text files and streams. What is Sed? sed is a non-interactive text editor that operates on pipeline inputs or text files. By providing directives, you can let it modify and process text in a file or stream. The most common use cases of sed include selecting text, replacing text, modifying original files, adding lines to text, or removing lines from text. It can be used from the command line in Bash and other command line shells. Sed command syntax sed
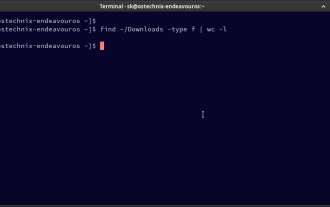 How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
How To Count Files And Directories In Linux: A Beginner's Guide
Mar 19, 2025 am 10:48 AM
Efficiently Counting Files and Folders in Linux: A Comprehensive Guide Knowing how to quickly count files and directories in Linux is crucial for system administrators and anyone managing large datasets. This guide demonstrates using simple command-l
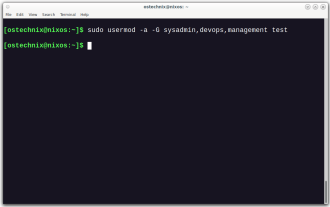 How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
How To Add A User To Multiple Groups In Linux
Mar 18, 2025 am 11:44 AM
Efficiently managing user accounts and group memberships is crucial for Linux/Unix system administration. This ensures proper resource and data access control. This tutorial details how to add a user to multiple groups in Linux and Unix systems. We
 The Secret Weapon to Supercharge Your Linux System With Liquorix Kernel
Mar 08, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
The Secret Weapon to Supercharge Your Linux System With Liquorix Kernel
Mar 08, 2025 pm 12:12 PM
Liquorix kernel: a powerful tool to improve Linux system performance Linux is known for its flexibility, security and high performance, becoming the operating system of choice for developers, system administrators, and advanced users. However, the universal Linux kernel is not always meeting the needs of users seeking maximum performance and responsiveness. This is where the Liquorix kernel comes into play—a performance-optimized alternative that promises to enhance your Linux system. This article will explore what the Liquorix kernel is, why you might want to use it, and how to install and configure it to get the most out of your system. Liquorix kernel detailed explanation Liquorix kernel is a precompiled Linux kernel designed for
 How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
How To List Or Check All Installed Linux Kernels From Commandline
Mar 23, 2025 am 10:43 AM
Linux Kernel is the core component of a GNU/Linux operating system. Developed by Linus Torvalds in 1991, it is a free, open-source, monolithic, modular, and multitasking Unix-like kernel. In Linux, it is possible to install multiple kernels on a sing
 How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
How To Type Indian Rupee Symbol In Ubuntu Linux
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:39 AM
This brief guide explains how to type Indian Rupee symbol in Linux operating systems. The other day, I wanted to type "Indian Rupee Symbol (₹)" in a word document. My keyboard has a rupee symbol on it, but I don't know how to type it. After
 Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Locating Leviathan Files in Linux
Mar 13, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Introduction In the realm of Linux, where the command line is often the compass by which we navigate, the efficient management of disk space is crucial. Whether you’re sailing through personal projects or steering the ship o
 How To Convert Unix Timestamps To Strings In Linux
Mar 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How To Convert Unix Timestamps To Strings In Linux
Mar 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Linux and Unix-like operating systems often use timestamps to represent dates and times in a machine-readable format. However, for human users, these timestamps may be difficult to interpret. In this blog post, we will explain the process of converting Unix timestamps to human-readable strings in Linux. We will explore various methods and provide practical examples to help you understand and implement these techniques. Table of contents - Understand Unix timestamps Why convert timestamps to strings? Methods to convert timestamps to strings Use the date command Use awk Use perl Using python Use with custom format




