
PowerShell is a cross-platform command line tool and scripting language that allows you to easily manage and automate a variety of tasks. PowerShell was originally designed for Windows systems, but since the release of PowerShell Core 6.0 in 2016, it can run on Linux and macOS systems. PowerShell Core 6.0 is an open source version based on .NET Core, which supports multiple Linux distributions, including Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Fedora, etc. In this article, we'll cover how to install and use PowerShell Core 6.0 on Linux, and how to leverage its power to manage your Linux system.

PowerShell provides full access to COM (Component Object Model) and WMI (Windows Management Instrumentation), allowing system administrators to Perform management tasks in local or remote Windows systems, and access WS-Management and CIM (Common Information Model) to achieve management of remote Linux systems and network devices.
With this framework, management tasks are basically performed by .NET classes called cmdlets (pronounced command-lets). Just like Linux shell scripts, users can make scripts or executable files by writing a set of cmdlets to a file according to certain rules. These scripts can be used as standalone command line programs or tools.
Install PowerShell Core 6.0 on Linux system
To install PowerShell Core 6.0 in Linux, we will use the Microsoft Software Repository, which allows us to install through the most popular Linux package manager tools, such as apt-get, yum, etc.
Installation in Ubuntu 16.04
First, import the GPG key for that public repository, then register the Microsoft Ubuntu repository into the APT source to install PowerShell:
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add - $ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/16.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install -y powershell
Installation in Ubuntu 14.04
$ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/keys/microsoft.asc | sudo apt-key add - $ curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/ubuntu/14.04/prod.list | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/microsoft.list $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install -y powershell
Installation in CentOS 7
First, register the Microsoft RedHat repository into the YUM package manager repository list, and then install PowerShell:
$ sudo curl https://packages.microsoft.com/config/rhel/7/prod.repo > /etc/yum.repos.d/microsoft.repo $ sudo yum install -y powershell
How to use PowerShell Core 6.0 in Linux
In this section, we will briefly introduce PowerShell; we will see how to start PowerShell, run some basic commands, and operate files, directories, and processes. Then learn how to list all available commands, display command help, and aliases.
Enter the following command to start PowerShell:
$ powershell
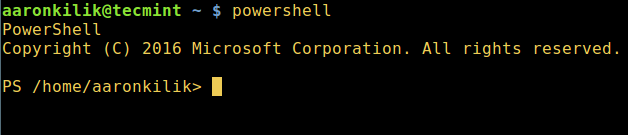
Start PowerShell in Linux
You can check the PowerShell version with the following command:
$PSVersionTable
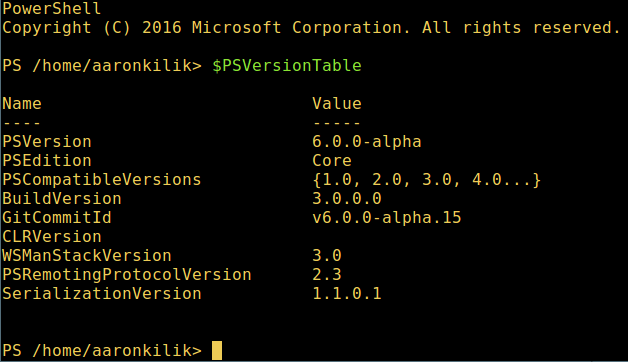
View PowerShell version
Run basic PowerShell commands in Linux.
get-date [# 显示当前日期] get-uptime [# 显示开机时间] get-location [# 显示当前工作目录]
Manipulating files and directories in PowerShell
1. You can create an empty file in two ways:
new-item tecmint.tex 或者 "">tecmint.tex
Then add content to it and view the file content.
set-content tecmint.tex -value "TecMint Linux How Tos Guides" get-content tecmint.tex
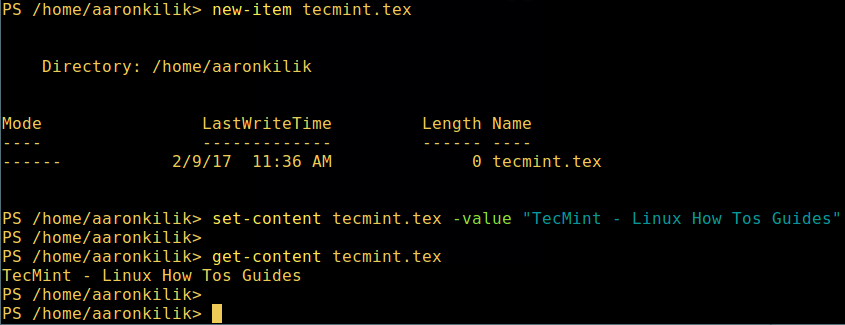
Create a new file in PowerShell
2. Delete a file in PowerShell
remove-item tecmint.tex get-content tecmint.tex
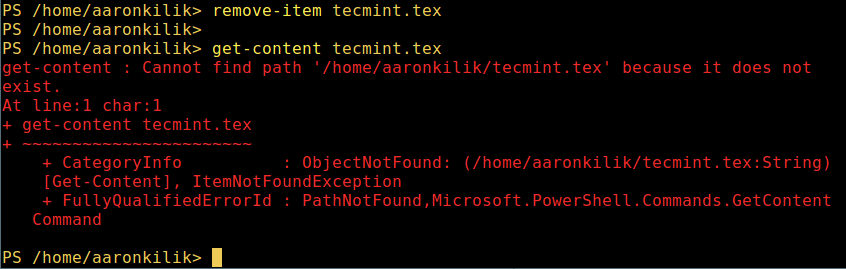
Delete a file in PowerShell
3. Create directory
mkdir tecmint-files cd tecmint-files “”>domains.list ls
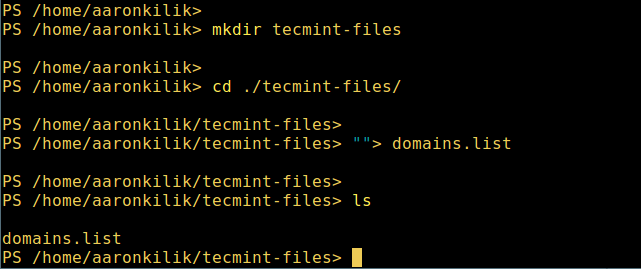
Create a directory in PowerShell
4. To perform a long-format list operation and list file/directory details, including mode (file type), last modification time, etc., use the following command:
dir
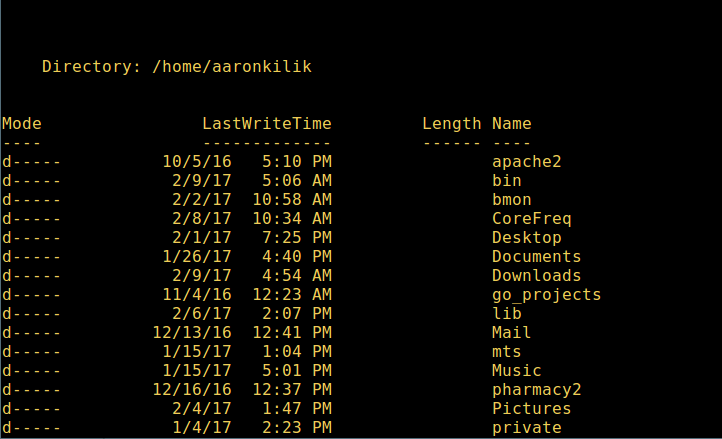
List a long list of directories in Powershell
5. Display all processes in the system:
get-process
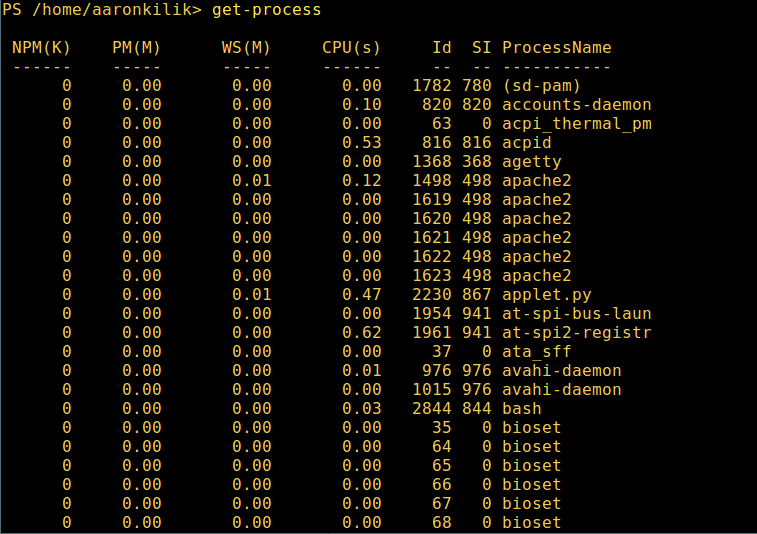
Show running processes in PowerShell
6. View the details of the running process/process group by the given name, and pass the process name as a parameter to the above command, as follows:
get-process apache2
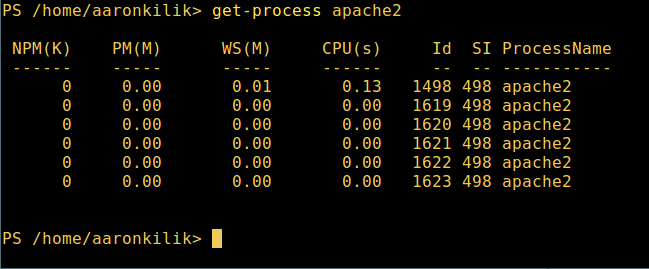
View the specified process in PowerShell
The meaning of each part in the output:
7、 想要了解更多,获取 PowerShell 命令列表:
get-command
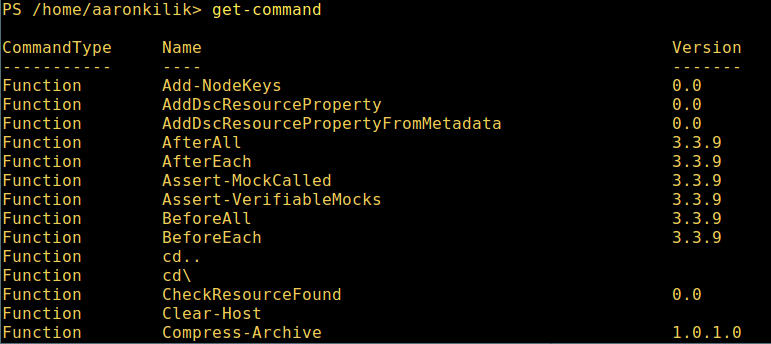
列出 PowerShell 的命令
8、 想知道如何使用一个命令,查看它的帮助(类似于 Unix/Linux 中的 man);举个例子,你可以这样获取命令 Describe 的帮助:
get-help Describe
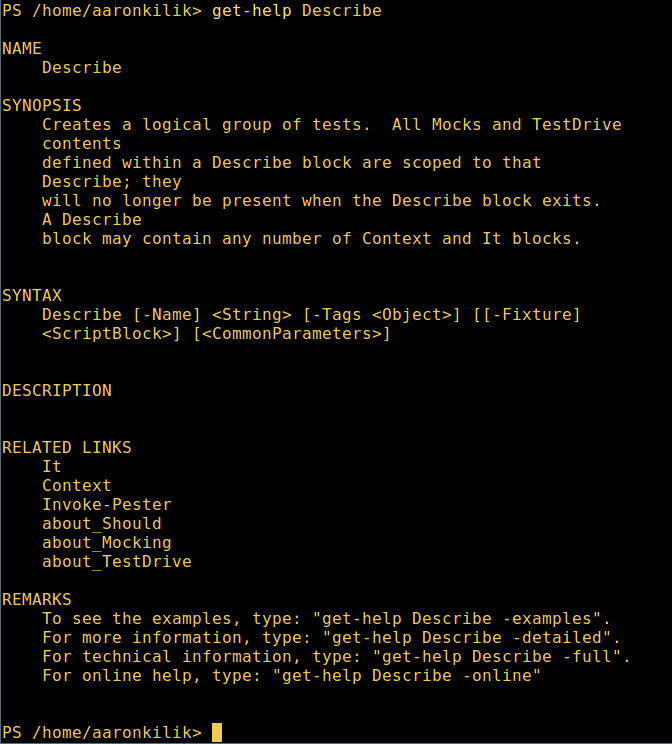
PowerShell 帮助手册
9、 显示所有命令的别名,輸入:
get-alias
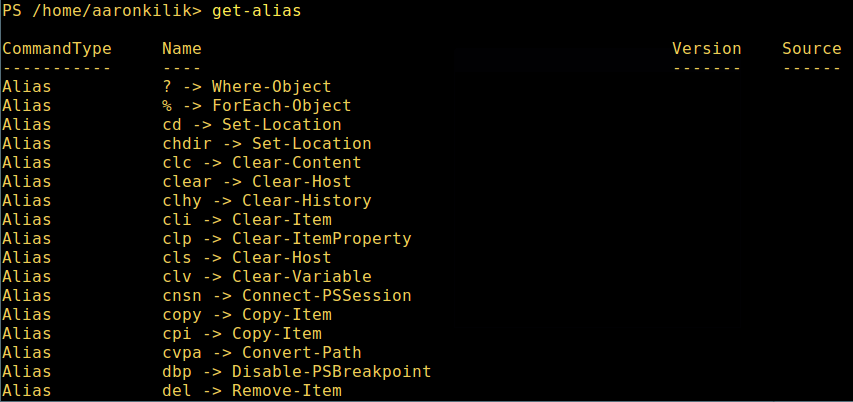
列出 PowerShell 命令别名
10、 最后,不过也很重要,显示命令历史记录(曾运行过的命令的列表):
history
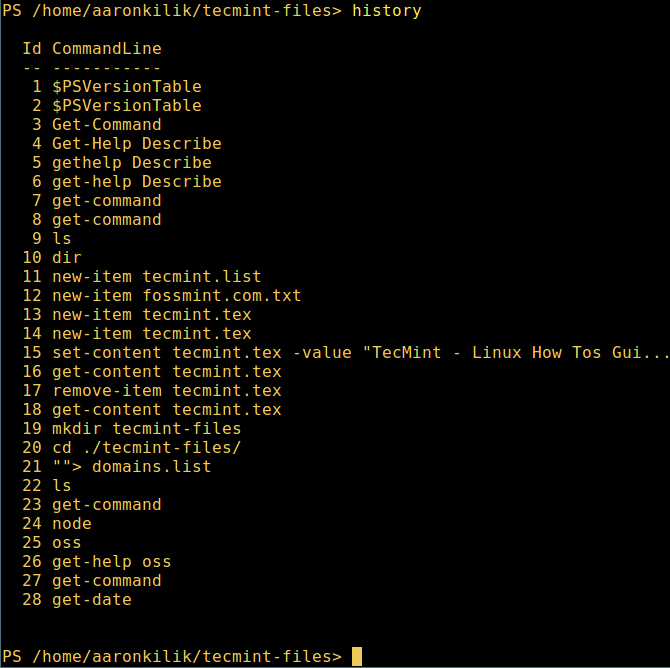
显示 PowerShell 命令历史记录
就是这些了!在这篇文章里,我们展示了如何在 Linux 中安装微软的 PowerShell Core 6.0。在我看来,与传统 Unix/Linux 的 shell 相比,PowerShell 还有很长的路要走。目前看来,PowerShell 还需要在命令行操作机器,更重要的是,编程(写脚本)等方面,提供更好、更多令人激动和富有成效的特性。
查看 PowerShell 的 GitHub 仓库:https://github.com/PowerShell/PowerShell。
在本文中,我们学习了如何在 Linux 上安装和使用 PowerShell Core 6.0 。我们了解了如何从微软软件仓库或者直接下载 DEB 或 RPM 文件来安装 PowerShell ,以及如何启动和退出 PowerShell 会话。我们还介绍了一些基本的 PowerShell 命令和概念,比如 cmdlet、参数、管道、变量、别名等。我们还展示了如何使用 PowerShell 来执行一些常见的 Linux 管理任务,比如查看系统信息、管理进程、操作文件和目录等。通过掌握这些技能,你可以在 Linux 上体验 PowerShell 的魅力,提高你的工作效率和灵活性。
The above is the detailed content of Experience the power of PowerShell on Linux: A beginner's guide. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




