How to list block devices of Linux system using lsblk command
sblk is a command used to list all available block device information in the Linux system. Block devices refer to devices that can transmit data in blocks, such as hard disks, optical drives, USB flash drives, etc. The lsblk command can display the dependencies between block devices, as well as various attributes such as size, type, file system, mount point, etc. The lsblk command obtains information from the /sys virtual file system and udev database. If there is no udev database or lsblk is not compiled with udev support, then it will try to read the label, UUID and file system type from the block device, which requires root privileges.
In this article, we will introduce how to use the lsblk command to list the block devices of the Linux system, as well as some common options and parameters. We'll be using Ubuntu 20.04 as the example system, but the content applies to other Linux distributions as well.
Installing lsblk in Linux
The default base installation in Linux does not have the lsblk command, so how can I use lsblk?
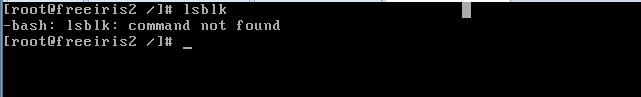
The service installation software in the centos series uses yum. Is it necessary to use yum -y install lsblk to install this command?
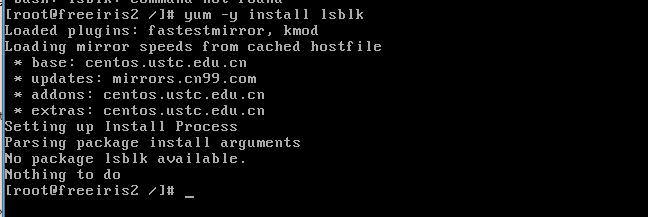
NO, that’s not the case, you’ve been tricked again
The lsblk command is included in the util-linux-ng package, which is now renamed util-linux. This package comes with several other tools, such as dmesg. To install lsblk, download the util-linux package here.
Fedora series (centos, RHEL, etc.) users can install this package through the following methods:
#yum install util-linux-ng
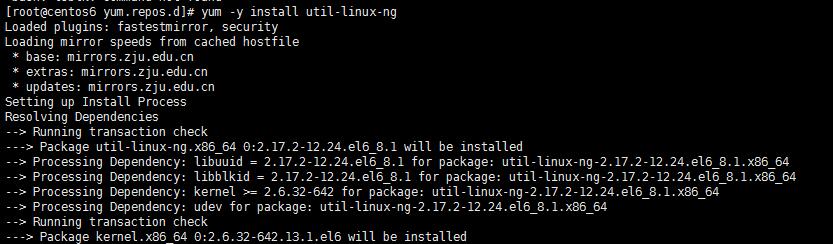
This command has several options:
Default options
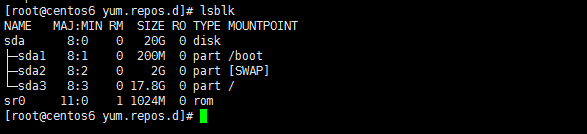
The lsblk command will list all block devices in a tree view by default. Open a terminal and enter the following command:
$ lsblk
The output is as follows:
lsblk default lsblk default
The seven column names are as follows:
NAME : 这是块设备名。 MAJ:MIN : 本栏显示主要和次要设备号。 RM : 本栏显示设备是否可移动设备。注意,在本例中设备sdb和sr0的RM值等于1,这说明他们是可移动设备。 SIZE : 本栏列出设备的容量大小信息。例如298.1G表明该设备大小为298.1GB,而1K表明该设备大小为1KB。 RO : 该项表明设备是否为只读。在本案例中,所有设备的RO值为0,表明他们不是只读的。 TYPE :本栏显示块设备是否是磁盘或磁盘上的一个分区。在本例中,sda和sdb是磁盘,而sr0是只读存储(rom)。 (LCTT译注,此处sr0的RO项没有标记为1,可能存在一些错误?) MOUNTPOINT : 本栏指出设备挂载的挂载点。
List all devices:
The default option will not list all empty devices. To view these empty devices, use the following command:
$ lsblk -a
This option will list all devices, including empty devices.
lsblk bytes sda
lsblk bytes sda
List device permissions and owners:
The lsblk command can also be used to list the ownership of a specific device, as well as groups and modes. This information can be obtained with the following command:
$ lsblk -m lsblk permissions lsblk permissions
List specified devices:
This command can also obtain only the information of the specified device. This is accomplished by specifying the device name after the options provided to the lsblk command. For example, you might be interested in knowing the size of your disk drive in bytes. You can do this by running the following command:
$ lsblk -b /dev/sda
Or, the following command is equivalent:
$ lsblk --bytes /dev/sda
List unheaded devices in list form:
You can also combine several options to obtain specified output. For example, you might want to list devices in a list format instead of the default tree format. You may also be interested in removing headers for different column names. Two different options can be combined to obtain the desired output with the following command:
$ lsblk -nl
Alternatively, you can use the long options below, which also give the same output.
$ lsblk --noheadings --list lsblk no header and list lsblk no header and list
List SCSI devices:
To get a list of SCSI devices, you can only use the -S option. This option is a capital S and should not be confused with the -s option, which prints dependencies in reverse order.
$ lsblk -S
lsblk列出SCSI设备,而-s是逆序选项(LCTT译注:将设备和分区的组织关系逆转过来显示),其将给出如下输出。输入命令:
$ lsblk -S
或者
$ lsblk --inverse
在本文中,我们学习了How to list block devices of Linux system using lsblk command,以及一些常用的选项和参数。我们了解了如何查看和过滤块设备的信息,以及如何改变输出格式和内容。我们还学习了如何使用lsblk命令获取一些高级信息,比如磁盘拓扑、磁盘对齐、磁盘丢弃(discard)等。
lsblk是一个简单而实用的命令,它可以让你更好地管理和使用你的块设备。通过使用lsblk命令,你可以提高你的存储效率和用户体验。我们建议你在使用Linux系统时,经常使用lsblk命令来列出你的块设备。
The above is the detailed content of How to list block devices of Linux system using lsblk command. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
Centos stops maintenance 2024
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:39 PM
CentOS will be shut down in 2024 because its upstream distribution, RHEL 8, has been shut down. This shutdown will affect the CentOS 8 system, preventing it from continuing to receive updates. Users should plan for migration, and recommended options include CentOS Stream, AlmaLinux, and Rocky Linux to keep the system safe and stable.
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
How to install centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
CentOS installation steps: Download the ISO image and burn bootable media; boot and select the installation source; select the language and keyboard layout; configure the network; partition the hard disk; set the system clock; create the root user; select the software package; start the installation; restart and boot from the hard disk after the installation is completed.
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 How to mount hard disk in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
How to mount hard disk in centos
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:15 PM
CentOS hard disk mount is divided into the following steps: determine the hard disk device name (/dev/sdX); create a mount point (it is recommended to use /mnt/newdisk); execute the mount command (mount /dev/sdX1 /mnt/newdisk); edit the /etc/fstab file to add a permanent mount configuration; use the umount command to uninstall the device to ensure that no process uses the device.
 What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
What to do after centos stops maintenance
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:48 PM
After CentOS is stopped, users can take the following measures to deal with it: Select a compatible distribution: such as AlmaLinux, Rocky Linux, and CentOS Stream. Migrate to commercial distributions: such as Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Oracle Linux. Upgrade to CentOS 9 Stream: Rolling distribution, providing the latest technology. Select other Linux distributions: such as Ubuntu, Debian. Evaluate other options such as containers, virtual machines, or cloud platforms.




