8 Ways to Secure SSH Server Connections on Linux
SSH is a widely used protocol for secure remote access to Linux servers. Most users use SSH connections with default settings to connect to remote servers. However, the default configuration presents security risks and requires caution.
In order to protect servers with open SSH access, especially when using public IP addresses, disabling root account logins is necessary. Cracking the root password will become easier, so we need to strengthen SSH security.
Here’s how to secure your SSH server connection on Linux:
Disable root user login:
In order to achieve this goal, you first need to disable SSH access for the root user and create a new user with root privileges. Turning off server access for the root user is a defensive strategy that prevents attackers from breaking into your system. For example, you can create a user named "exampleroot" as follows:
useradd -m exampleroot passwd exampleroot usermod -aG sudo exampleroot
The following is a brief description of the above commands:
- useradd Create a new user, and the **-m parameter creates a folder in the home** directory of the user you created.
- The passwd command is used to assign a password to a new user. Remember, the passwords you assign to your users should be complex and difficult to guess.
- usermod -aG sudoAdd the newly created user to the Administrators group.
After the user creation process, some changes need to be made to the sshd_config file. You can find this file in /etc/ssh/sshd_config. Open the file using any text editor and make the following changes to it:
# Authentication: #LoginGraceTime 2m PermitRootLogin no AllowUsers exampleroot
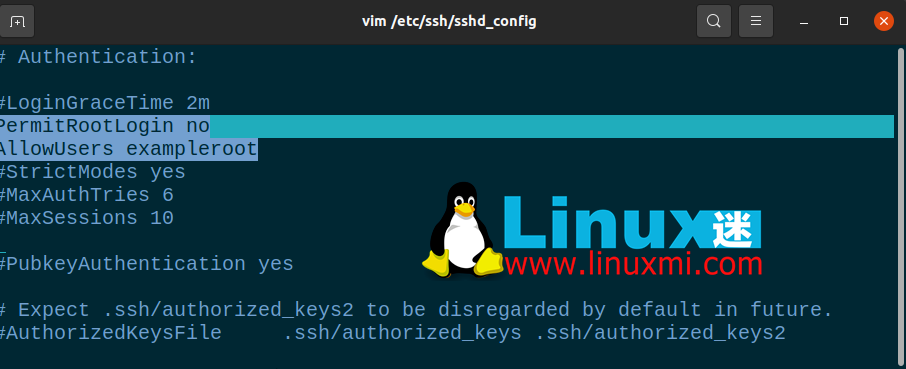
PermitRootLogin line will prevent the root user from gaining remote access using SSH. Including exampleroot in the AllowUsers list will grant the necessary permissions to the user.
Finally, restart the SSH service using the following command:
linuxmi@linuxmi /home/linuxmi/www.linuxmi.com ⚡ sudo systemctl restart ssh
If it fails and you receive an error message, try the following commands. This may vary depending on the Linux distribution you are using.
linuxmi@linuxmi /home/linuxmi/www.linuxmi.com sudo systemctl restart sshd
2. Change the default port
The default SSH connection port is 22. Of course, all attackers know this and therefore need to change the default port number to ensure SSH security. Although an attacker can easily find new port numbers through an Nmap scan, the goal here is to make the attacker's job more difficult.
To change the port number, open **/etc/ssh/sshd_config** and make the following changes to the file:
Include /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/*.confPort 22099
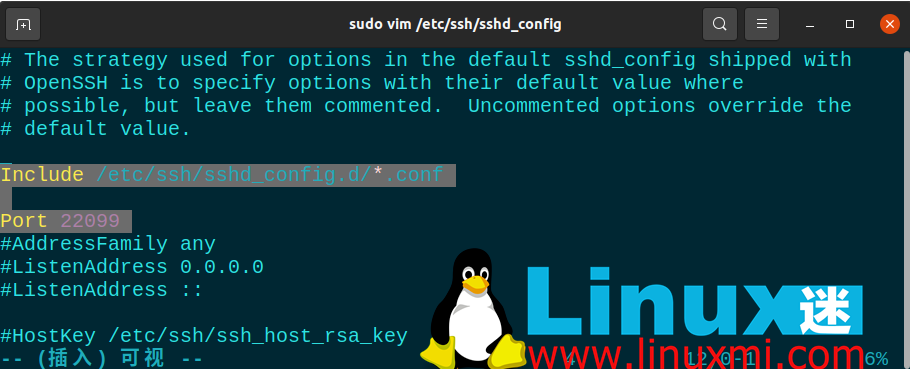
After this step, use sudo systemctl restart ssh to restart the SSH service again. Now you can access your server using the port you just defined. If you are using a firewall, you must also make the necessary rule changes here. When running the netstat -tlpn command, you can see that your SSH port number has changed.
3. Prohibit access to users with blank passwords
There may be users on your system that you accidentally created without a password. To prevent such users from accessing the server, you can set the PermitEmptyPasswords line value in the sshd_config file to no.
PermitEmptyPasswords no
4. Limit login/access attempts
By default, you can try entering your password as many times as necessary to access the server. However, an attacker could exploit this vulnerability to brute force the server. You can automatically terminate an SSH connection after a certain number of attempts by specifying the number of allowed password attempts.
To do this, change the MaxAuthTries value in the sshd_config file.
MaxAuthTries 3
5. 使用 SSH 版本 2
SSH 的第二个版本发布是因为第一个版本中存在许多漏洞。默认情况下,您可以通过将Protocol参数添加到sshd_config文件来启用服务器使用第二个版本。这样,您未来的所有连接都将使用第二个版本的 SSH。
Include /etc/ssh/sshd_config.d/*.conf Protocol 2
6.关闭TCP端口转发和X11转发
攻击者可以尝试通过 SSH 连接的端口转发来访问您的其他系统。为了防止这种情况,您可以在sshd_config文件中关闭AllowTcpForwarding和X11Forwarding功能。
X11Forwarding no AllowTcpForwarding no
7. 使用 SSH 密钥连接
连接到服务器的最安全方法之一是使用 SSH 密钥。使用 SSH 密钥时,无需密码即可访问服务器。另外,您可以通过更改sshd_config文件中与密码相关的参数来完全关闭对服务器的密码访问。
创建 SSH 密钥时,有两个密钥:Public和Private。公钥将上传到您要连接的服务器,而私钥则存储在您将用来建立连接的计算机上。
在您的计算机上使用ssh-keygen命令创建 SSH 密钥。不要将密码短语字段留空并记住您在此处输入的密码。如果将其留空,您将只能使用 SSH 密钥文件访问它。但是,如果您设置了密码,则可以防止拥有密钥文件的攻击者访问它。例如,您可以使用以下命令创建 SSH 密钥:
ssh-keygen
8. SSH 连接的 IP 限制
大多数情况下,防火墙使用自己的标准框架阻止访问,旨在保护服务器。但是,这并不总是足够的,您需要增加这种安全潜力。
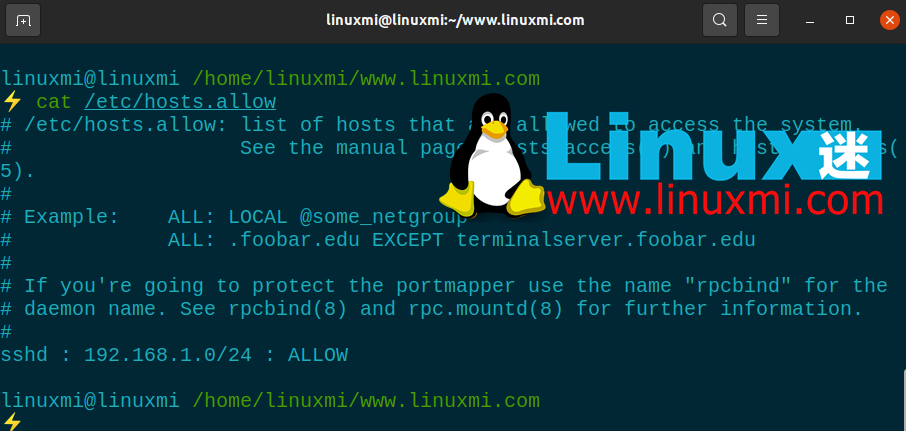
为此,请打开**/etc/hosts.allow**文件。通过对该文件进行的添加,您可以限制 SSH 权限,允许特定 IP 块,或输入单个 IP 并使用拒绝命令阻止所有剩余的 IP 地址。
下面您将看到一些示例设置。完成这些之后,像往常一样重新启动 SSH 服务以保存更改。
Linux 服务器安全的重要性
所有服务器管理员都应该考虑数据和数据安全问题。服务器安全是一个非常敏感的问题,因为攻击的主要焦点是 Web 服务器,它们几乎包含有关系统的所有信息。由于大多数服务器都在 Linux 基础架构上运行,因此熟悉 Linux 系统和服务器管理非常重要。
SSH 安全只是保护服务器的方法之一。可以通过停止、阻挡或减缓攻击来最大程度地减少您受到的伤害。除了提供 SSH 安全性之外,您还可以实施许多不同的方法来保护您的 Linux 服务器。
The above is the detailed content of 8 Ways to Secure SSH Server Connections on Linux. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
deepseek web version entrance deepseek official website entrance
Feb 19, 2025 pm 04:54 PM
DeepSeek is a powerful intelligent search and analysis tool that provides two access methods: web version and official website. The web version is convenient and efficient, and can be used without installation; the official website provides comprehensive product information, download resources and support services. Whether individuals or corporate users, they can easily obtain and analyze massive data through DeepSeek to improve work efficiency, assist decision-making and promote innovation.
 How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
How to install deepseek
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:48 PM
There are many ways to install DeepSeek, including: compile from source (for experienced developers) using precompiled packages (for Windows users) using Docker containers (for most convenient, no need to worry about compatibility) No matter which method you choose, Please read the official documents carefully and prepare them fully to avoid unnecessary trouble.
 Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi okx installation package is directly included
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Ouyi OKX, the world's leading digital asset exchange, has now launched an official installation package to provide a safe and convenient trading experience. The OKX installation package of Ouyi does not need to be accessed through a browser. It can directly install independent applications on the device, creating a stable and efficient trading platform for users. The installation process is simple and easy to understand. Users only need to download the latest version of the installation package and follow the prompts to complete the installation step by step.
 BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet official website installation (2025 beginner's guide)
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:42 PM
BITGet is a cryptocurrency exchange that provides a variety of trading services including spot trading, contract trading and derivatives. Founded in 2018, the exchange is headquartered in Singapore and is committed to providing users with a safe and reliable trading platform. BITGet offers a variety of trading pairs, including BTC/USDT, ETH/USDT and XRP/USDT. Additionally, the exchange has a reputation for security and liquidity and offers a variety of features such as premium order types, leveraged trading and 24/7 customer support.
 Get the gate.io installation package for free
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Get the gate.io installation package for free
Feb 21, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Gate.io is a popular cryptocurrency exchange that users can use by downloading its installation package and installing it on their devices. The steps to obtain the installation package are as follows: Visit the official website of Gate.io, click "Download", select the corresponding operating system (Windows, Mac or Linux), and download the installation package to your computer. It is recommended to temporarily disable antivirus software or firewall during installation to ensure smooth installation. After completion, the user needs to create a Gate.io account to start using it.
 Ouyi Exchange Download Official Portal
Feb 21, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Ouyi Exchange Download Official Portal
Feb 21, 2025 pm 07:51 PM
Ouyi, also known as OKX, is a world-leading cryptocurrency trading platform. The article provides a download portal for Ouyi's official installation package, which facilitates users to install Ouyi client on different devices. This installation package supports Windows, Mac, Android and iOS systems. Users can choose the corresponding version to download according to their device type. After the installation is completed, users can register or log in to the Ouyi account, start trading cryptocurrencies and enjoy other services provided by the platform.
 How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set the permissions of unixsocket after the system restarts. Every time the system restarts, we need to execute the following command to modify the permissions of unixsocket: sudo...
 Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Causes and solutions for errors when using PECL to install extensions in Docker environment When using Docker environment, we often encounter some headaches...