What are the commonly used shell scripts in Linux?

1、检测两台服务器指定目录下的文件一致性
#!/bin/bash
######################################
检测两台服务器指定目录下的文件一致性
#####################################
#通过对比两台服务器上文件的md5值,达到检测一致性的目的
dir=/data/web
b_ip=192.168.88.10
#将指定目录下的文件全部遍历出来并作为md5sum命令的参数,进而得到所有文件的md5值,并写入到指定文件中
find $dir -type f|xargs md5sum > /tmp/md5_a.txt
ssh $b_ip "find $dir -type f|xargs md5sum > /tmp/md5_b.txt"
scp $b_ip:/tmp/md5_b.txt /tmp
#将文件名作为遍历对象进行一一比对
for f in `awk '{print 2} /tmp/md5_a.txt'`do
#以a机器为标准,当b机器不存在遍历对象中的文件时直接输出不存在的结果
if grep -qw "$f" /tmp/md5_b.txt
then
md5_a=`grep -w "$f" /tmp/md5_a.txt|awk '{print 1}'`
md5_b=`grep -w "$f" /tmp/md5_b.txt|awk '{print 1}'`
#当文件存在时,如果md5值不一致则输出文件改变的结果
if [ $md5_a != $md5_b ]then
echo "$f changed."
fi
else
echo "$f deleted."
fi
done2、定时清空文件内容,定时记录文件大小
#!/bin/bash ################################################################# 每小时执行一次脚本(任务计划),当时间为0点或12点时,将目标目录下的所有文件内#容清空,但不删除文件,其他时间则只统计各个文件的大小,一个文件一行,输出到以时#间和日期命名的文件中,需要考虑目标目录下二级、三级等子目录的文件 ################################################################ logfile=/tmp/`date +%H-%F`.log n=`date +%H` if [ $n -eq 00 ] || [ $n -eq 12 ] then #通过for循环,以find命令作为遍历条件,将目标目录下的所有文件进行遍历并做相应操作 for i in `find /data/log/ -type f` do true > $i done else for i in `find /data/log/ -type f` do du -sh $i >> $logfile done fi
3、检测网卡流量,并按规定格式记录在日志中
#!/bin/bash
#######################################################
#检测网卡流量,并按规定格式记录在日志中#规定一分钟记录一次
#日志格式如下所示:
#2019-08-12 20:40
#ens33 input: 1234bps
#ens33 output: 1235bps
######################################################3
while :
do
#设置语言为英文,保障输出结果是英文,否则会出现bug
LANG=en
logfile=/tmp/`date +%d`.log
#将下面执行的命令结果输出重定向到logfile日志中
exec >> $logfile
date +"%F %H:%M"
#sar命令统计的流量单位为kb/s,日志格式为bps,因此要*1000*8
sar -n DEV 1 59|grep Average|grep ens33|awk '{print $2,"t","input:","t",$5*1000*8,"bps","n",$2,"t","output:","t",$6*1000*8,"bps"}'
echo "####################"
#因为执行sar命令需要59秒,因此不需要sleep
done4、计算文档每行出现的数字个数,并计算整个文档的数字总数
#!/bin/bash
#########################################################
#计算文档每行出现的数字个数,并计算整个文档的数字总数
########################################################
#使用awk只输出文档行数(截取第一段)
n=`wc -l a.txt|awk '{print $1}'`
sum=0
#文档中每一行可能存在空格,因此不能直接用文档内容进行遍历
for i in `seq 1 $n`do
#输出的行用变量表示时,需要用双引号
line=`sed -n "$i"p a.txt`#wc -L选项,统计最长行的长度
n_n=`echo $line|sed s'/[^0-9]//'g|wc -L`
echo $n_nsum=$[$sum+$n_n]
done
echo "sum:$sum"杀死所有脚本
#!/bin/bash
################################################################
#有一些脚本加入到了cron之中,存在脚本尚未运行完毕又有新任务需要执行的情况,
#导致系统负载升高,因此可通过编写脚本,筛选出影响负载的进程一次性全部杀死。
################################################################
ps aux|grep 指定进程名|grep -v grep|awk '{print $2}'|xargs kill -95、从 FTP 服务器下载文件
#!/bin/bash if [ $# -ne 1 ]; then echo "Usage: $0 filename" fi dir=$(dirname $1) file=$(basename $1) ftp -n -v << EOF # -n 自动登录 open 192.168.1.10# ftp服务器 user admin password binary # 设置ftp传输模式为二进制,避免MD5值不同或.tar.gz压缩包格式错误 cd $dir get "$file" EOF
6、连续输入5个100以内的数字,统计和、最小和最大
#!/bin/bash COUNT=1 SUM=0 MIN=0 MAX=100 while [ $COUNT -le 5 ]; do read -p "请输入1-10个整数:" INT if [[ ! $INT =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]; then echo "输入必须是整数!" exit 1 elif [[ $INT -gt 100 ]]; then echo "输入必须是100以内!" exit 1 fi SUM=$(($SUM+$INT)) [ $MIN -lt $INT ] && MIN=$INT [ $MAX -gt $INT ] && MAX=$INT let COUNT++ done echo "SUM: $SUM" echo "MIN: $MIN" echo "MAX: $MAX
用户猜数字
#!/bin/bash# 脚本生成一个 100 以内的随机数,提示用户猜数字,根据用户的输入,提示用户猜对了, # 猜小了或猜大了,直至用户猜对脚本结束。 # RANDOM 为系统自带的系统变量,值为 0‐32767的随机数 # 使用取余算法将随机数变为 1‐100 的随机数num=$[RANDOM%100+1]echo "$num" # 使用 read 提示用户猜数字 # 使用 if 判断用户猜数字的大小关系:‐eq(等于),‐ne(不等于),‐gt(大于),‐ge(大于等于), # ‐lt(小于),‐le(小于等于) while : do read -p "计算机生成了一个 1‐100 的随机数,你猜: " cai if [ $cai -eq $num ] then echo "恭喜,猜对了" exit elif [ $cai -gt $num ] then echo "Oops,猜大了" else echo "Oops,猜小了" fi done
7、监测 Nginx 访问日志 502 情况,并做相应动作
假设服务器环境为 lnmp,近期访问经常出现 502 现象,且 502 错误在重启 php-fpm 服务后消失,因此需要编写监控脚本,一旦出现 502,则自动重启 php-fpm 服务。
#场景: #1.访问日志文件的路径:/data/log/access.log #2.脚本死循环,每10秒检测一次,10秒的日志条数为300条,出现502的比例不低于10%(30条)则需要重启php-fpm服务 #3.重启命令为:/etc/init.d/php-fpm restart #!/bin/bash ########################################################### #监测Nginx访问日志502情况,并做相应动作 ########################################################### log=/data/log/access.log N=30 #设定阈值 while :do #查看访问日志的最新300条,并统计502的次数 err=`tail -n 300 $log |grep -c '502" '` if [ $err -ge $N ] then /etc/init.d/php-fpm restart 2> /dev/null #设定60s延迟防止脚本bug导致无限重启php-fpm服务 sleep 60 fi sleep 10 done
8、将结果分别赋值给变量
应用场景:希望将执行结果或者位置参数赋值给变量,以便后续使用。
方法1:
for i in $(echo "4 5 6"); do eval a$i=$idone echo $a4 $a5 $a6
方法2:将位置参数192.168.1.1{1,2}拆分为到每个变量
num=0
for i in $(eval echo $*);do #eval将{1,2}分解为1 2
let num+=1
eval node${num}="$i"
done
echo $node1 $node2 $node3
# bash a.sh 192.168.1.1{1,2}
192.168.1.11 192.168.1.12
方法3:arr=(4 5 6)
INDEX1=$(echo ${arr[0]})
INDEX2=$(echo ${arr[1]})
INDEX3=$(echo ${arr[2]})9、批量修改文件名
示例:
# touch article_{1..3}.html
# lsarticle_1.htmlarticle_2.htmlarticle_3.html
目的:把article改为bbs方法1:
for file in $(ls *html); do
mv $file bbs_${file#*_}
# mv $file $(echo $file |sed -r 's/.*(_.*)/bbs1/')
# mv $file $(echo $file |echo bbs_$(cut -d_ -f2)方法2:
for file in $(find . -maxdepth 1 -name "*html"); do
mv $file bbs_${file#*_}done 方法3:
# rename article bbs *.html 把一个文档前五行中包含字母的行删掉,同时删除6到10行包含的所有字母 1)准备测试文件,文件名为2.txt 第1行1234567不包含字母 第2行56789BBBBBB 第3行67890CCCCCCCC 第4行78asdfDDDDDDDDD 第5行123456EEEEEEEE 第6行1234567ASDF 第7行56789ASDF 第8行67890ASDF 第9行78asdfADSF 第10行123456AAAA 第11行67890ASDF 第12行78asdfADSF 第13行123456AAAA
2)脚本如下:
#!/bin/bash ############################################################### 把一个文档前五行中包含字母的行删掉,同时删除6到10行包含的所有字母 ############################################################## sed -n '1,5'p 2.txt |sed '/[a-zA-Z]/'d sed -n '6,10'p 2.txt |sed s'/[a-zA-Z]//'g sed -n '11,$'p 2.txt #最终结果只是在屏幕上打印结果,如果想直接更改文件,可将输出结果写入临时文件中,再替换2.txt或者使用-i选项
10、统计当前目录中以.html结尾的文件总大
方法1:
# find . -name "*.html" -exec du -k {} ; |awk '{sum+=$1}END{print sum}'
方法2:
```bash
for size in $(ls -l *.html |awk '{print $5}'); do
sum=$(($sum+$size))
done
echo $sum11、扫描主机端口状态
#!/bin/bash HOST=$1 PORT="22 25 80 8080" for PORT in $PORT; do if echo &>/dev/null > /dev/tcp/$HOST/$PORT; then echo "$PORT open" else echo "$PORT close" fi done 用 shell 打印示例语句中字母数小于6的单词 #示例语句: #Bash also interprets a number of multi-character options. #!/bin/bash ############################################################## #shell打印示例语句中字母数小于6的单词 ############################################################## for s in Bash also interprets a number of multi-character options. do n=`echo $s|wc -c` if [ $n -lt 6 ] then echo $s fi done
12、输入数字运行相应命令
#!/bin/bash ############################################################## #输入数字运行相应命令 ############################################################## echo "*cmd menu* 1-date 2-ls 3-who 4-pwd 0-exit " while : do #捕获用户键入值 read -p "please input number :" n n1=`echo $n|sed s'/[0-9]//'g` #空输入检测 if [ -z "$n" ] then continue fi #非数字输入检测 if [ -n "$n1" ] then exit 0 fi break done case $n in 1) date ;; 2) ls ;; 3) who ;; 4) pwd ;; 0) break ;; #输入数字非1-4的提示 *) echo "please input number is [1-4]" esac
13、Expect 实现 SSH 免交互执行命令
Expect是一个自动交互式应用程序的工具,如telnet,ftp,passwd等。
需先安装expect软件包。
方法1:EOF标准输出作为expect标准输入
#!/bin/bash
USER=root
PASS=123.com
IP=192.168.1.120
expect << EOFset timeout 30spawn ssh $USER@$IP expect {"(yes/no)" {send "yesr"; exp_continue}"password:" {send "$PASSr"}
}
expect "$USER@*"{send "$1r"}
expect "$USER@*"{send "exitr"}
expect eof
EOF方法2:
#!/bin/bash
USER=root
PASS=123.com
IP=192.168.1.120
expect -c "
spawn ssh $USER@$IP
expect {
"(yes/no)" {send "yesr"; exp_continue}
"password:" {send "$PASSr"; exp_continue}
"$USER@*" {send "df -hr exitr"; exp_continue}
}"方法3:将expect脚本独立出来
登录脚本:
# cat login.exp
#!/usr/bin/expect
set ip [lindex $argv 0]
set user [lindex $argv 1]
set passwd [lindex $argv 2]
set cmd [lindex $argv 3]
if { $argc != 4 } {
puts "Usage: expect login.exp ip user passwd"
exit 1
}
set timeout 30
spawn ssh $user@$ip
expect {
"(yes/no)" {send "yesr"; exp_continue}
"password:" {send "$passwdr"}
}
expect "$user@*"{send "$cmdr"}
expect "$user@*"{send "exitr"}
expect eof执行命令脚本:写个循环可以批量操作多台服务器
#!/bin/bash
HOST_INFO=user_info.txt
for ip in $(awk '{print $1}' $HOST_INFO)
do
user=$(awk -v I="$ip" 'I==$1{print $2}' $HOST_INFO)
pass=$(awk -v I="$ip" 'I==$1{print $3}' $HOST_INFO)
expect login.exp $ip $user $pass $1
done
Linux主机SSH连接信息:
# cat user_info.txt
192.168.1.120 root 123456
创建10个用户,并分别设置密码,密码要求10位且包含大小写字母以及数字,最后需要把每个用户的密码存在指定文件中
```bash
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
#创建10个用户,并分别设置密码,密码要求10位且包含大小写字母以及数字
#最后需要把每个用户的密码存在指定文件中#前提条件:安装mkpasswd命令
##############################################################
#生成10个用户的序列(00-09)
for u in `seq -w 0 09`do
#创建用户
useradd user_$u
#生成密码
p=`mkpasswd -s 0 -l 10`
#从标准输入中读取密码进行修改(不安全)
echo $p|passwd --stdin user_$u
#常规修改密码
echo -e "$pn$p"|passwd user_$u
#将创建的用户及对应的密码记录到日志文件中
echo "user_$u $p" >> /tmp/userpassworddone14、监控 httpd 的进程数,根据监控情况做相应处理
#!/bin/bash
###############################################################################################################################
#需求:
#1.每隔10s监控httpd的进程数,若进程数大于等于500,则自动重启Apache服务,并检测服务是否重启成功
#2.若未成功则需要再次启动,若重启5次依旧没有成功,则向管理员发送告警邮件,并退出检测
#3.如果启动成功,则等待1分钟后再次检测httpd进程数,若进程数正常,则恢复正常检测(10s一次),否则放弃重启并向管理员发送告警邮件,并退出检测
###############################################################################################################################
#计数器函数
check_service()
{
j=0
for i in `seq 1 5`
do
#重启Apache的命令
/usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl restart 2> /var/log/httpderr.log
#判断服务是否重启成功
if [ $? -eq 0 ] then
break
else
j=$[$j+1] fi
#判断服务是否已尝试重启5次
if [ $j -eq 5 ] then
mail.py exit
fi
done }while :do
n=`pgrep -l httpd|wc -l`
#判断httpd服务进程数是否超过500
if [ $n -gt 500 ] then
/usr/local/apache2/bin/apachectl restart
if [ $? -ne 0 ]
then
check_service
else
sleep 60
n2=`pgrep -l httpd|wc -l`
#判断重启后是否依旧超过500
if [ $n2 -gt 500 ]
then
mail.py exit
fi
fi
fi
#每隔10s检测一次
sleep 10done15、批量修改服务器用户密码
Linux主机SSH连接信息:旧密码
# cat old_pass.txt
192.168.18.217root123456 22
192.168.18.218root123456 22
内容格式:IP User Password Port
SSH远程修改密码脚本:新密码随机生成
https://www.linuxprobe.com/books
#!/bin/bash
OLD_INFO=old_pass.txt
NEW_INFO=new_pass.txt
for IP in $(awk '/^[^#]/{print $1}' $OLD_INFO); do
USER=$(awk -v I=$IP 'I==$1{print $2}' $OLD_INFO)
PASS=$(awk -v I=$IP 'I==$1{print $3}' $OLD_INFO)
PORT=$(awk -v I=$IP 'I==$1{print $4}' $OLD_INFO)
NEW_PASS=$(mkpasswd -l 8)# 随机密码
echo "$IP $USER $NEW_PASS $PORT" >> $NEW_INFO
expect -c "
spawn ssh -p$PORT $USER@$IP
set timeout 2
expect {
"(yes/no)" {send "yesr";exp_continue}
"password:" {send "$PASSr";exp_continue}
"$USER@*" {send "echo '$NEW_PASS' |passwd --stdin $USERr exitr";exp_continue}
}"
done
生成新密码文件:
# cat new_pass.txt
192.168.18.217rootn8wX3mU%22
192.168.18.218rootc87;ZnnL2216、iptables 自动屏蔽访问网站频繁的IP
场景:恶意访问,安全防范
1)屏蔽每分钟访问超过200的IP
方法1:根据访问日志(Nginx为例)
#!/bin/bash
DATE=$(date +%d/%b/%Y:%H:%M)
ABNORMAL_IP=$(tail -n5000 access.log |grep $DATE |awk '{a[$1]++}END{for(i in a)if(a[i]>100)print i}')
#先tail防止文件过大,读取慢,数字可调整每分钟最大的访问量。awk不能直接过滤日志,因为包含特殊字符。
for IP in $ABNORMAL_IP; do
if [ $(iptables -vnL |grep -c "$IP") -eq 0 ]; then
iptables -I INPUT -s $IP -j DROPfidone方法2:通过TCP建立的连接
#!/bin/bash
ABNORMAL_IP=$(netstat -an |awk '$4~/:80$/ && $6~/ESTABLISHED/{gsub(/:[0-9]+/,"",$5);{a[$5]++}}END{for(i in a)if(a[i]>100)print i}')
#gsub是将第五列(客户端IP)的冒号和端口去掉
for IP in $ABNORMAL_IP; do
if [ $(iptables -vnL |grep -c "$IP") -eq 0 ]; then
iptables -I INPUT -s $IP -j DROP
fi
done2)屏蔽每分钟SSH尝试登录超过10次的IP
方法1:通过lastb获取登录状态:
#!/bin/bash
DATE=$(date +"%a %b %e %H:%M") #星期月天时分%e单数字时显示7,而%d显示07
ABNORMAL_IP=$(lastb |grep "$DATE" |awk '{a[$3]++}END{for(i in a)if(a[i]>10)print i}')for IP in $ABNORMAL_IP; do
if [ $(iptables -vnL |grep -c "$IP") -eq 0 ]; then
iptables -I INPUT -s $IP -j DROPfidone方法2:通过日志获取登录状态
#!/bin/bash
DATE=$(date +"%b %d %H")
ABNORMAL_IP="$(tail -n10000 /var/log/auth.log |grep "$DATE" |awk '/Failed/{a[$(NF-3)]++}END{for(i in a)if(a[i]>5)print i}')"
for IP in $ABNORMAL_IP; do
if [ $(iptables -vnL |grep -c "$IP") -eq 0 ]; then
iptables -A INPUT -s $IP -j DROP
echo "$(date +"%F %T") - iptables -A INPUT -s $IP -j DROP" >>~/ssh-login-limit.log
fi
done17、根据web访问日志,封禁请求量异常的IP,如IP在半小时后恢复正常,则解除封禁
#!/bin/bash
####################################################################################
#根据web访问日志,封禁请求量异常的IP,如IP在半小时后恢复正常,则解除封禁
####################################################################################
logfile=/data/log/access.log
#显示一分钟前的小时和分钟
d1=`date -d "-1 minute" +%H%M`
d2=`date +%M`
ipt=/sbin/iptables
ips=/tmp/ips.txt
block()
{
#将一分钟前的日志全部过滤出来并提取IP以及统计访问次数
grep '$d1:' $logfile|awk '{print $1}'|sort -n|uniq -c|sort -n > $ips
#利用for循环将次数超过100的IP依次遍历出来并予以封禁
for i in `awk '$1>100 {print $2}' $ips`
do
$ipt -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -s $i -j REJECT
echo "`date +%F-%T` $i" >> /tmp/badip.log
done
}
unblock()
{
#将封禁后所产生的pkts数量小于10的IP依次遍历予以解封
for a in `$ipt -nvL INPUT --line-numbers |grep '0.0.0.0/0'|awk '$2<10 {print $1}'|sort -nr`
do
$ipt -D INPUT $a
done
$ipt -Z
}
#当时间在00分以及30分时执行解封函数
if [ $d2 -eq "00" ] || [ $d2 -eq "30" ]
then
#要先解再封,因为刚刚封禁时产生的pkts数量很少
unblock
block
else
block
fi18、判断用户输入的是否为IP地址
方法1:
#!/bin/bash
function check_ip(){
IP=$1
VALID_CHECK=$(echo $IP|awk -F. '$1< =255&&$2<=255&&$3<=255&&$4<=255{print "yes"}')
if echo $IP|grep -E "^[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}$">/dev/null; then
if [ $VALID_CHECK == "yes" ]; then
echo "$IP available."
else
echo "$IP not available!"
fi
else
echo "Format error!"
fi
}
check_ip 192.168.1.1
check_ip 256.1.1.1方法2:
#!/bin/bash
function check_ip(){
IP=$1
if [[ $IP =~ ^[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}$ ]]; then
FIELD1=$(echo $IP|cut -d. -f1)
FIELD2=$(echo $IP|cut -d. -f2)
FIELD3=$(echo $IP|cut -d. -f3)
FIELD4=$(echo $IP|cut -d. -f4)
if [ $FIELD1 -le 255 -a $FIELD2 -le 255 -a $FIELD3 -le 255 -a $FIELD4 -le 255 ]; then
echo "$IP available."
else
echo "$IP not available!"
fi
else
echo "Format error!"
fi
}
check_ip 192.168.1.1
check_ip 256.1.1.1增加版:
加个死循环,如果IP可用就退出,不可用提示继续输入,并使用awk判断。
#!/bin/bash
function check_ip(){
local IP=$1
VALID_CHECK=$(echo $IP|awk -F. '$1< =255&&$2<=255&&$3<=255&&$4<=255{print "yes"}')
if echo $IP|grep -E "^[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}.[0-9]{1,3}$" >/dev/null; then
if [ $VALID_CHECK == "yes" ]; then
return 0
else
echo "$IP not available!"
return 1
fi
else
echo "Format error! Please input again."
return 1
fi
}
while true; do
read -p "Please enter IP: " IP
check_ip $IP
[ $? -eq 0 ] && break || continue
doneThe above is the detailed content of What are the commonly used shell scripts in Linux?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Specific steps for expanding the C drive using the partition tool diskgenius
May 08, 2024 pm 08:04 PM
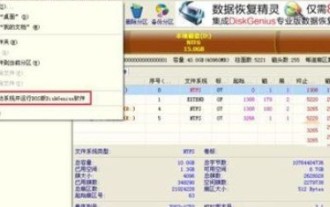
Specific steps for expanding the C drive using the partition tool diskgenius
May 08, 2024 pm 08:04 PM
First, download and install the [DiskGenius] tool on your computer, then open the tool, then click [File Menu] at the top, and then click [Restart the system and run the DiskGenius software], as shown in the figure. Then click [OK] in the pop-up prompt box, as shown in the figure. After that, the computer will restart and then enter the Diskgen hard disk partition interface. At this time, if we want to expand the C drive, we only need to right-click the D drive next to the logical partition and click "Adjust Partition Size" in the pop-up menu, as shown in the figure shown. Then you need to adjust the size of the D drive partition. For example, the current capacity of the D drive is 14.99GB, as shown in the figure below. At this time, we can adjust the installment of the D drive. For example, if we want to allocate 1.03GB to the C drive, we only need to allocate 1.03GB to the C drive.
 How to skip the network installation system in win11 24h2? The latest version of win11 24h2 skips the online installation tutorial
May 03, 2024 pm 09:13 PM
How to skip the network installation system in win11 24h2? The latest version of win11 24h2 skips the online installation tutorial
May 03, 2024 pm 09:13 PM
The 24h2 version is the latest operating system released by Microsoft. I believe many users have seen some download packages on the Internet. So how can win1124h2 skip the Internet installation system? Let this site carefully introduce the latest version of win1124h2 to users. Skip the Internet installation tutorial. The latest version of win1124h2 skips the online installation tutorial. Method 1: Skip by modifying the registry. 1. Press the Shift+F10 keys to bring up the cmd command prompt window and enter the following command: regedit and press Enter to quickly open the registry editor. If users feel that the 24h2 version is not used to the operation, they can click on the 23h2 version below to reinstall it. Win1123H22263
 Tutorial on assembling a computer and installing a system? How to install win11 system when assembling a computer?
Apr 27, 2024 pm 03:38 PM
Tutorial on assembling a computer and installing a system? How to install win11 system when assembling a computer?
Apr 27, 2024 pm 03:38 PM
Tutorial on assembling a computer and installing a system? Nowadays, the system installation for assembling computers is very simple and convenient, and only requires a CD. First enter the bios settings, set the computer to boot first with the CD-ROM drive, then restart the computer and load the system CD into the CD-ROM drive. The CD will automatically enter the installation state. At this time, you only need to manually repartition the partitions, and the rest will be completed automatically. How to install win11 system when assembling a computer? 1. First, we need to download a win11 image file from this site before installing it. 2. The win11 image file has undergone a large number of professional tests to ensure stable installation and smooth operation. 3. After the download is completed, load the folder in the download path and run the "windowssetup" process in it.
 The computer fan suddenly makes a loud sound and then the screen goes black
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:10 PM
The computer fan suddenly makes a loud sound and then the screen goes black
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:10 PM
Why does the laptop have a black screen when it starts up and the fan keeps beeping? 1. When the computer starts up and the screen goes black but the fan spins, it is usually caused by poor contact between the monitor cable and memory and other hardware. You can disassemble the computer to check each component, remove dust and reinstall it. 2. Power supply problem: The battery is exhausted or the power adapter fails, which may cause the computer to fail to boot. Try replacing the power adapter or rechargeable battery to see if the computer can boot normally. Hardware failure: If there is a problem with the computer hardware device, it may not start properly. 3. The fault may be caused by a problem with the hard disk, or the computer may not have good heat dissipation. 4. The fan keeps beeping after the computer is turned on, but the monitor screen is black and unresponsive. Determine what the problem is based on the sound of the buzzer when the computer is turned on. The long beep is that the graphics card is not connected properly. first check
 How to set up the Chinese version of navicat
Apr 06, 2024 am 08:15 AM
How to set up the Chinese version of navicat
Apr 06, 2024 am 08:15 AM
Yes, just follow these steps: Download and install the Chinese version of Navicat. Run Navicat and select Tools > Preferences. In the Preferences dialog box, select the Appearance tab. In the Language drop-down list, select Simplified Chinese or Traditional Chinese. Click OK to save settings and restart Navicat.
 What is the appropriate temperature for playing Apex computer?
May 06, 2024 am 09:31 AM
What is the appropriate temperature for playing Apex computer?
May 06, 2024 am 09:31 AM
What is the appropriate temperature for playing Apex computer? 80 degrees is suitable. When running large-scale games or playing high-definition videos, the temperature can reach about 80°C. Generally, it is considered normal to not exceed 90°C under high load. Graphics cards are generally the hardware that generates the most heat among computer hardware. Generally, it is normal for the temperature of a graphics card to be around 30℃-80℃. Due to external temperature, it is normal for most graphics card temperatures to be between 50℃-85℃ in summer. range, if you are running large-scale 3D games or playing high-definition videos for a long time, the highest temperature may reach about 95°C. This temperature range will affect the life of the computer hardware. No matter how high the temperature is, you must consider strengthening heat dissipation and cleaning dust. How to play with the apex handle and the computer ? Method/step-by-step reading: 1. Use wired or wireless
 Computer settings to automatically restart
Apr 26, 2024 pm 06:10 PM
Computer settings to automatically restart
Apr 26, 2024 pm 06:10 PM
How to set the computer to automatically restart 1. Find the computer on your computer desktop and right-click the mouse. In the pop-up window, we find properties and click. After entering the system properties, we select. 2. You can set it in the task scheduler to set up automatic startup: right-click this computer, select Manage, and enter the page. Expand System Tools, click Task Scheduler, and click Create Basic Task on the right. 3. How to set the computer to automatically restart when a call comes in. First, restart your computer and click Restart with the left button of the mouse. Because the XP system was used for testing, the startup time is very short. Press and hold DEL during startup to enter the BIOS interface. The BIOS interface is shown in the figure below. This is the main BIOS interface. How to set the computer to automatically start after a power outage. First, restart
 Why does Huawei mobile phone frequently restart automatically?
Apr 20, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
Why does Huawei mobile phone frequently restart automatically?
Apr 20, 2024 pm 09:22 PM
There are three reasons why Huawei mobile phones frequently automatically restart, including abnormal mobile phone system software, short circuit of the mobile phone's power button, and mobile phone motherboard problems. In order to solve these problems, we can try to restart the phone or restore factory settings. If these methods cannot solve the problem, we need to send the phone to a professional mobile phone repair shop for repair. The following are more detailed explanations and suggestions: 1. The mobile phone system software is abnormal. Some incompatible software is installed on the phone or the phone memory is too full, causing the phone to automatically turn on or off or restart. We need to delete some files in the phone or directly restore the phone to factory settings to solve the problem. If the phone can no longer enter the system, we can try to turn it off first, then press and hold the volume up button + power button, and wait for the phone to enter recovery.




