 Computer Tutorials
Computer Tutorials
 Computer Knowledge
Computer Knowledge
 What is the difference between ext3 and ext4 in Linux system?
What is the difference between ext3 and ext4 in Linux system?
What is the difference between ext3 and ext4 in Linux system?

A file system is a method of organizing files stored on storage devices such as disks. The Linux system can support a variety of currently popular file systems, including: EXT2, EXT3, EXT4, FAT, FAT32, etc. So what are the differences between ext3 and ext4 in Linux systems? The following is a detailed introduction.
What is the difference between ext3 and ext4 in Linux system?
1. Larger file system and larger files
ext3: 16TB file system and maximum 2TB file;
ext4: 1EB file system and maximum 16TB file.
2. Unlimited number of subdirectories
ext3:32000 subdirectory;
ext4: unlimited number of subdirectories.
3. Extents
ext3: uses indirect block mapping, which is extremely inefficient when operating large files. For example, for a 100MB file, a mapping table of 25,600 data blocks needs to be established in ext3.
ext4: The concept of Extents is introduced. Each Extent is a set of continuous data blocks. The above file is represented as the file data is stored in the next 25,600 data blocks, which improves a lot of efficiency.
4. Multi-block allocation
The data block allocator of ext3 can only allocate one 4KB block at a time. To write a 100MB file, the data block allocator must be called 25,600 times, while the multiblock allocator of ext4 multiblock
allocator supports allocating multiple blocks in one call. data block.
5. Delayed allocation
The data block allocation strategy of ext3 is to allocate as soon as possible, while ext4 delays allocation as much as possible until the file is written in the cache before starting to allocate data blocks and write them to the disk, so that the data block allocation of the entire file can be optimized. Paired with the first two features, performance can be significantly improved.
6. Inode related features
ext3:128byte;
ext4:256byte.
The above is the detailed content of What is the difference between ext3 and ext4 in Linux system?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
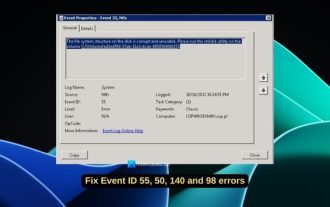 Fix event ID 55, 50, 98, 140 disk error in event viewer
Mar 19, 2024 am 09:43 AM
Fix event ID 55, 50, 98, 140 disk error in event viewer
Mar 19, 2024 am 09:43 AM
If you find event ID 55, 50, 140 or 98 in the Event Viewer of Windows 11/10, or encounter an error that the disk file system structure is damaged and cannot be used, please follow the guide below to resolve the issue. What does Event 55, File system structure on disk corrupted and unusable mean? At session 55, the file system structure on the Ntfs disk is corrupted and unusable. Please run the chkMSK utility on the volume. When NTFS is unable to write data to the transaction log, an error with event ID 55 is triggered, which will cause NTFS to fail to complete the operation unable to write the transaction data. This error usually occurs when the file system is corrupted, possibly due to the presence of bad sectors on the disk or the file system's inadequacy of the disk subsystem.
 How to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems
Jun 29, 2023 pm 04:05 PM
How to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems
Jun 29, 2023 pm 04:05 PM
How to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems Introduction: With the continuous development of computer technology, the stability and reliability of the operating system are becoming more and more important. However, although Linux systems are widely regarded as a stable and reliable operating system, there is still the possibility of file system corruption. A file system crash may lead to serious consequences such as data loss and system abnormalities. Therefore, this article will introduce how to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems to help users better protect their data and systems.
 An in-depth discussion of the physical storage structure of the Linux ext2 file system
Mar 14, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
An in-depth discussion of the physical storage structure of the Linux ext2 file system
Mar 14, 2024 pm 09:06 PM
The Linuxext2 file system is a file system used on most Linux operating systems. It uses an efficient disk storage structure to manage the storage of files and directories. Before we delve into the physical storage structure of the Linuxext2 file system, we first need to understand some basic concepts. In the ext2 file system, data is stored in data blocks (blocks), which are the smallest allocable units in the file system. Each data block has a fixed size, usually 1KB, 2KB or 4
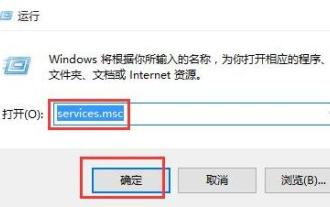 How to handle file system error 2147416359 in WIN10
Mar 27, 2024 am 11:31 AM
How to handle file system error 2147416359 in WIN10
Mar 27, 2024 am 11:31 AM
1. Press win+r to enter the run window, enter [services.msc] and press Enter. 2. In the service window, find [windows license manager service] and double-click to open it. 3. In the interface, change the startup type to [Automatic], and then click [Apply → OK]. 4. Complete the above settings and restart the computer.
 fstab(File System Table)
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
fstab(File System Table)
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
fstab (FileSystemTable) is a configuration file in the Linux system, used to define the rules for mounting file systems when the system starts. The fstab file is located in the /etc directory and can be created manually or modified by an editor. Each line specifies a file system to be mounted. Each line has six fields, and their meanings are as follows: The file system device file or UUID can be used to specify the device of the file system to be mounted. The UUID is a unique identifier. The UUID of the device can be obtained through the blkid command. 2. Mount point: Specify the directory to which the file system is to be mounted, which can be an absolute path (such as /mnt/data) or a relative path (such as ../data). 3. File system class
 The Difference: NTFS vs. FAT32
Feb 18, 2024 pm 10:18 PM
The Difference: NTFS vs. FAT32
Feb 18, 2024 pm 10:18 PM
NTFS and FAT32 are two common file systems used to organize and manage data on your computer's hard drive. While they all share some common functions and features, there are also some important differences in many ways. This article will explore several key differences between NTFS and FAT32. Functions and performance: NTFS (New Technology File System) is a newer file system in Microsoft Windows operating system. It has many advanced functions, such as data compression, file encryption,
 In-depth understanding of Linux's standard file system (Ext2/Ext3/Ext4)
Dec 31, 2023 pm 10:18 PM
In-depth understanding of Linux's standard file system (Ext2/Ext3/Ext4)
Dec 31, 2023 pm 10:18 PM
The full name of Ext is Linux extended file system, extfs, which is the Linux extended file system. Ext2 represents the second generation file extension system, Ext3/Ext4 and so on. They are all upgraded versions of Ext2, but they add the log function and are backward compatible with each other. So Ext2 is called an indexed file system, and Ext3/Ext4 is called a journaled file system. Note: Linux supports many file systems, including Network File System (NFS) and Windows’ Fat file system. View the file systems supported by Linux: ls-l/lib/modules/$(uname-r)/kernel/fs view
 How to deal with file system file locks and inter-process file sharing issues for concurrent files in Go language?
Oct 09, 2023 pm 05:53 PM
How to deal with file system file locks and inter-process file sharing issues for concurrent files in Go language?
Oct 09, 2023 pm 05:53 PM
Introduction to file system file locks and inter-process file sharing issues in handling concurrent files in the Go language: In the Go language, we often need to deal with concurrent access to files, including file system file locks and inter-process file sharing. This article will introduce how to use Go language to deal with these problems and provide specific code examples. 1. File system file lock When multiple concurrent programs access the same file at the same time, in order to avoid race conditions and data inconsistencies, we can use file system file locks for synchronization. Go language provides s





