Linux SIGPIPE signal
Among the TCP communication parties, for the convenience of description, the communication parties are replaced by A and B below.
According to the TCP protocol, if B continues to send data after A closes the connection, B will receive A's RST response. If B continues to send data, the system will send a SIGPIPE signal to inform that the connection has been disconnected and stop sending.
The system's default processing behavior for the SIGPIPE signal is to let process B exit.
The default processing behavior of the operating system for the SIGPIPE signal is very unfriendly, let us analyze it.
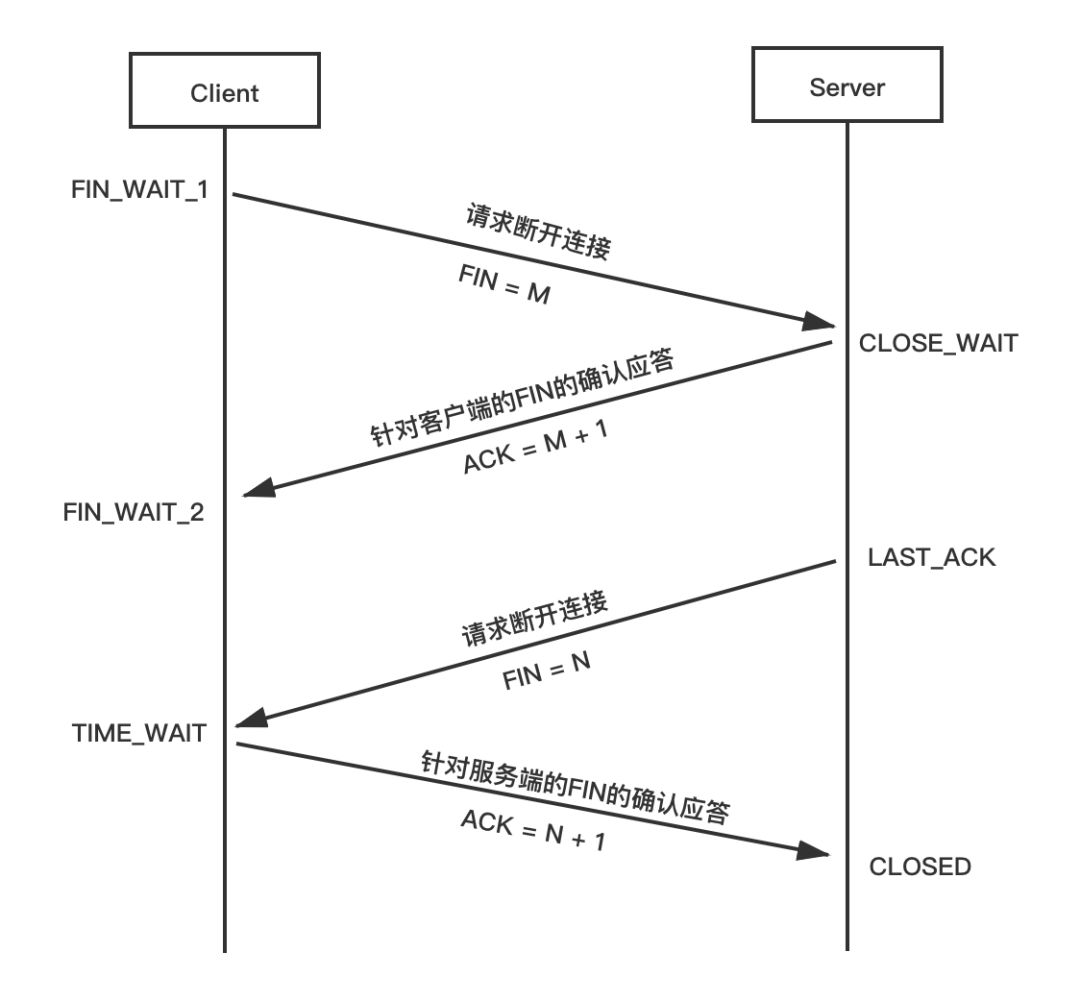
TCP communication is a full-duplex channel, which is equivalent to two simplex channels, and each end of the connection is responsible for one.
When the peer "closes", although the intention is to close the entire two channels, the local end only receives the FIN packet.
According to the provisions of the TCP protocol, when one end closes the one-way channel it is responsible for, it can still receive data but no longer send data.
In other words, due to the limitations of the TCP protocol, the communicating party cannot know whether the peer's socket has called close or shutdown.
int shutdown(int socket, int how);
The parameter "how" of the shutdown function can be set to close SHUT_RD, SHUT_WR or SHUT_RDWR, which is used to indicate closing the receiving and sending individual channels or closing the sending and receiving channels at the same time.
Call the read/recv method on a socket that has received a FIN packet. If the receiving buffer is empty, 0 is returned, which is often said to indicate that the connection is closed. However, when the write/send method is called for the first time, if there is no problem with the sending buffer, correct writing will be returned (that is, the return value of the write/send function is greater than 0), but the message sent will cause the peer to respond with an RST message. Because the last time the program called write/send, it was normal. When trying to call the write/send function again, the SIGPIPE signal was generated, causing the process to exit.
This default behavior is for us to develop programs, especially for back-end services, which need to serve many clients at the same time. The entire process cannot exit and cannot continue to serve other clients because there is a problem with the connection to a certain client. .
In order to avoid this phenomenon, you can capture the SIGPIPE signal and process it or ignore the signal. The code for ignoring the signal is as follows:
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
After this setting, when the write/send method is called for the second time, -1 will be returned, and the errno error code will be set to SIGPIPE, so the program will know that the peer has been closed.
The above is the detailed content of Linux SIGPIPE signal. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? How to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in windows 10
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AM
How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? How to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in windows 10
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:07 AM
How to reset tcp/ip protocol in win10? In fact, the method is very simple. Users can directly enter the command prompt, and then press the ctrl shift enter key combination to perform the operation, or directly execute the reset command to set it up. Let this site do the following. Let us carefully introduce to users how to reset the TCP/IP protocol stack in Windows 10. Method 1 to reset the tcp/ip protocol stack in Windows 10. Administrator permissions 1. We use the shortcut key win R to directly open the run window, then enter cmd and hold down the ctrl shift enter key combination. 2. Or we can directly search for command prompt in the start menu and right-click
 How to use TCP to implement conversation between client and server in python
May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
How to use TCP to implement conversation between client and server in python
May 17, 2023 pm 03:40 PM
TCP client A client sample code that uses the TCP protocol to achieve continuous dialogue: importsocket#Client configuration HOST='localhost'PORT=12345#Create a TCP socket and connect to the server client_socket=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket .SOCK_STREAM)client_socket.connect((HOST,PORT))whileTrue:#Get user input message=input("Please enter the message to be sent:&
 See you soon! TCP waves twice, have you seen it? What about the four handshakes?
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:18 PM
See you soon! TCP waves twice, have you seen it? What about the four handshakes?
Jul 24, 2023 pm 05:18 PM
The "connection-oriented" mentioned here means that you need to establish a connection, use the connection, and release the connection. Establishing a connection refers to the well-known TCP three-way handshake. When using a connection, data is transmitted in the form of one send and one confirmation. There is also the release of the connection, which is our common TCP four wave waves.
 Using Netty4 for TCP communication in Java API development
Jun 17, 2023 pm 11:18 PM
Using Netty4 for TCP communication in Java API development
Jun 17, 2023 pm 11:18 PM
TCP is a type of computer network communication protocol and a connection-oriented transmission protocol. In Java application development, TCP communication is widely used in various scenarios, such as data transmission between client and server, real-time transmission of audio and video, etc. Netty4 is a high-performance, highly scalable, and high-performance network programming framework that can optimize the data exchange process between the server and the client to make it more efficient and reliable. The specific implementation steps of using Netty4 for TCP communication are as follows: Introduction
 How to send multiple files using a single TCP connection in Java?
Apr 27, 2023 am 08:49 AM
How to send multiple files using a single TCP connection in Java?
Apr 27, 2023 am 08:49 AM
Why is there this blog about using one TCP connection to send multiple files? I have been reading some related things recently. There is no problem in simply using Socket for programming, but this only establishes some basic concepts. Still nothing can be done about the real problem. When I need to transfer files, I find that I seem to have just sent the data (binary data), but some information about the file is lost (the file extension). And each time I can only use one Socket to send one file, there is no way to send files continuously (because I rely on closing the stream to complete sending files, which means that I actually don’t know the length of the file, so I can only send files as one Socket connection represents a file).
 The unit of channel transmission rate in data communication is bps. What does it represent?
Jan 18, 2021 pm 02:58 PM
The unit of channel transmission rate in data communication is bps. What does it represent?
Jan 18, 2021 pm 02:58 PM
The unit of channel transmission rate in data communication is bps, which means "bits/second" or "bits/second". That is, the data transmission rate is numerically equal to the number of binary bits that constitute the data code transmitted per second, also called "bit rate". ". The bit rate represents the number of bits transmitted per unit time and is used to measure the transmission speed of digital information; based on the number of bits occupied by each frame of image storage and the transmission bit rate, the speed of digital image information transmission can be calculated.
 Linux SIGPIPE signal
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
Linux SIGPIPE signal
Feb 19, 2024 pm 04:00 PM
Among the TCP communication parties, for the convenience of description, the communication parties are replaced by A and B in the following. According to the TCP protocol, if B continues to send data after A closes the connection, B will receive A's RST response. If B continues to send data, the system will send a SIGPIPE signal to inform that the connection has been disconnected and stop sending. The system's default processing behavior for the SIGPIPE signal is to let process B exit. The default processing behavior of the operating system for the SIGPIPE signal is very unfriendly. Let us analyze it. TCP communication is a full-duplex channel, which is equivalent to two simplex channels, and each end of the connection is responsible for one. When the opposite end "closes", although the intention is to close the entire two channels, the local end only receives the FIN packet. According to the provisions of the TCP protocol, when a
 High-concurrency TCP long connection processing skills for swoole development function
Aug 25, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
High-concurrency TCP long connection processing skills for swoole development function
Aug 25, 2023 pm 10:01 PM
[Title] Highly concurrent TCP long connection processing techniques for Swoole development functions [Introduction] With the rapid development of the Internet, applications have increasingly higher demands for concurrent processing. As a high-performance network communication engine based on PHP, Swoole provides powerful asynchronous, multi-process, and coroutine capabilities, which greatly improves the concurrent processing capabilities of applications. This article will introduce how to use the Swoole development function to handle high-concurrency TCP long connection processing techniques, and provide detailed explanations with code examples. 【Text】1. Swo




