 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Reaching the pinnacle of persistence layer development: mastering the knowledge points of the Hibernate framework
Reaching the pinnacle of persistence layer development: mastering the knowledge points of the Hibernate framework
Reaching the pinnacle of persistence layer development: mastering the knowledge points of the Hibernate framework

-
php editor Apple brings you knowledge about the Hibernate framework. Mastering this technology is crucial for persistence layer development. Hibernate is an excellent ORM framework that can simplify database operations and improve development efficiency. By having an in-depth understanding of Hibernate's core concepts and common functions, developers can better utilize its powerful features to implement persistent data operations. In the process of learning and mastering the knowledge points of the Hibernate framework, you will be able to better cope with the challenges in actual development, making you more proficient in controlling the persistence layer development technology.
One of the core ideas of Hibernate is entity mapping, which maps Java objects to database tables, thus achieving object-oriented persistence. It provides a variety of mapping methods, including annotation mapping, XML mapping, etc., which can meet the needs of different developers. For example, using annotation mapping, developers only need to add @Entity annotations on Java classes to map them to
databasetables, and field mapping is implemented through @Column annotations.
@Entity public class User { @Id @GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY) private Long id; @Column(name = "username") private String username; @Column(name = "passWord") private String password; }Copy after login - Query Language
Hibernate provides query languages called HQL (Hibernate Query Language) and QBE (Query By Example) for querying the database. HQL is an object-oriented query language whose syntax is similar to
sql, but is more concise and easy to understand, avoiding the need to write lengthy SQL statements.
// 使用 HQL 查询所有用户 List<User> users = session.createQuery("from User").list(); // 使用 QBE 查询用户名为 "admin" 的用户 User user = session.createNamedQuery("findUserByUsername") .setParameter("username", "admin") .getSingleResult();Copy after login - Transaction Management
Transactionis the logical unit of database operations. Hibernate provides transaction management functions to ensure the atomicity and consistency of database operations. Hibernate's transaction management is based on Java transactions api, which declares transaction boundaries through @Transactional annotations, and Hibernate framework automatically handles transaction submission and rollback.
@Transactional public void saveUser(User user) { session.save(user); }Copy after login - Persistence and Transient
Hibernate divides objects into two states: persistent and transient. Persistent objects refer to objects that have been saved to the database, while transient objects refer to objects that have not yet been saved to the database. Hibernate automatically tracks the persistent and transient state of objects and performs necessary database operations as needed.
- Cascade operation
Cascading operations allow developers to automatically perform corresponding operations on associated child objects when operating on the parent object, thus simplifying the developer's work. Hibernate provides a variety of cascade operation types, including cascade save, cascade update, cascade delete, etc.
@OneToMany(cascade = CascadeType.ALL) private List<Order> orders;
Copy after login - Lazy loading
Lazy loading is a
performance optimizationtechnique that defers the loading of associated objects or collections until they are actually needed. This helps reduce the number of database queries, thereby improving application performance.
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.LAZY) private Company company;
Copy after login - Optimistic locking and pessimistic locking
Hibernate provides two
concurrencycontrol mechanisms, optimistic locking and pessimistic locking, to prevent data inconsistency caused by concurrent operations. Optimistic locking achieves concurrency control by checking the version number of data when updating data, while pessimistic locking achieves concurrency control by locking data when updating data.
@Version private Long version;
Copy after login - Second level cache
Hibernate provides a secondary
cachingfunction, which can cache frequently accessed data in memory to reduce the number of accesses to the database and thereby improve application performance. Hibernate provides multiple second-level cache implementations, including ehcache, infinispan, etc.
<property name="hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache">true</property> <property name="hibernate.cache.region.factory_class">org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory</property>
Copy after login - Conclusion
Hibernate is the leader in Java persistence layer development framework. Its powerful functions and good performance make it the first choice of many developers. This article provides an in-depth and simple explanation of the knowledge points of the Hibernate framework, helping readers master the essence of persistence layer development and easily cope with various challenges in
projectdevelopment.
The above is the detailed content of Reaching the pinnacle of persistence layer development: mastering the knowledge points of the Hibernate framework. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 What is the architecture and working principle of Spring Data JPA?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
What is the architecture and working principle of Spring Data JPA?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 02:48 PM
SpringDataJPA is based on the JPA architecture and interacts with the database through mapping, ORM and transaction management. Its repository provides CRUD operations, and derived queries simplify database access. Additionally, it uses lazy loading to only retrieve data when necessary, thus improving performance.
 What is the original meaning of dynamic linking and static linking in Linux?
Feb 05, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
What is the original meaning of dynamic linking and static linking in Linux?
Feb 05, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
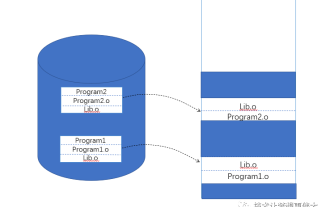
As usual, let’s ask a few questions: Why dynamic linking? How to do dynamic linking? What is address-independent code technology? What is delayed binding technology? How to do explicit linking while the program is running? Why dynamic linking? The emergence of dynamic linking is to solve some shortcomings of static linking: saving memory and disk space: As shown in the figure below, Program1 and Program2 contain two modules, Program1.o and Program2.o respectively, and they both require the Lib.o module. In the case of static linking, both target files use the Lib.o module, so they have copies in the executable files Program1 and program2 output by the link and run at the same time.
 What to do if the html image is too large
Apr 05, 2024 pm 12:24 PM
What to do if the html image is too large
Apr 05, 2024 pm 12:24 PM
Here are some ways to optimize HTML images that are too large: Optimize image file size: Use a compression tool or image editing software. Use media queries: Dynamically resize images based on device. Implement lazy loading: only load the image when it enters the visible area. Use a CDN: Distribute images to multiple servers. Use image placeholder: Display a placeholder image while the image is loading. Use thumbnails: Displays a smaller version of the image and loads the full-size image on click.
 Decoding Laravel performance bottlenecks: Optimization techniques fully revealed!
Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
Decoding Laravel performance bottlenecks: Optimization techniques fully revealed!
Mar 06, 2024 pm 02:33 PM
Decoding Laravel performance bottlenecks: Optimization techniques fully revealed! Laravel, as a popular PHP framework, provides developers with rich functions and a convenient development experience. However, as the size of the project increases and the number of visits increases, we may face the challenge of performance bottlenecks. This article will delve into Laravel performance optimization techniques to help developers discover and solve potential performance problems. 1. Database query optimization using Eloquent delayed loading When using Eloquent to query the database, avoid
 Java JPA performance optimization tips: make your application fly
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
Java JPA performance optimization tips: make your application fly
Feb 19, 2024 pm 09:03 PM
Article keywords: JavaJPA performance optimization ORM entity management JavaJPA (JavaPersistance API) is an object-relational mapping (ORM) framework that allows you to use Java objects to operate data in the database. JPA provides a unified API for interacting with databases, allowing you to use the same code to access different databases. In addition, JPA also supports features such as lazy loading, caching, and dirty data detection, which can improve application performance. However, if used incorrectly, JPA performance can become a bottleneck for your application. The following are some common performance problems: N+1 query problem: When you use JPQL queries in your application, you may encounter N+1 query problems. In this kind of
 How does Hibernate optimize database query performance?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
How does Hibernate optimize database query performance?
Apr 17, 2024 pm 03:00 PM
Tips for optimizing Hibernate query performance include: using lazy loading to defer loading of collections and associated objects; using batch processing to combine update, delete, or insert operations; using second-level cache to store frequently queried objects in memory; using HQL outer connections , retrieve entities and their related entities; optimize query parameters to avoid SELECTN+1 query mode; use cursors to retrieve massive data in blocks; use indexes to improve the performance of specific queries.
 How to prevent iframe loading event
Feb 19, 2024 am 08:02 AM
How to prevent iframe loading event
Feb 19, 2024 am 08:02 AM
How to prevent iframe loading events In web development, we often use iframe tags to embed other web pages or content. By default, when the browser loads an iframe, the loading event is triggered. However, in some cases we may want to delay the loading of an iframe, or prevent the loading event entirely. In this article, we'll explore how to achieve this through code examples. 1. Delay loading of iframe If you want to delay loading of iframe, we can use
 What are the disadvantages of Hibernate ORM framework?
Apr 18, 2024 am 08:30 AM
What are the disadvantages of Hibernate ORM framework?
Apr 18, 2024 am 08:30 AM
The HibernateORM framework has the following shortcomings: 1. Large memory consumption because it caches query results and entity objects; 2. High complexity, requiring in-depth understanding of the architecture and configuration; 3. Delayed loading delays, leading to unexpected delays; 4. Performance bottlenecks, in May occur when a large number of entities are loaded or updated at the same time; 5. Vendor-specific implementation, resulting in differences between databases.



