How to set up overclocking in BIOS
BIOS (Basic Input/Output System) is a key part of the computer system, responsible for managing the interaction between computer hardware and software. Through the BIOS, users can configure and adjust various computer settings, including overclocking settings. Overclocking is a commonly used method to improve the performance of hardware components such as CPU, memory, and graphics cards, thereby increasing the overall running speed of the computer. This article will introduce you to how to set overclocking in the BIOS.
First, start the computer and quickly press the designated button to enter the BIOS setup interface. This button often appears at the bottom or top of the screen when you turn on the computer, depending on the make and model of your computer. Common keys include F2, Delete, F10 and F12. Once you enter the BIOS setup interface, you will see an interface containing various options and menus.
Next, use the arrow keys on your keyboard to navigate the menu and find an option like "Overclocking" or "Frequency Settings" or similar. Different BIOS versions and manufacturers may place the overclocking options in different locations, so you may need to spend some time looking for them in the menus. After finding the overclocking option, press the Enter key to enter the detailed settings interface.
In the overclocking setting interface, you will see related settings for the CPU, memory, bus and other components. First, focus on the CPU overclocking settings. Generally speaking, you can choose to use the automatic overclocking function or manually adjust the frequency. If you are a beginner, it is recommended to use the automatic overclocking function. This allows the motherboard to automatically provide optimal overclocking performance based on hardware and system requirements. If you want to get more in-depth and adjust your overclocking settings, you can choose to adjust the frequency manually.
If you choose to adjust the frequency manually, you need to adjust the basic clock frequency (BCLK) and multiplier. The base clock frequency is the unit of the CPU's internal clock, while the multiplier is a multiple factor based on the base clock frequency. By adjusting these two parameters, you can control the working speed of the CPU.
However, overclocking is not limited to the CPU, but can also involve memory, graphics cards and other hardware components. Some BIOS also provide corresponding options to adjust the frequency of these hardware. In the overclocking settings interface, you can find these options and adjust them as needed.
When adjusting overclocking settings, be careful and pay attention to the following points:
- Temperature monitoring: Frequent overclocking may cause the temperature of the hardware to rise, so it is recommended to install temperature monitoring software. Monitor the temperature of hardware. Make sure the temperature is within a safe range to avoid hardware damage.
- Stability test: Before applying overclocking settings, it is best to conduct a stability test to ensure that the system can run stably at high frequencies. Some stability testing tools can be used, such as Prime95 and Memtest86.
- Small step adjustments: When you start overclocking, it is recommended to adjust the frequency in small steps. Increasing or decreasing too much at once may cause the system to become unstable or even unable to boot. After each adjustment, test and observe how the system performs.
Finally, save and exit BIOS settings. Once you've finished adjusting all your overclocking settings, make sure to save the changes to the BIOS and exit setup. The computer will restart and apply the new overclocking settings.
Summary:
Setting overclocking through BIOS is a technical job and needs to be done with caution. Before performing overclocking settings, please back up your data in advance and ensure that you understand and master your computer hardware specifications and the manufacturer's recommended overclocking setting methods. At the same time, the hardware temperature is always monitored and stability tests are performed to ensure the stability and operating results of the system.
Please remember that overclocking may shorten the life of your hardware and may even cause hardware damage. If you are not sure how to set up overclocking, it is best to consult a professional to avoid unnecessary risks and losses.
The above is the detailed content of How to set up overclocking in BIOS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 When I turn on the computer, it always stops at the motherboard logo screen. Nothing happens when I press anything, and I can't enter the bios?
Apr 23, 2024 am 09:13 AM
When I turn on the computer, it always stops at the motherboard logo screen. Nothing happens when I press anything, and I can't enter the bios?
Apr 23, 2024 am 09:13 AM
When I turn on the computer, it always stops at the motherboard logo screen. Nothing happens when I press anything, and I can't enter the bios? This is usually because the BIOS battery voltage is too low, and the system time has returned to the BIOS preset time, such as 2000.1.1, 00:00. You can use it after pressing F1 to enter the bios and set the time. Do not turn off the AC power after shutting down at night. Generally, the system time will not be lost when you turn on the computer the next day, and you can still enter the system normally. If the AC power is cut off, the battery voltage cannot sustain the power consumption of the bios, and the computer will be in the same state again the next day when it is turned on. Replacing the bios battery is the ultimate solution. Win11 is stuck on the motherboard logo interface when booting? 1. It is a problem with bios settings. We only need to find the corresponding setting items.
 In which folder is the win10 graphics card driver located?
Apr 18, 2024 am 09:20 AM
In which folder is the win10 graphics card driver located?
Apr 18, 2024 am 09:20 AM
What is the installation path of the graphics card driver? 1. Turn on the computer, click Computer, and open the Device Manager. For all devices on our computer, find the installation directory location of the graphics card driver. Click on the display adapter, find the device to which the driver belongs, and click to select properties. After entering properties, select Update Driver. 2. The graphics card driver is best installed on the C drive. By default, some drives are installed on the system disk. Cannot make selection. If you want to choose, you can install it on other disks. It is better to divide the hard disk into multiple areas than one area. The access speed through the C drive is faster than the D drive, and the access speed through the D drive is faster than the E drive. 3. It cannot be changed otherwise problems will occur. The driver is installed in C:\ProgramFiles, and C:\WINDOW
 How to enter bios on hp motherboard
May 04, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
How to enter bios on hp motherboard
May 04, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
How to set up the U disk boot in the HP notebook bios (how to enter the HP computer bios) and then insert the U disk to be booted first into the USB port of the notebook. If you want to install the system, the system program must have been prepared in the U disk. First, open the laptop. Make sure the laptop is turned off. Setting the bios must be done with the computer turned off. Then insert the U disk that you want to boot first into the USB port of the notebook. If you want to install the system, the prerequisite is that the system program has been prepared in the U disk. Take the HP ProDesk400G5SFF desktop computer as an example. Set the BIOS disk startup method: First, restart the computer and wait for the startup screen to appear. There are two ways to set up USB disk startup on HP notebooks. One is to directly press the shortcut key to select
 Tutorial on assembling a computer and installing a system? How to install win11 system when assembling a computer?
Apr 27, 2024 pm 03:38 PM
Tutorial on assembling a computer and installing a system? How to install win11 system when assembling a computer?
Apr 27, 2024 pm 03:38 PM
Tutorial on assembling a computer and installing a system? Nowadays, the system installation for assembling computers is very simple and convenient, and only requires a CD. First enter the bios settings, set the computer to boot first with the CD-ROM drive, then restart the computer and load the system CD into the CD-ROM drive. The CD will automatically enter the installation state. At this time, you only need to manually repartition the partitions, and the rest will be completed automatically. How to install win11 system when assembling a computer? 1. First, we need to download a win11 image file from this site before installing it. 2. The win11 image file has undergone a large number of professional tests to ensure stable installation and smooth operation. 3. After the download is completed, load the folder in the download path and run the "windowssetup" process in it.
 MSI motherboard boot logo
May 08, 2024 pm 02:20 PM
MSI motherboard boot logo
May 08, 2024 pm 02:20 PM
How to cancel the MSI motherboard icon when booting 1. Press the DEL key when booting to enter the BIOS. Generally, in the "Advanced Features" item, you can find the words MSI motherboard LOGO screen. Select DISABLED, save and exit. There will no longer be this MSI motherboard LOGO screen when you turn on the computer in the future. MSI motherboard refers to the motherboard brand developed by MSI (MSI Technology Company). 2. The logo displayed when the computer is turned on is basically that of the motherboard manufacturer. You can set QUICKPOST to DISENABLE in the BIOS, so that the logo will generally no longer be displayed. It will display computer configuration-related information and give you more details. 3. First, teach you how to flash the BIOS in Windows environment. First: Go online
 How to enter bios after assembling a computer? How to enter bios when assembling a computer?
May 07, 2024 am 09:13 AM
How to enter bios after assembling a computer? How to enter bios when assembling a computer?
May 07, 2024 am 09:13 AM
How to enter bios after assembling a computer? Before entering the BIOS, you need to make sure that the computer is completely shut down and powered off. Here are several common ways to enter the BIOS: 1. Use shortcut keys: Most computer manufacturers will display a prompt message at startup telling you which key to press to enter the BIOS settings. Usually the F2, F10, F12 or Delete key. After pressing the appropriate keys, you should be able to see a screen with information about your computer's hardware and BIOS settings. 2. Use the button on the motherboard: Some computer motherboards have a dedicated button for entering BIOS settings. This button is usually labeled "BIOS" or "UEFI". After pressing the button you should be able to see
 How to solve the problem of notebook CPU frequency reduction
Apr 14, 2024 pm 09:04 PM
How to solve the problem of notebook CPU frequency reduction
Apr 14, 2024 pm 09:04 PM
Notebook computer frequency reduction method 1. Open the control panel on the computer desktop. Click Power Options in Control Panel. Change the power plan in Power Options to Energy Saving. After changing to energy saving, you can see in the task manager that the notebook CPU operating frequency has been reduced. 2. The heat dissipation function is realized simply through the physical thermal conduction principle. Place a plastic or metal cooling base on the bottom of your notebook and raise it to promote air circulation and heat radiation, which can achieve cooling effects. Install several cooling fans on the heat dissipation base to improve heat dissipation performance. 3. When no program is running, the CPU automatically reduces the frequency to save power; when the CPU temperature or the operating environment temperature is too high, the CPU automatically reduces the frequency to prevent burning. You can also try the suggestions from friends on the first floor. Please refer to the setting method.
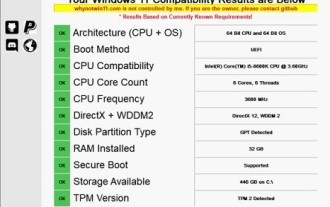 How to upgrade Gigabyte motherboard to Win11_How to upgrade Gigabyte motherboard to Win11
May 06, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
How to upgrade Gigabyte motherboard to Win11_How to upgrade Gigabyte motherboard to Win11
May 06, 2024 pm 12:04 PM
1. Win11 does not have very high requirements for the motherboard. You can first download healthcheck or whynotwin11 to check whether your other hardware devices support it (you can download it from this site). 2. If other conditions are met and only tpm does not meet the requirements, you can enable tpm in the bios settings. 3. Restart the system, and then press [DEL] on the keyboard to enter the BIOS settings when the logo pops up. 4. Enter the [Settings] option and [Miscellaneous] option in sequence. 5. Find [Intel Platform Trust Technology (PTT)] below and set it to [Start]. 6. If it is an AMD platform, then




