What are the methods to view Linux file mappings?
1. Definition of file mapping
File mapping is a mechanism that maps files on disk to the virtual memory space of a process.
In this way, the process can read and write files directly through the memory address without having to go through regular system calls such as read and write.
In file mapping, we connect the file to the virtual memory of the process through the Linux mechanism, so that the process can directly read and write file data in the memory without directly accessing the disk. This mechanism provides a more efficient file access method and also simplifies the file operation process.
File mapping is often called memory mapping, and the two are usually the same. Memory mapping covers the operations of mapping files to memory and mapping anonymous memory to the process address space.
File mapping is a special case of memory mapping.
2. How to view file mapping [two methods]
Method 1: Use pmap tool
View the file mapping information of the corresponding process
$ pmap -X 12345#查看指定PID的文件映射信息 12345: ./example 0000555555554000100K r-x-- example 00005555556730004K r---- example 00005555556740004K rw--- example 00007ffff7de0000 1360K r-x-- libc-2.31.so ... mapped: 1448Kwriteable/private: 8Kshared: 0K
- Each line represents a memory mapped area.
- Address range, permissions, mapping type, file path and other information.
- "mapped" represents the total size of the map, "writeable/private" represents the writable and private size, and "shared" represents the shared size.
Method 2: Use cat to view the file mapping file
Use the cat /proc/PID/maps command to view the memory mapping of the process.
Each line represents a memory mapped area, the format is as follows:
address perms offsetdev inodepathname 00400000-0040b000 r-xp 00000000 08:01 1167685/usr/bin/cat 0060a000-0060b000 r--p 0000a000 08:01 1167685/usr/bin/cat 0060b000-0060c000 rw-p 0000b000 08:01 1167685/usr/bin/cat
- address: The mapped virtual memory address range.
- perms: Permissions, including read (r), write (w), execute (x), etc.
- offset: The offset of the mapped area in the file.
- dev: Device number.
- inode: The node number of the file in the file system.
- pathname: mapped file path or anonymous mapping.
3. How to use file mapping under Linux
Now we demonstrate through an example how to use file mapping to map a file into memory, then modify the contents in memory, and finally demonstrate by unmapping the memory.
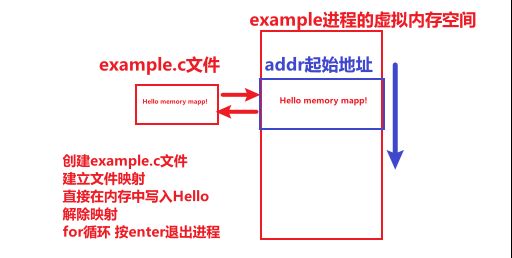
example.c file
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
const char *file_path = "example.txt";
const size_t file_size = 4096;
int fd = open(file_path, O_RDWR | O_CREAT, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
if (fd == -1) {
perror("open");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (ftruncate(fd, file_size) == -1) {
perror("ftruncate");
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Create a memory-mapped region
void *addr = mmap(NULL, file_size, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, fd, 0);
if (addr == MAP_FAILED) {
perror("mmap");
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Now 'addr' points to the beginning of the file in memory
// 现在addr表示文件在进程的内存空间代表区域的起始位置
// Write a message to the memory-mapped file
// 向映射文件写入一句消息。
const char *message = "Hello, Memory Mapping!n";
strncpy(addr, message, strlen(message));
printf("Press Enter to exit...n");
getchar();// Wait for user to press Enter
// Unmap the memory region解除文件和内存区域的映射关系
if (munmap(addr, file_size) == -1) {
perror("munmap");
close(fd);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// Close the file descriptor
close(fd);
return 0;
}Compile and execute:
$ ls example.c $ gcc example.c -o example $ ./example Press Enter to exit...
View the file mapping information of the process:
$ ps aux|grep example codersong 15245420.00.0 27761152 pts/0S+ 19:23 0:00 ./example codersong 15245470.00.0121882432 pts/2S+ 19:23 0:00 grep --color=auto example $ pmap -X 1524542 1524542: ./example 地址 Perm 偏移量 设备 Inode SizeRss Pss Pss_Dirty Referenced Anonymous LazyFree ShmemPmdMapped FilePmdMapped Shared_Hugetlb Private_Hugetlb Swap SwapPss Locked THPeligible Mapping 557b482c3000 r--p0000000008:03 712405144 4 04 000 00 00 00 0 example 557b482c4000 r-xp0000100008:03 712405144 4 04 000 00 00 00 0 example 557b482c5000 r--p0000200008:03 712405144 4 04 000 00 00 00 0 example 557b482c6000 r--p0000200008:03 712405144 4 44 400 00 00 00 0 example 557b482c7000 rw-p0000300008:03 712405144 4 44 400 00 00 00 0 example 557b48e9e000 rw-p0000000000:00 01324 4 44 400 00 00 00 0 [heap] 7f8fe5600000 r--p0000000008:03264612160160 7 0160 000 00 00 00 0 libc.so.6 7f8fe5628000 r-xp0002800008:03264612 162078824 0788 000 00 00 00 0 libc.so.6 7f8fe57bd000 r--p001bd00008:03264612352 64 1 0 64 000 00 00 00 0 libc.so.6 7f8fe5815000 r--p0021400008:03264612 16 161616 161600 00 00 00 0 libc.so.6 7f8fe5819000 rw-p0021800008:0326461288 8 88 800 00 00 00 0 libc.so.6 7f8fe581b000 rw-p0000000000:00 0 52 202020 202000 00 00 00 0 7f8fe58f6000 rw-p0000000000:00 0 128 8 88 800 00 00 00 0 7f8fe5908000 rw-p0000000000:00 084 4 44 400 00 00 00 0 7f8fe590a000 r--p0000000008:0326460088 0 08 000 00 00 00 0 ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7f8fe590c000 r-xp0000200008:03264600168168 7 0168 000 00 00 00 0 ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7f8fe5936000 r--p0002c00008:03264600 44 40 1 0 40 000 00 00 00 0 ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7f8fe5941000 rw-s0000000008:03 712405244 4 04 000 00 00 00 0 example.txt 7f8fe5942000 r--p0003700008:0326460088 8 88 800 00 00 00 0 ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7f8fe5944000 rw-p0003900008:0326460088 8 88 800 00 00 00 0 ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7ffef93f2000 rw-p0000000000:00 0132 121212 121200 00 00 00 0 [stack] 7ffef9485000 r--p0000000000:00 0 160 0 00 000 00 00 00 0 [vvar] 7ffef9489000 r-xp0000000000:00 084 0 04 000 00 00 00 0 [vdso] ffffffffff600000 --xp0000000000:00 040 0 00 000 00 00 00 0 [vsyscall] ==== ==== === ========= ========== ========= ======== ============== ============= ============== =============== ==== ======= ====== =========== 2780 1344 15296 13449600 00 00 00 0 KB $ $ $ cat /proc/1524542/maps 557b482c3000-557b482c4000 r--p 00000000 08:03 7124051/home/codersong/zhengshihong/example 557b482c4000-557b482c5000 r-xp 00001000 08:03 7124051/home/codersong/zhengshihong/example 557b482c5000-557b482c6000 r--p 00002000 08:03 7124051/home/codersong/zhengshihong/example 557b482c6000-557b482c7000 r--p 00002000 08:03 7124051/home/codersong/zhengshihong/example 557b482c7000-557b482c8000 rw-p 00003000 08:03 7124051/home/codersong/zhengshihong/example 557b48e9e000-557b48ebf000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0[heap] 7f8fe5600000-7f8fe5628000 r--p 00000000 08:03 264612 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 7f8fe5628000-7f8fe57bd000 r-xp 00028000 08:03 264612 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 7f8fe57bd000-7f8fe5815000 r--p 001bd000 08:03 264612 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 7f8fe5815000-7f8fe5819000 r--p 00214000 08:03 264612 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 7f8fe5819000-7f8fe581b000 rw-p 00218000 08:03 264612 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 7f8fe581b000-7f8fe5828000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 7f8fe58f6000-7f8fe58f9000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 7f8fe5908000-7f8fe590a000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0 7f8fe590a000-7f8fe590c000 r--p 00000000 08:03 264600 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7f8fe590c000-7f8fe5936000 r-xp 00002000 08:03 264600 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7f8fe5936000-7f8fe5941000 r--p 0002c000 08:03 264600 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7f8fe5941000-7f8fe5942000 rw-s 00000000 08:03 7124052/home/byzoro/zhengshihong/example.txt 7f8fe5942000-7f8fe5944000 r--p 00037000 08:03 264600 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7f8fe5944000-7f8fe5946000 rw-p 00039000 08:03 264600 /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 7ffef93f2000-7ffef9413000 rw-p 00000000 00:00 0[stack] 7ffef9485000-7ffef9489000 r--p 00000000 00:00 0[vvar] 7ffef9489000-7ffef948b000 r-xp 00000000 00:00 0[vdso] ffffffffff600000-ffffffffff601000 --xp 00000000 00:00 0[vsyscall]
Now press ctrl C to exit the example program and view the contents of the example.txt file:
$ cat example.txt Hello, Memory Mapping!
The above is the detailed content of What are the methods to view Linux file mappings?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Large memory optimization, what should I do if the computer upgrades to 16g/32g memory speed and there is no change?
Jun 18, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
Large memory optimization, what should I do if the computer upgrades to 16g/32g memory speed and there is no change?
Jun 18, 2024 pm 06:51 PM
For mechanical hard drives or SATA solid-state drives, you will feel the increase in software running speed. If it is an NVME hard drive, you may not feel it. 1. Import the registry into the desktop and create a new text document, copy and paste the following content, save it as 1.reg, then right-click to merge and restart the computer. WindowsRegistryEditorVersion5.00[HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SessionManager\MemoryManagement]"DisablePagingExecutive"=d
 How to check memory usage on Xiaomi Mi 14Pro?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:19 PM
How to check memory usage on Xiaomi Mi 14Pro?
Mar 18, 2024 pm 02:19 PM
Recently, Xiaomi released a powerful high-end smartphone Xiaomi 14Pro, which not only has a stylish design, but also has internal and external black technology. The phone has top performance and excellent multitasking capabilities, allowing users to enjoy a fast and smooth mobile phone experience. However, performance will also be affected by memory. Many users want to know how to check the memory usage of Xiaomi 14Pro, so let’s take a look. How to check memory usage on Xiaomi Mi 14Pro? Introduction to how to check the memory usage of Xiaomi 14Pro. Open the [Application Management] button in [Settings] of Xiaomi 14Pro phone. To view the list of all installed apps, browse the list and find the app you want to view, click on it to enter the app details page. In the application details page
 What to do if the 0x80004005 error code appears. The editor will teach you how to solve the 0x80004005 error code.
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
What to do if the 0x80004005 error code appears. The editor will teach you how to solve the 0x80004005 error code.
Mar 21, 2024 pm 09:17 PM
When deleting or decompressing a folder on your computer, sometimes a prompt dialog box "Error 0x80004005: Unspecified Error" will pop up. How should you solve this situation? There are actually many reasons why the error code 0x80004005 is prompted, but most of them are caused by viruses. We can re-register the dll to solve the problem. Below, the editor will explain to you the experience of handling the 0x80004005 error code. Some users are prompted with error code 0X80004005 when using their computers. The 0x80004005 error is mainly caused by the computer not correctly registering certain dynamic link library files, or by a firewall that does not allow HTTPS connections between the computer and the Internet. So how about
 Samsung announced the completion of 16-layer hybrid bonding stacking process technology verification, which is expected to be widely used in HBM4 memory
Apr 07, 2024 pm 09:19 PM
Samsung announced the completion of 16-layer hybrid bonding stacking process technology verification, which is expected to be widely used in HBM4 memory
Apr 07, 2024 pm 09:19 PM
According to the report, Samsung Electronics executive Dae Woo Kim said that at the 2024 Korean Microelectronics and Packaging Society Annual Meeting, Samsung Electronics will complete the verification of the 16-layer hybrid bonding HBM memory technology. It is reported that this technology has passed technical verification. The report also stated that this technical verification will lay the foundation for the development of the memory market in the next few years. DaeWooKim said that Samsung Electronics has successfully manufactured a 16-layer stacked HBM3 memory based on hybrid bonding technology. The memory sample works normally. In the future, the 16-layer stacked hybrid bonding technology will be used for mass production of HBM4 memory. ▲Image source TheElec, same as below. Compared with the existing bonding process, hybrid bonding does not need to add bumps between DRAM memory layers, but directly connects the upper and lower layers copper to copper.
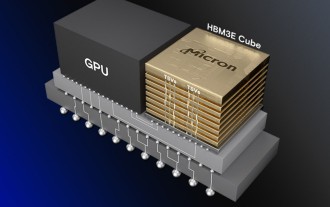 Micron: HBM memory consumes 3 times the wafer volume, and production capacity is basically booked for next year
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
Micron: HBM memory consumes 3 times the wafer volume, and production capacity is basically booked for next year
Mar 22, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
This site reported on March 21 that Micron held a conference call after releasing its quarterly financial report. At the conference, Micron CEO Sanjay Mehrotra said that compared to traditional memory, HBM consumes significantly more wafers. Micron said that when producing the same capacity at the same node, the current most advanced HBM3E memory consumes three times more wafers than standard DDR5, and it is expected that as performance improves and packaging complexity intensifies, in the future HBM4 This ratio will further increase. Referring to previous reports on this site, this high ratio is partly due to HBM’s low yield rate. HBM memory is stacked with multi-layer DRAM memory TSV connections. A problem with one layer means that the entire
 Lexar launches Ares Wings of War DDR5 7600 16GB x2 memory kit: Hynix A-die particles, 1,299 yuan
May 07, 2024 am 08:13 AM
Lexar launches Ares Wings of War DDR5 7600 16GB x2 memory kit: Hynix A-die particles, 1,299 yuan
May 07, 2024 am 08:13 AM
According to news from this website on May 6, Lexar launched the Ares Wings of War series DDR57600CL36 overclocking memory. The 16GBx2 set will be available for pre-sale at 0:00 on May 7 with a deposit of 50 yuan, and the price is 1,299 yuan. Lexar Wings of War memory uses Hynix A-die memory chips, supports Intel XMP3.0, and provides the following two overclocking presets: 7600MT/s: CL36-46-46-961.4V8000MT/s: CL38-48-49 -1001.45V In terms of heat dissipation, this memory set is equipped with a 1.8mm thick all-aluminum heat dissipation vest and is equipped with PMIC's exclusive thermal conductive silicone grease pad. The memory uses 8 high-brightness LED beads and supports 13 RGB lighting modes.
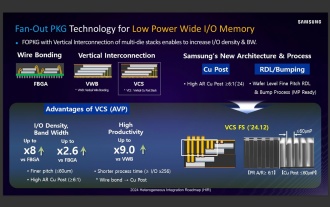 Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
Sources say Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix will commercialize stacked mobile memory after 2026
Sep 03, 2024 pm 02:15 PM
According to news from this website on September 3, Korean media etnews reported yesterday (local time) that Samsung Electronics and SK Hynix’s “HBM-like” stacked structure mobile memory products will be commercialized after 2026. Sources said that the two Korean memory giants regard stacked mobile memory as an important source of future revenue and plan to expand "HBM-like memory" to smartphones, tablets and laptops to provide power for end-side AI. According to previous reports on this site, Samsung Electronics’ product is called LPWide I/O memory, and SK Hynix calls this technology VFO. The two companies have used roughly the same technical route, which is to combine fan-out packaging and vertical channels. Samsung Electronics’ LPWide I/O memory has a bit width of 512
 Kingbang launches new DDR5 8600 memory, offering CAMM2, LPCAMM2 and regular models to choose from
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:35 PM
Kingbang launches new DDR5 8600 memory, offering CAMM2, LPCAMM2 and regular models to choose from
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:35 PM
According to news from this site on June 7, GEIL launched its latest DDR5 solution at the 2024 Taipei International Computer Show, and provided SO-DIMM, CUDIMM, CSODIMM, CAMM2 and LPCAMM2 versions to choose from. ▲Picture source: Wccftech As shown in the picture, the CAMM2/LPCAMM2 memory exhibited by Jinbang adopts a very compact design, can provide a maximum capacity of 128GB, and a speed of up to 8533MT/s. Some of these products can even be stable on the AMDAM5 platform Overclocked to 9000MT/s without any auxiliary cooling. According to reports, Jinbang’s 2024 Polaris RGBDDR5 series memory can provide up to 8400






