fstab(File System Table)
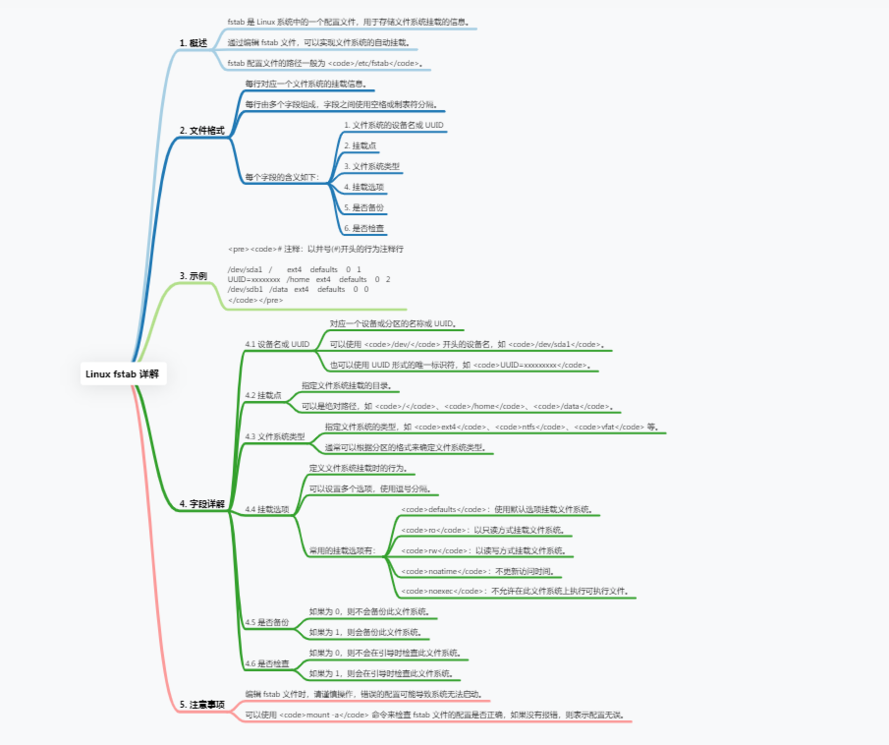
fstab (File System Table) is a configuration file in the Linux system, used to define the rules for mounting file systems when the system starts.
The fstab file is located in the /etc directory and can be created manually or modified by an editor. Each line specifies a file system to be mounted.
Each row has six fields, their meanings are as follows:
The file system device file or UUID can be used to specify the device of the file system to be mounted. The UUID is a unique identifier and the UUID of the device can be obtained through the blkid command.
2. Mount point: Specify the directory to which the file system is to be mounted, which can be an absolute path (such as /mnt/data) or a relative path (such as ../data).
3. File system type: Specify the type of file system, such as ext4, ntfs, vfat, etc.
4. Mount options: When mounting the file system, you can specify some options, such as read and write permissions, automatic mounting, etc. Common options include allowing reading and writing, automatic mounting, etc.
– ro: Mount the file system in read-only mode.
– rw: Mount the file system in read-write mode.
– auto: Automatically mount the file system.
– noauto: Do not automatically mount the file system.
– exec: Allow file execution.
– noexec: Disable execution of files.
For detailed options, please refer to the man man page (man fstab).
5. dump option: used for backup tools, such as dump command.
6. fsck option: used for file system checking tools, such as fsck command.
The following is an example fstab file content:
“`
/dev/sda1 /mnt/data ext4 rw 0 0
UUID=xxxxxxxx /mnt/backups ext4 ro 0 2
“`
The first line in this example indicates that the ext4 file system on the /dev/sda1 device is mounted to the /mnt/data directory and allows reading and writing. The second line indicates to mount the ext4 file system on the device with UUID xxxxxxxx to the /mnt/backups directory and only allow reading.
After modifying the fstab file, you can use the command mount -a to remount all file systems defined in the fstab file.
To summarize, by editing the fstab file, you can automatically mount the specified file system when the system starts and specify some mounting options. This is useful for systems that manage multiple file systems and can improve system stability and security.
The above is the detailed content of fstab(File System Table). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Fix event ID 55, 50, 98, 140 disk error in event viewer
Mar 19, 2024 am 09:43 AM
Fix event ID 55, 50, 98, 140 disk error in event viewer
Mar 19, 2024 am 09:43 AM
If you find event ID 55, 50, 140 or 98 in the Event Viewer of Windows 11/10, or encounter an error that the disk file system structure is damaged and cannot be used, please follow the guide below to resolve the issue. What does Event 55, File system structure on disk corrupted and unusable mean? At session 55, the file system structure on the Ntfs disk is corrupted and unusable. Please run the chkMSK utility on the volume. When NTFS is unable to write data to the transaction log, an error with event ID 55 is triggered, which will cause NTFS to fail to complete the operation unable to write the transaction data. This error usually occurs when the file system is corrupted, possibly due to the presence of bad sectors on the disk or the file system's inadequacy of the disk subsystem.
![You don't have permission to mount the file [FIXED]](https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/000/164/170824952191099.jpg?x-oss-process=image/resize,m_fill,h_207,w_330) You don't have permission to mount the file [FIXED]
Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
You don't have permission to mount the file [FIXED]
Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:45 PM
If you encounter permission errors when mounting an ISO image, this article may help. The error message is as follows: The file cannot be loaded. You do not have permission to load the file. Fortunately, you can fix it by following some simple suggestions. Why can't my ISO file be mounted? The ISO file may be corrupted or incomplete, which may cause mounting issues. Other causes include file corruption, storage media failure, or download errors. The ISO file is sparse. Interruption from security software. The disk image is not initialized. Sorry, there was a problem loading the file. The disc image file is corrupted. Fix the error that you do not have permission to mount the file. If you receive the Unable to mount file when trying to mount an ISO image, you No permission to mount file error, please follow these suggestions: Check the file
 How to modify the Linux fstab file to cancel the read-only attribute
Jan 15, 2024 pm 05:57 PM
How to modify the Linux fstab file to cancel the read-only attribute
Jan 15, 2024 pm 05:57 PM
After experimenting with mounting options to prohibit the execution of set bit programs and binary programs [root@localhost~]#vi/etc/fstab/# after adding /dev/sdc1/varext3defaults,noexec12[root@localhost~]#mount-oremount/var After the system restarts, it is found that /dev/sdc1 cannot be entered and can only enter the character interface. I want to delete that line, but when saving the file, it prompts the read-only attribute Read-onlyfilesystem. I have tried using (1) chmod+w/etc/fstab (2):w! The file is still read-only and cannot be modified. Method#
 How to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems
Jun 29, 2023 pm 04:05 PM
How to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems
Jun 29, 2023 pm 04:05 PM
How to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems Introduction: With the continuous development of computer technology, the stability and reliability of the operating system are becoming more and more important. However, although Linux systems are widely regarded as a stable and reliable operating system, there is still the possibility of file system corruption. A file system crash may lead to serious consequences such as data loss and system abnormalities. Therefore, this article will introduce how to deal with file system crash problems in Linux systems to help users better protect their data and systems.
 How to handle file system error 2147416359 in WIN10
Mar 27, 2024 am 11:31 AM
How to handle file system error 2147416359 in WIN10
Mar 27, 2024 am 11:31 AM
1. Press win+r to enter the run window, enter [services.msc] and press Enter. 2. In the service window, find [windows license manager service] and double-click to open it. 3. In the interface, change the startup type to [Automatic], and then click [Apply → OK]. 4. Complete the above settings and restart the computer.
 fstab(File System Table)
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
fstab(File System Table)
Feb 19, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
fstab (FileSystemTable) is a configuration file in the Linux system, used to define the rules for mounting file systems when the system starts. The fstab file is located in the /etc directory and can be created manually or modified by an editor. Each line specifies a file system to be mounted. Each line has six fields, and their meanings are as follows: The file system device file or UUID can be used to specify the device of the file system to be mounted. The UUID is a unique identifier. The UUID of the device can be obtained through the blkid command. 2. Mount point: Specify the directory to which the file system is to be mounted, which can be an absolute path (such as /mnt/data) or a relative path (such as ../data). 3. File system class
 Detailed tutorial on hard disk mounting in Ubuntu system.
Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
Detailed tutorial on hard disk mounting in Ubuntu system.
Feb 18, 2024 pm 05:39 PM
To mount a hard drive in an Ubuntu system, you can follow the detailed tutorial below: Check the hard drive: Insert the hard drive to be mounted and make sure the system can correctly identify it. You can view the list of connected hard disks using the following command: sudofdisk -l Make sure you find the hard disk device you want to mount (for example, /dev/sdb). Create a mount point: In Ubuntu systems, the hard disk is usually mounted to a directory. Execute the following command to create the mount point directory: sudomkdir/mnt/mydisk This will create a directory named "mydisk" in the /mnt directory as a mount point. Mount the hard disk: Execute the following command to mount the hard disk to the mount point: sudomoun
 Is the command to mount a hard disk in Linux the mount command?
Jan 28, 2023 pm 05:34 PM
Is the command to mount a hard disk in Linux the mount command?
Jan 28, 2023 pm 05:34 PM
The command to mount a hard disk in Linux is the mount command. Mount is a mounting command that can mount a partition under a folder to connect the partition and the directory. In the future, simply accessing this folder will be equivalent to accessing the partition. The syntax is "mount [-t system type] [- L volume name] [-o special option] [-n] device file name mount point".




