 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 The Complete Guide: Making sure you view Django versions accurately
The Complete Guide: Making sure you view Django versions accurately
The Complete Guide: Making sure you view Django versions accurately

Professional Guide: How to accurately view Django version, specific code examples required
Introduction:
Django is a highly popular Python web framework that is constantly updated The version is very important for developers. Checking the Django version is crucial to ensure you are using the latest features and bug fixes. This article will explain how to accurately check the Django version and provide specific code examples.
1. Use the command line to check the Django version
Using the command line is the easiest and fastest way to check the Django version. First, make sure you have Django installed correctly. Next, open a terminal or command line window and enter the following command:
python -m django --version
After running the above command, you will be able to see the version number of Django in the terminal.
2. View the version in the settings.py file of the Django project
The settings.py file in the Django project contains various settings and configuration information for the project. By reading this file you can easily check Django's version.
Open the settings.py file of your Django project and find the following line:
import django print(django.get_version())
Add the above code to the end of the settings.py file. Save and run your Django project and you will be able to see Django's version number in the terminal or console.
3. Check the Django version in the Python script
If you are writing a Python script and need to check the Django version, you can use the following code:
import django print(django.get_version())
Add the above code to your Python script and run the script. You will see Django's version number in your terminal or console.
4. Check the installed Django version through pip
If you want to check the installed Django version and the version information of other installed Python packages, you can use the pip tool. Enter the following command in the command line:
pip show django
After running the above command, you will be able to see the installed Django version and other related information.
5. Use the requirements.txt file to view the Django version
The requirements.txt file is usually used to record the dependency packages and their versions required by the Python project. You can get Django's version information by viewing this file.
Open the requirements.txt file of your Django project and search for the "Django" keyword in it. You will be able to find the line related to Django which contains the version number of Django.
Conclusion:
The above are several ways to accurately check the Django version. During the development process, knowing and using the latest Django version is crucial to the successful implementation of the project. You can easily obtain and confirm the Django version information you are using through the command line, settings.py file, Python script, pip tool, and requirements.txt file.
Please note that in order to ensure the stability and security of the project, it is recommended to always use the latest version of Django and update your project in a timely manner.
Reference:
- Django Documentation - Version Management: https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/3.2/topics/version/
- Django Project GitHub Repository: https://github.com/django/django
The above is the detailed content of The Complete Guide: Making sure you view Django versions accurately. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Reasons and solutions for scipy library installation failure
Feb 22, 2024 pm 06:27 PM
Reasons and solutions for scipy library installation failure
Feb 22, 2024 pm 06:27 PM
Reasons and solutions for scipy library installation failure, specific code examples are required When performing scientific calculations in Python, scipy is a very commonly used library, which provides many functions for numerical calculations, optimization, statistics, and signal processing. However, when installing the scipy library, sometimes you encounter some problems, causing the installation to fail. This article will explore the main reasons why scipy library installation fails and provide corresponding solutions. Installation of dependent packages failed. The scipy library depends on some other Python libraries, such as nu.
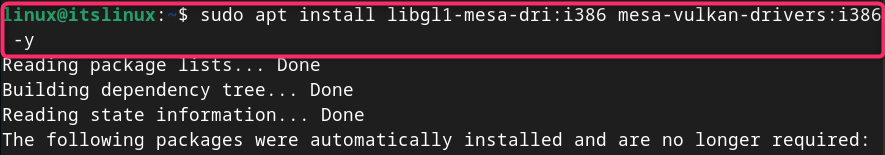 How to install Steam on Debian 12
Mar 21, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
How to install Steam on Debian 12
Mar 21, 2024 pm 10:10 PM
STEAM is a popular gaming platform developed by Valve Corporation that allows you to buy, download, install and play games. It provides features such as automatic updates, matchmaking, and a community forum to resolve software-related issues. In addition to this, you can also use Steam to interact with other players and developers as it has extensive community support. In this guide you will learn: How to install Steam on Debian12 How to run Steam on Debian12 How to remove Steam from Debian12 Conclusion How to install Steam on Debian12 You can install Steam on Debian12: Debian Official Repository deb packages
 Do you know some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed?
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Do you know some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed?
Mar 09, 2024 am 09:49 AM
Summary of some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed. Update time: January 9, 2019 09:34:57 Author: Hope on the field. This article mainly summarizes and introduces to you some reasons why crontab scheduled tasks are not executed. For everyone Solutions are given for each of the possible triggers, which have certain reference and learning value for colleagues who encounter this problem. Students in need can follow the editor to learn together. Preface: I have encountered some problems at work recently. The crontab scheduled task was not executed. Later, when I searched on the Internet, I found that the Internet mainly mentioned these five incentives: 1. The crond service is not started. Crontab is not a function of the Linux kernel, but relies on a cron.
 What software is good for python programming?
Apr 20, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
What software is good for python programming?
Apr 20, 2024 pm 08:11 PM
IDLE and Jupyter Notebook are recommended for beginners, and PyCharm, Visual Studio Code and Sublime Text are recommended for intermediate/advanced students. Cloud IDEs Google Colab and Binder provide interactive Python environments. Other recommendations include Anaconda Navigator, Spyder, and Wing IDE. Selection criteria include skill level, project size and personal preference.
 Tutorial on installing PyCharm with PyTorch
Feb 24, 2024 am 10:09 AM
Tutorial on installing PyCharm with PyTorch
Feb 24, 2024 am 10:09 AM
As a powerful deep learning framework, PyTorch is widely used in various machine learning projects. As a powerful Python integrated development environment, PyCharm can also provide good support when implementing deep learning tasks. This article will introduce in detail how to install PyTorch in PyCharm and provide specific code examples to help readers quickly get started using PyTorch for deep learning tasks. Step 1: Install PyCharm First, we need to make sure we have
 Exploring Orange3: Opening up a new world of data mining and machine learning!
Mar 04, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
Exploring Orange3: Opening up a new world of data mining and machine learning!
Mar 04, 2024 pm 08:16 PM
Orange3 is a powerful open source data visualization and machine learning tool. It has rich data processing, analysis and modeling functions, providing users with simple and fast data mining and machine learning solutions. This article will briefly introduce the basic functions and usage of Orange3, and combine it with actual application scenarios and Python code cases to help readers better master the usage skills of Orange3. The basic functions of Orange3 include data loading, data preprocessing, feature selection, model establishment and evaluation, etc. Users can use the intuitive interface to drag and drop components to easily build data processes. At the same time, more complex data processing and modeling tasks can also be completed through Python scripts. Below we will go through a practical
 How to read excel data in pycharm
Apr 03, 2024 pm 08:42 PM
How to read excel data in pycharm
Apr 03, 2024 pm 08:42 PM
How to read Excel data using PyCharm? The steps are as follows: install the openpyxl library; import the openpyxl library; load the Excel workbook; access a specific worksheet; access cells in the worksheet; traverse rows and columns.
 How to repeat a string in python_python repeating string tutorial
Apr 02, 2024 pm 03:58 PM
How to repeat a string in python_python repeating string tutorial
Apr 02, 2024 pm 03:58 PM
1. First open pycharm and enter the pycharm homepage. 2. Then create a new python script, right-click - click new - click pythonfile. 3. Enter a string, code: s="-". 4. Then you need to repeat the symbols in the string 20 times, code: s1=s*20. 5. Enter the print output code, code: print(s1). 6. Finally run the script and you will see our return value at the bottom: - repeated 20 times.



