 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 Extension and customization of Java Map: Create your own data structure to meet your customization needs
Extension and customization of Java Map: Create your own data structure to meet your customization needs
Extension and customization of Java Map: Create your own data structure to meet your customization needs

Written by PHP editor Xigua, this article will discuss the expansion and customization of Java Map, allowing you to create an exclusive data structure that meets your individual needs. Through customized operations, you can achieve more flexible and efficient data management to meet various customization needs. Let's take a deeper look at how to use the powerful functions of Java Map to provide better data processing solutions for your projects.
1. Extend Java Map
The simplest way to extend Java Map is to create a new class that inherits from the java.util.Map interface. This new class can add new methods or properties, and can also override methods in the Map interface. For example, we can create a new Map class and add a new method to calculate the sum of key-value pairs:
public class SummingMap<K, V extends Number> extends HashMap<K, V> {
public double sumValues() {
double sum = 0;
for (V value : values()) {
sum += value.doubleValue();
}
return sum;
}
}This new Map class can be used like a normal Map, but it also has the new functionality of calculating the sum of key-value pairs.
2. Customize the traversal order of Java Map
By default, Java Map is traversed according to the hash value of the key. But sometimes, we may need to traverse the Map in other order, such as in the natural order of keys or insertion order. We can customize the traversal order of the Map by overriding the keySet() method in the Map interface. For example, we can create a new Map class that traverses the keys in their natural order:
public class TreeMap<K extends Comparable<K>, V> extends HashMap<K, V> {
@Override
public Set<K> keySet() {
return new TreeSet<>(super.keySet());
}
}This new Map class can be used like a normal Map, but it will traverse the keys in their natural order.
3. Create a custom serializer
By default, Java Maps are serialized using Java's built-in serialization mechanism. But sometimes, we may need to use a custom serializer to serialize the Map. We can create a custom serializer by implementing the java.io.Serializable interface and defining a writeObject() method in the class. For example, we can create a new Map class and use a custom serializer to serialize the Map:
public class CustomMap<K, V> extends HashMap<K, V> implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
@Override
private void writeObject(ObjectOutputStream out) throws IOException {
out.writeInt(size());
for (Entry<K, V> entry : entrySet()) {
out.writeObject(entry.geTKEy());
out.writeObject(entry.getValue());
}
}
}This new Map class can be used like a normal Map, but it will use a custom serializer to serialize the Map.
4. Use third-party libraries to extend and customize Java Map
In addition to the above methods, we can also use third-party libraries to extend and customize Java Map. For example, we can use the Guava library to create a concurrent Map, the Apache Commons Collections library to create a sorted Map, or the Jackson library to create a JSON formatted Map .
5. Precautions
When extending and customizing Java Map, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- Ensure that the extended or customized Map class still conforms to the contract of the Map interface.
- When extending or customizing the Map class, consider performance and memory usage.
- If you need to share the extended or customized Map class with other applications, you need to ensure that these applications also have the same extension or customized library installed.
I hope this article is helpful to you, thank you for reading!
The above is the detailed content of Extension and customization of Java Map: Create your own data structure to meet your customization needs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to fine-tune deepseek locally
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:21 PM
How to fine-tune deepseek locally
Feb 19, 2025 pm 05:21 PM
Local fine-tuning of DeepSeek class models faces the challenge of insufficient computing resources and expertise. To address these challenges, the following strategies can be adopted: Model quantization: convert model parameters into low-precision integers, reducing memory footprint. Use smaller models: Select a pretrained model with smaller parameters for easier local fine-tuning. Data selection and preprocessing: Select high-quality data and perform appropriate preprocessing to avoid poor data quality affecting model effectiveness. Batch training: For large data sets, load data in batches for training to avoid memory overflow. Acceleration with GPU: Use independent graphics cards to accelerate the training process and shorten the training time.
 What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory
May 09, 2024 am 11:10 AM
What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory What to do if the Edge browser takes up too much memory
May 09, 2024 am 11:10 AM
1. First, enter the Edge browser and click the three dots in the upper right corner. 2. Then, select [Extensions] in the taskbar. 3. Next, close or uninstall the plug-ins you do not need.
 The impact of the AI wave is obvious. TrendForce has revised up its forecast for DRAM memory and NAND flash memory contract price increases this quarter.
May 07, 2024 pm 09:58 PM
The impact of the AI wave is obvious. TrendForce has revised up its forecast for DRAM memory and NAND flash memory contract price increases this quarter.
May 07, 2024 pm 09:58 PM
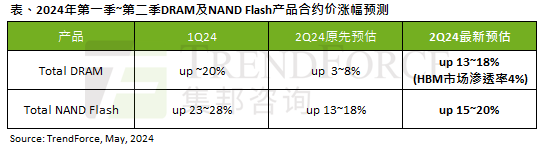
According to a TrendForce survey report, the AI wave has a significant impact on the DRAM memory and NAND flash memory markets. In this site’s news on May 7, TrendForce said in its latest research report today that the agency has increased the contract price increases for two types of storage products this quarter. Specifically, TrendForce originally estimated that the DRAM memory contract price in the second quarter of 2024 will increase by 3~8%, and now estimates it at 13~18%; in terms of NAND flash memory, the original estimate will increase by 13~18%, and the new estimate is 15%. ~20%, only eMMC/UFS has a lower increase of 10%. ▲Image source TrendForce TrendForce stated that the agency originally expected to continue to
 Java data structures and algorithms: in-depth explanation
May 08, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Java data structures and algorithms: in-depth explanation
May 08, 2024 pm 10:12 PM
Data structures and algorithms are the basis of Java development. This article deeply explores the key data structures (such as arrays, linked lists, trees, etc.) and algorithms (such as sorting, search, graph algorithms, etc.) in Java. These structures are illustrated through practical examples, including using arrays to store scores, linked lists to manage shopping lists, stacks to implement recursion, queues to synchronize threads, and trees and hash tables for fast search and authentication. Understanding these concepts allows you to write efficient and maintainable Java code.
 Detailed explanation of JVM command line parameters: the secret weapon to control JVM operation
May 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
Detailed explanation of JVM command line parameters: the secret weapon to control JVM operation
May 09, 2024 pm 01:33 PM
JVM command line parameters allow you to adjust JVM behavior at a fine-grained level. The common parameters include: Set the Java heap size (-Xms, -Xmx) Set the new generation size (-Xmn) Enable the parallel garbage collector (-XX:+UseParallelGC) Reduce the memory usage of the Survivor area (-XX:-ReduceSurvivorSetInMemory) Eliminate redundancy Eliminate garbage collection (-XX:-EliminateRedundantGCs) Print garbage collection information (-XX:+PrintGC) Use the G1 garbage collector (-XX:-UseG1GC) Set the maximum garbage collection pause time (-XX:MaxGCPau
 PHP data structure: The balance of AVL trees, maintaining an efficient and orderly data structure
Jun 03, 2024 am 09:58 AM
PHP data structure: The balance of AVL trees, maintaining an efficient and orderly data structure
Jun 03, 2024 am 09:58 AM
AVL tree is a balanced binary search tree that ensures fast and efficient data operations. To achieve balance, it performs left- and right-turn operations, adjusting subtrees that violate balance. AVL trees utilize height balancing to ensure that the height of the tree is always small relative to the number of nodes, thereby achieving logarithmic time complexity (O(logn)) search operations and maintaining the efficiency of the data structure even on large data sets.
 The meaning of double in c language
May 08, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
The meaning of double in c language
May 08, 2024 pm 02:45 PM
In the C language, double is a data type used to represent double-precision floating-point numbers. It has higher precision than the float type and is used to handle larger numerical ranges or more precise calculations. It can store high-precision numeric values, representing large floating-point numbers and decimals, ranging from -1.7976931348623157e308 to 1.7976931348623157e308, with a precision of approximately 15 significant digits and occupying 8 bytes in memory.
 Confusion for Java Beginners: Application of Algorithms and Data Structures
May 07, 2024 pm 05:57 PM
Confusion for Java Beginners: Application of Algorithms and Data Structures
May 07, 2024 pm 05:57 PM
Beginner's Guide to Java: Real-World Applications of Algorithms and Data Structures Algorithms and data structures are the cornerstones of Java programming. Understanding their application is critical to writing efficient, maintainable code. This article explores common uses of algorithms and data structures in real-world scenarios to help you understand their value. Sorting Algorithms Sorting algorithms are used to arrange a list of elements in an orderly manner. For example: int[]numbers={5,2,8,3,9};//Use the quick sort algorithm to sort the numbers array Arrays.sort(numbers);//Output the sorted array for(intnumber: numbers){





