Dive into the core concepts of Java JPA: entities, mappings, and queries

entity
php editor Apple will take you to deeply explore the core concepts of Java JPA in this article: entities, mapping and queries. As the complexity of modern applications increases, an understanding of JPA becomes critical. This article will help you understand the key concepts in JPA so that you can better apply them to actual projects.
@Entity
public class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
// 省略 getter 和 setter 方法
}Mapping
Mapping is the mechanism used by JPA to map properties in an entity class to fields in the database . JPA provides many types of mappings, including:
- One-to-one mapping: An attribute in an entity class corresponds to a column in the database table.
- One-to-many mapping: One attribute in an entity class corresponds to multiple columns in the database table.
- Many-to-one mapping: Multiple attributes in an entity class correspond to one column in the database table.
- Many-to-many mapping: Multiple attributes in an entity class correspond to multiple columns in the database table.
Mapping can also specify the attribute type, length, whether it is allowed to be empty, and other information.
@Entity
public class Person {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(length = 50, nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = false)
private int age;
// 省略 getter 和 setter 方法
}Inquire
JPA provides a variety of query mechanisms, including:
- JPQL (Java Persistence Query Language): A query language similar to sql that can be used to query entity objects.
- Criteria api: An object-oriented query API that can be used to query entity objects.
- Native query: Use native SQL to query the database.
// JPQL 查询
List<Person> persons = entityManager.createQuery("SELECT p FROM Person p WHERE p.age > 18", Person.class)
.getResultList();
// Criteria API 查询
CriteriaBuilder cb = entityManager.getCriteriaBuilder();
CriteriaQuery<Person> cq = cb.createQuery(Person.class);
Root<Person> root = cq.from(Person.class);
cq.select(root).where(cb.gt(root.get("age"), 18));
List<Person> persons = entityManager.createQuery(cq).getResultList();
// 本机查询
List<Person> persons = entityManager.createNativeQuery("SELECT * FROM Person WHERE age > 18", Person.class)
.getResultList();Summarize
JPA is a powerful persistence framework that provides unified access to relational databases. By using JPA, we can easily persist Java objects into the database and query entity objects using JPQL, Criteria API or native queries.
The above is the detailed content of Dive into the core concepts of Java JPA: entities, mappings, and queries. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com
Mar 28, 2024 pm 04:31 PM
How to check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com
Mar 28, 2024 pm 04:31 PM
How to check my academic qualifications on Xuexin.com? You can check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com, but many users don’t know how to check their academic qualifications on Xuexin.com. Next, the editor brings you a graphic tutorial on how to check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com. Interested users come and take a look! Xuexin.com usage tutorial: How to check your academic qualifications on Xuexin.com 1. Xuexin.com entrance: https://www.chsi.com.cn/ 2. Website query: Step 1: Click on the Xuexin.com address above to enter the homepage Click [Education Query]; Step 2: On the latest webpage, click [Query] as shown by the arrow in the figure below; Step 3: Then click [Login Academic Credit File] on the new page; Step 4: On the login page Enter the information and click [Login];
 12306 How to check historical ticket purchase records How to check historical ticket purchase records
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:11 PM
12306 How to check historical ticket purchase records How to check historical ticket purchase records
Mar 28, 2024 pm 03:11 PM
Download the latest version of 12306 ticket booking app. It is a travel ticket purchasing software that everyone is very satisfied with. It is very convenient to go wherever you want. There are many ticket sources provided in the software. You only need to pass real-name authentication to purchase tickets online. All users You can easily buy travel tickets and air tickets and enjoy different discounts. You can also start booking reservations in advance to grab tickets. You can book hotels or special car transfers. With it, you can go where you want to go and buy tickets with one click. Traveling is simpler and more convenient, making everyone's travel experience more comfortable. Now the editor details it online Provides 12306 users with a way to view historical ticket purchase records. 1. Open Railway 12306, click My in the lower right corner, and click My Order 2. Click Paid on the order page. 3. On the paid page
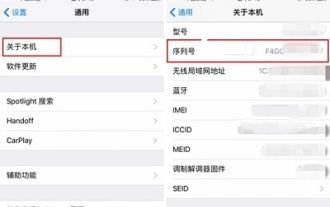 How to check the activation date on Apple mobile phone
Mar 08, 2024 pm 04:07 PM
How to check the activation date on Apple mobile phone
Mar 08, 2024 pm 04:07 PM
If you want to check the activation date using an Apple mobile phone, the best way is to check it through the serial number in the mobile phone. You can also check it by visiting Apple's official website, connecting it to a computer, and downloading third-party software to check it. How to check the activation date of Apple mobile phone Answer: Serial number query, Apple official website query, computer query, third-party software query 1. The best way for users is to know the serial number of their mobile phone. You can see the serial number by opening Settings, General, About This Machine. . 2. Using the serial number, you can not only know the activation date of your mobile phone, but also check the mobile phone version, mobile phone origin, mobile phone factory date, etc. 3. Users visit Apple's official website to find technical support, find the service and repair column at the bottom of the page, and check the iPhone activation information there. 4. User
 How to use Oracle to query whether a table is locked?
Mar 06, 2024 am 11:54 AM
How to use Oracle to query whether a table is locked?
Mar 06, 2024 am 11:54 AM
Title: How to use Oracle to query whether a table is locked? In Oracle database, table lock means that when a transaction is performing a write operation on the table, other transactions will be blocked when they want to perform write operations on the table or make structural changes to the table (such as adding columns, deleting rows, etc.). In the actual development process, we often need to query whether the table is locked in order to better troubleshoot and deal with related problems. This article will introduce how to use Oracle statements to query whether a table is locked, and give specific code examples. To check whether the table is locked, we
 Comparison of similarities and differences between MySQL and PL/SQL
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:15 AM
Comparison of similarities and differences between MySQL and PL/SQL
Mar 16, 2024 am 11:15 AM
MySQL and PL/SQL are two different database management systems, representing the characteristics of relational databases and procedural languages respectively. This article will compare the similarities and differences between MySQL and PL/SQL, with specific code examples to illustrate. MySQL is a popular relational database management system that uses Structured Query Language (SQL) to manage and operate databases. PL/SQL is a procedural language unique to Oracle database and is used to write database objects such as stored procedures, triggers and functions. same
 How to check the latest price of Tongshen Coin?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
How to check the latest price of Tongshen Coin?
Mar 21, 2024 pm 02:46 PM
How to check the latest price of Tongshen Coin? Token is a digital currency that can be used to purchase in-game items, services, and assets. It is decentralized, meaning it is not controlled by governments or financial institutions. Transactions of Tongshen Coin are conducted on the blockchain, which is a distributed ledger that records the information of all Tongshen Coin transactions. To check the latest price of Token, you can use the following steps: Choose a reliable price check website or app. Some commonly used price query websites include: CoinMarketCap: https://coinmarketcap.com/Coindesk: https://www.coindesk.com/ Binance: https://www.bin
 Discuz database location query skills sharing
Mar 10, 2024 pm 01:36 PM
Discuz database location query skills sharing
Mar 10, 2024 pm 01:36 PM
Forum is one of the most common website forms on the Internet. It provides users with a platform to share information, exchange and discuss. Discuz is a commonly used forum program, and I believe many webmasters are already very familiar with it. During the development and management of the Discuz forum, it is often necessary to query the data in the database for analysis or processing. In this article, we will share some tips for querying the location of the Discuz database and provide specific code examples. First, we need to understand the database structure of Discuz
 How to check the latest price of INJ coin?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
How to check the latest price of INJ coin?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Check the latest price of INJ coin. INJ coin is a decentralized finance (DeFi) token based on the Ethereum blockchain developed by InjectiveProtocol and aims to provide an efficient and transparent platform for derivatives transactions. Holders can use INJ coins to pay transaction fees, stake to receive rewards, and participate in the governance of InjectiveProtocol. The total amount of INJ tokens issued is limited, which gives it scarcity and the potential to store value. InjectiveProtocol’s vision is to promote broader financial inclusion through INJ tokens and provide users with an open, borderless financial services experience. The use of INJ tokens not only promotes the innovative development of the DeFi industry, but also provides users with






