
In natural language generation tasks, sampling method is a technique to obtain text output from a generative model. This article will discuss 5 common methods and implement them using PyTorch.
In greedy decoding, the generative model predicts the words of the output sequence based on the input sequence time step by time. At each time step, the model calculates the conditional probability distribution of each word, and then selects the word with the highest conditional probability as the output of the current time step. This word becomes the input to the next time step, and the generation process continues until some termination condition is met, such as a sequence of a specified length or a special end marker. The characteristic of Greedy Decoding is that each time the word with the highest current conditional probability is selected as the output, without considering the global optimal solution. This method is simple and efficient, but may result in generated sequences that are less accurate or diverse. Greedy Decoding is suitable for some simple sequence generation tasks, but for complex tasks, more complex decoding strategies may be needed to improve the quality of generation.
Although this method is faster in calculation, since greedy decoding only focuses on the local optimal solution, it may cause the generated text to lack diversity or be inaccurate, and the global optimal solution cannot be obtained.
Although greedy decoding has its limitations, it is still widely used in many sequence generation tasks, especially when fast execution is required or the task is relatively simple.
def greedy_decoding(input_ids, max_tokens=300): with torch.inference_mode(): for _ in range(max_tokens): outputs = model(input_ids) next_token_logits = outputs.logits[:, -1, :] next_token = torch.argmax(next_token_logits, dim=-1) if next_token == tokenizer.eos_token_id: break input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, rearrange(next_token, 'c -> 1 c')], dim=-1) generated_text = tokenizer.decode(input_ids[0]) return generated_text
Beam Search is an extension of greedy decoding, which is overcome by retaining multiple candidate sequences at each time step. Local optimal problem of greedy decoding.
Beam search is a method of generating text that retains the candidate words with the highest probability at each time step, and then continues to expand based on these candidate words at the next time step until the end of generation. This method can improve the diversity of generated text by considering multiple candidate word paths.
In beam search, the model generates multiple candidate sequences simultaneously instead of selecting just one best sequence. It predicts possible words at the next time step based on the currently generated partial sequence and hidden states, and calculates the conditional probability distribution of each word. This method of generating multiple candidate sequences in parallel helps improve search efficiency, allowing the model to more quickly find the sequence with the highest overall probability.
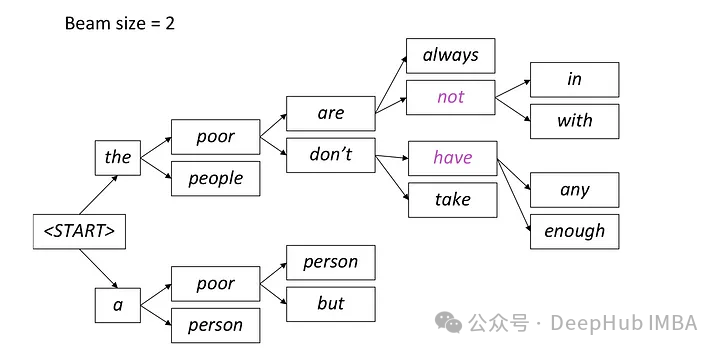
In each step, only the two most likely paths are retained, and the remaining paths are discarded according to the setting of beam = 2. This process continues until a stopping condition is met, either by generating an end-of-sequence token or reaching the maximum sequence length set by the model. The final output will be the sequence with the highest overall probability among the last set of paths.
from einops import rearrange import torch.nn.functional as F def beam_search(input_ids, max_tokens=100, beam_size=2): beam_scores = torch.zeros(beam_size).to(device) beam_sequences = input_ids.clone() active_beams = torch.ones(beam_size, dtype=torch.bool) for step in range(max_tokens): outputs = model(beam_sequences) logits = outputs.logits[:, -1, :] probs = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1) top_scores, top_indices = torch.topk(probs.flatten(), k=beam_size, sorted=False) beam_indices = top_indices // probs.shape[-1] token_indices = top_indices % probs.shape[-1] beam_sequences = torch.cat([ beam_sequences[beam_indices], token_indices.unsqueeze(-1)], dim=-1) beam_scores = top_scores active_beams = ~(token_indices == tokenizer.eos_token_id) if not active_beams.any(): print("no active beams") break best_beam = beam_scores.argmax() best_sequence = beam_sequences[best_beam] generated_text = tokenizer.decode(best_sequence) return generated_textTemperature parameter sampling (Temperature Sampling) is often used in probability-based generative models, such as language models. It controls the diversity of generated text by introducing a parameter called "Temperature" to adjust the probability distribution of model output.
In temperature parameter sampling, when the model generates words at each time step, it will calculate the conditional probability distribution of the words. The model then divides the probability value of each word in this conditional probability distribution by the temperature parameter, normalizes the result, and obtains a new normalized probability distribution. Higher temperature values make the probability distribution smoother, thus increasing the diversity of the generated text. Low-probability words also have a higher probability of being selected; while a lower temperature value will make the probability distribution more concentrated and more likely to select high-probability words, so the generated text is more deterministic. Finally, the model randomly samples according to this new normalized probability distribution and selects the generated words.
import torch import torch.nn.functional as F def temperature_sampling(logits, temperature=1.0): logits = logits / temperature probabilities = F.softmax(logits, dim=-1) sampled_token = torch.multinomial(probabilities, 1) return sampled_token.item()
Top-K Sampling (select the top K words with conditional probability ranking at each time step, and then select the top K words in these K words Random sampling is performed in the process. This method can not only maintain a certain generation quality, but also increase the diversity of the text, and can control the diversity of the generated text by limiting the number of candidate words.
This process makes the generation While maintaining a certain generation quality, the text also has a certain diversity, because there is still a certain degree of competition among the candidate words.
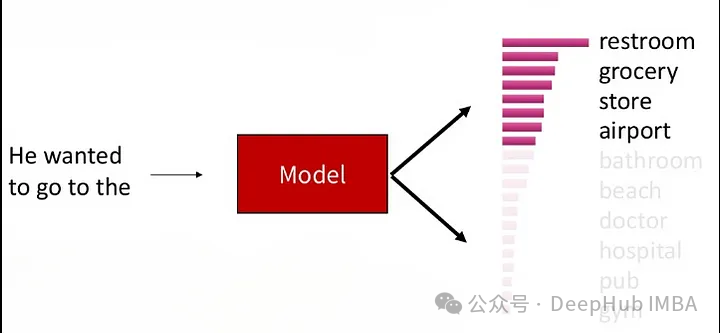
Parameter K controls the The number of candidate words to retain at each time step. Smaller K values will lead to more greedy behavior, because only a few words participate in random sampling, while larger K values will increase the diversity of the generated text, but also Will increase computational overhead.
def top_k_sampling(input_ids, max_tokens=100, top_k=50, temperature=1.0):for _ in range(max_tokens): with torch.inference_mode(): outputs = model(input_ids) next_token_logits = outputs.logits[:, -1, :] top_k_logits, top_k_indices = torch.topk(next_token_logits, top_k) top_k_probs = F.softmax(top_k_logits / temperature, dim=-1) next_token_index = torch.multinomial(top_k_probs, num_samples=1) next_token = top_k_indices.gather(-1, next_token_index) input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_token], dim=-1) generated_text = tokenizer.decode(input_ids[0]) return generated_text
Nucleus Sampling(核采样),也被称为Top-p Sampling旨在在保持生成文本质量的同时增加多样性。这种方法可以视作是Top-K Sampling的一种变体,它在每个时间步根据模型输出的概率分布选择概率累积超过给定阈值p的词语集合,然后在这个词语集合中进行随机采样。这种方法会动态调整候选词语的数量,以保持一定的文本多样性。

在Nucleus Sampling中,模型在每个时间步生成词语时,首先按照概率从高到低对词汇表中的所有词语进行排序,然后模型计算累积概率,并找到累积概率超过给定阈值p的最小词语子集,这个子集就是所谓的“核”(nucleus)。模型在这个核中进行随机采样,根据词语的概率分布来选择最终输出的词语。这样做可以保证所选词语的总概率超过了阈值p,同时也保持了一定的多样性。
参数p是Nucleus Sampling中的重要参数,它决定了所选词语的概率总和。p的值会被设置在(0,1]之间,表示词语总概率的一个下界。
Nucleus Sampling 能够保持一定的生成质量,因为它在一定程度上考虑了概率分布。通过选择概率总和超过给定阈值p的词语子集进行随机采样,Nucleus Sampling 能够增加生成文本的多样性。
def top_p_sampling(input_ids, max_tokens=100, top_p=0.95): with torch.inference_mode(): for _ in range(max_tokens): outputs = model(input_ids) next_token_logits = outputs.logits[:, -1, :] sorted_logits, sorted_indices = torch.sort(next_token_logits, descending=True) sorted_probabilities = F.softmax(sorted_logits, dim=-1) cumulative_probs = torch.cumsum(sorted_probabilities, dim=-1) sorted_indices_to_remove = cumulative_probs > top_p sorted_indices_to_remove[..., 0] = False indices_to_remove = sorted_indices[sorted_indices_to_remove] next_token_logits.scatter_(-1, indices_to_remove[None, :], float('-inf')) probs = F.softmax(next_token_logits, dim=-1) next_token = torch.multinomial(probs, num_samples=1) input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_token], dim=-1) generated_text = tokenizer.decode(input_ids[0]) return generated_text自然语言生成任务中,采样方法是非常重要的。选择合适的采样方法可以在一定程度上影响生成文本的质量、多样性和效率。上面介绍的几种采样方法各有特点,适用于不同的应用场景和需求。
贪婪解码是一种简单直接的方法,适用于速度要求较高的情况,但可能导致生成文本缺乏多样性。束搜索通过保留多个候选序列来克服贪婪解码的局部最优问题,生成的文本质量更高,但计算开销较大。Top-K 采样和核采样可以控制生成文本的多样性,适用于需要平衡质量和多样性的场景。温度参数采样则可以根据温度参数灵活调节生成文本的多样性,适用于需要平衡多样性和质量的任务。
The above is the detailed content of Introduction to five sampling methods in natural language generation tasks and Pytorch code implementation. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Application of artificial intelligence in life
Application of artificial intelligence in life
 What is the basic concept of artificial intelligence
What is the basic concept of artificial intelligence
 what does title mean
what does title mean
 How to obtain the serial number of a physical hard disk under Windows
How to obtain the serial number of a physical hard disk under Windows
 array_push
array_push
 antivirus software
antivirus software
 What is the working principle and process of mybatis
What is the working principle and process of mybatis
 HTML to create web pages
HTML to create web pages
 What is the difference between USB-C and TYPE-C
What is the difference between USB-C and TYPE-C




