Java Kubernetes vs. Java: A Complete Guide from Beginner to Mastery

kubernetes Introduction
"Java Kubernetes and Java: A Complete Guide from Beginner to Master" recommended by php editor Zimo is a guide that comprehensively introduces Java and Kubernetes. This book explains the relevant knowledge of Java and Kubernetes in detail from entry to mastery, helping readers quickly master the skills in these two fields. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced developer, you can benefit from it. This guide will provide you with a comprehensive and systematic learning path, allowing you to easily master the practical skills of Java and Kubernetes.
Why use Kubernetes
Kubernetes offers a range of advantages that make it ideal for managing containerized applications:
- Resource Scheduling: Kubernetes can automatically discover and schedule containers, and allocate resources according to the needs of the application to ensure the stable operation of the application.
- Service Discovery: Kubernetes provides a unified entry point for containers so that applications can easily discover and connect to other services.
- Load balancing: Kubernetes can automatically adjust the number of copies of containers based on application traffic to ensure the stability and availability of services.
- Storage orchestration: Kubernetes supports a variety of storage systems and provides persistent storage volumes for applications to ensure application data security and recoverability.
- Network management: Kubernetes provides a powerful set of network management functions, including network policies, service mesh, etc., helping developers easily build safe and reliable network architecture.
Java Kubernetes Getting Started
1. Install Kubernetes
The installation process for Kubernetes varies depending on the operating system. For linux users, you can use kubeadm or kubespray and other tools to install. For windows users, you can use Docker Desktop and other tools to install.
2. Create Kubernetes Cluster
After creating a Kubernetes cluster, you can use the kubectl command line tool to manage resources in the cluster. kubectl is the command line client for Kubernetes, used to create, modify, and delete resources in the cluster.
3. Deploying Java applications
To deploy a Java application to a Kubernetes cluster, you can use the following steps:
- Package Java applications as container images.
- Push the container image to the image warehouse.
- Create resources such as Deployment or Service in the Kubernetes cluster and specify the container image to be deployed.
- Use the kubectl command line tool to monitor and manage the running status of the application.
4. Manage Kubernetes cluster
Kubernetes clusters require regular maintenance and management to ensure the stability and security of the cluster. You can use the kubectl command line tool to perform the following operations:
- Check the usage of cluster resources.
- Upgrade Kubernetes version.
- Back up and restore cluster data.
- Manage the security and access control of the cluster.
5. Java Kubernetes Advanced
Once you have mastered the basics of Kubernetes, you can further learn the following:
- Use Helm to manage Kubernetes applications.
- Use Istio to build a service mesh.
- Use prometheus and Grafana Monitor Kubernetes cluster.
- Build serverless applications using Knative.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between Kubernetes and Docker?
Kubernetes is a container orchestration system used to manage the deployment and operation of containerized applications. Docker is a container engine used to create and manage container images.
2. What languages does Kubernetes support?
Kubernetes is a language-agnostic system that supports any language that can run in a container, including Java, python, c , etc.
3. Does Kubernetes support Windows?
Yes, Kubernetes supports Windows. However, Windows supports relatively few Kubernetes versions.
Summarize
Kubernetes is a powerful container orchestration system that provides Java developers with rich features to help them easily build and manage distributed applications. This article provides an introductory guide to Kubernetes to help Java developers learn Kubernetes from scratch and apply it to the deployment and management of applications.
The above is the detailed content of Java Kubernetes vs. Java: A Complete Guide from Beginner to Mastery. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
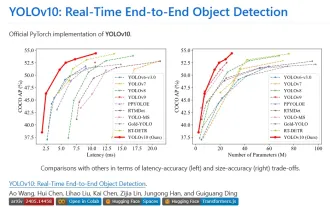 Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
1. Introduction Over the past few years, YOLOs have become the dominant paradigm in the field of real-time object detection due to its effective balance between computational cost and detection performance. Researchers have explored YOLO's architectural design, optimization goals, data expansion strategies, etc., and have made significant progress. At the same time, relying on non-maximum suppression (NMS) for post-processing hinders end-to-end deployment of YOLO and adversely affects inference latency. In YOLOs, the design of various components lacks comprehensive and thorough inspection, resulting in significant computational redundancy and limiting the capabilities of the model. It offers suboptimal efficiency, and relatively large potential for performance improvement. In this work, the goal is to further improve the performance efficiency boundary of YOLO from both post-processing and model architecture. to this end
 Do Laravel and CodeIgniter support cloud platform deployment?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 01:51 PM
Do Laravel and CodeIgniter support cloud platform deployment?
Jun 05, 2024 pm 01:51 PM
Both Laravel and CodeIgniter support cloud platform deployment. Laravel provides native support out of the box, simplifying the deployment process. CodeIgniter requires additional configuration and modifications to run in a cloud environment.
 How does the Java framework support horizontal scaling of microservices?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
How does the Java framework support horizontal scaling of microservices?
Jun 04, 2024 pm 04:34 PM
The Java framework supports horizontal expansion of microservices. Specific methods include: Spring Cloud provides Ribbon and Feign for server-side and client-side load balancing. NetflixOSS provides Eureka and Zuul to implement service discovery, load balancing and failover. Kubernetes simplifies horizontal scaling with autoscaling, health checks, and automatic restarts.
 PHP Frameworks and Microservices: Cloud Native Deployment and Containerization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
PHP Frameworks and Microservices: Cloud Native Deployment and Containerization
Jun 04, 2024 pm 12:48 PM
Benefits of combining PHP framework with microservices: Scalability: Easily extend the application, add new features or handle more load. Flexibility: Microservices are deployed and maintained independently, making it easier to make changes and updates. High availability: The failure of one microservice does not affect other parts, ensuring higher availability. Practical case: Deploying microservices using Laravel and Kubernetes Steps: Create a Laravel project. Define microservice controllers. Create Dockerfile. Create a Kubernetes manifest. Deploy microservices. Test microservices.
 What are the challenges in building a microservices architecture using Java frameworks?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 03:22 PM
What are the challenges in building a microservices architecture using Java frameworks?
Jun 02, 2024 pm 03:22 PM
Building a microservice architecture using a Java framework involves the following challenges: Inter-service communication: Choose an appropriate communication mechanism such as REST API, HTTP, gRPC or message queue. Distributed data management: Maintain data consistency and avoid distributed transactions. Service discovery and registration: Integrate mechanisms such as SpringCloudEureka or HashiCorpConsul. Configuration management: Use SpringCloudConfigServer or HashiCorpVault to centrally manage configurations. Monitoring and observability: Integrate Prometheus and Grafana for indicator monitoring, and use SpringBootActuator to provide operational indicators.
 Create distributed systems using the Golang microservices framework
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Create distributed systems using the Golang microservices framework
Jun 05, 2024 pm 06:36 PM
Create a distributed system using the Golang microservices framework: Install Golang, choose a microservices framework (such as Gin), create a Gin microservice, add endpoints to deploy the microservice, build and run the application, create an order and inventory microservice, use the endpoint to process orders and inventory Use messaging systems such as Kafka to connect microservices Use the sarama library to produce and consume order information
 Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in Java framework
Jun 02, 2024 pm 12:39 PM
Microservice architecture monitoring and alarming in the Java framework In the microservice architecture, monitoring and alarming are crucial to ensuring system health and reliable operation. This article will introduce how to use Java framework to implement monitoring and alarming of microservice architecture. Practical case: Use SpringBoot+Prometheus+Alertmanager1. Integrate Prometheus@ConfigurationpublicclassPrometheusConfig{@BeanpublicSpringBootMetricsCollectorspringBootMetric
 PHP framework and microservices: data consistency and transaction management
Jun 02, 2024 pm 04:59 PM
PHP framework and microservices: data consistency and transaction management
Jun 02, 2024 pm 04:59 PM
In PHP microservice architecture, data consistency and transaction management are crucial. The PHP framework provides mechanisms to implement these requirements: use transaction classes, such as DB::transaction in Laravel, to define transaction boundaries. Use an ORM framework, such as Doctrine, to provide atomic operations such as the lock() method to prevent concurrency errors. For distributed transactions, consider using a distributed transaction manager such as Saga or 2PC. For example, transactions are used in online store scenarios to ensure data consistency when adding to a shopping cart. Through these mechanisms, the PHP framework effectively manages transactions and data consistency, improving application robustness.






