Quick terminal session sharing tool:tmate
tmate means teammates, which is a fork of tmux and uses the same configuration information (such as shortcut key configuration, color scheme, etc.). It is a terminal multiplexer with the ability to share terminals on the fly. It allows the creation and manipulation of multiple terminals from a single screen, which can also be shared with other colleagues.
You can detach the session, let the job run in the background, and then reconnect to the session when you want to view the status. tmate provides an instant pairing solution that allows you to share a terminal with one or more teammates.
There is a status bar on the screen, which displays some shared information of the current session such as ssh commands.
When running tmate, an ssh connection to tmate.io (the backend server maintained by the tmate developer) will be created in the background through libssh.
The tmate.io server's ssh keys are verified via a DH exchange.
Clients authenticate via local ssh keys.
After the connection is created, the local tmux server generates a 150-bit (unguessable random characters) session token.
Teammates can connect to tmate.io via a user-supplied SSH session ID.
Since the tmate.io server requires a local ssh key to authenticate the client, one of the prerequisites is to generate an SSH key. Remember, each system needs its own SSH key.
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa Generating public/private rsa key pair. Enter file in which to save the key (/home/magi/.ssh/id_rsa): Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase): Enter same passphrase again: Your identification has been saved in /home/magi/.ssh/id_rsa. Your public key has been saved in /home/magi/.ssh/id_rsa.pub. The key fingerprint is: SHA256:3ima5FuwKbWyyyNrlR/DeBucoyRfdOtlUmb5D214NC8 magi@magi-VirtualBox The key's randomart image is: +---[RSA 2048]----+ | | | | | . | | . . = o | | *ooS= . + o | | . =.@*o.o.+ E .| | =o==B++o = . | | o.+*o+.. . | | ..o+o=. | +----[SHA256]-----+
tmate is already included in the official repositories of some distributions and can be installed through the package manager.
For Debian/Ubuntu, you can use the APT-GET command or the APT command to install.
$ sudo apt-get install software-properties-common $ sudo add-apt-repository ppa:tmate.io/archive $ sudo apt-get update $ sudo apt-get install tmate
You can also install tmate from the official repository.
$ sudo apt-get install tmate
For Fedora, use the DNF command to install.
$ sudo dnf install tmate
For systems based on Arch Linux, use the Yaourt command or the Packer command to install from the AUR repository.
$ yaourt -S tmate
or
$ packer -S tmate
For openSUSE, use the Zypper command to install.
$ sudo zypper in tmate
After successful installation, open a terminal and enter the following command. A new session will open. At the bottom of the screen, you can see the SSH session ID.
$ tmate <img src="/static/imghw/default1.png" data-src="https://img.php.cn/upload/article/000/465/014/170839825763674.png" class="lazy" alt="Quick terminal session sharing tool:tmate">
It should be noted that the SSH session ID will disappear after a few seconds, but it does not matter, you can obtain these details through the following command.
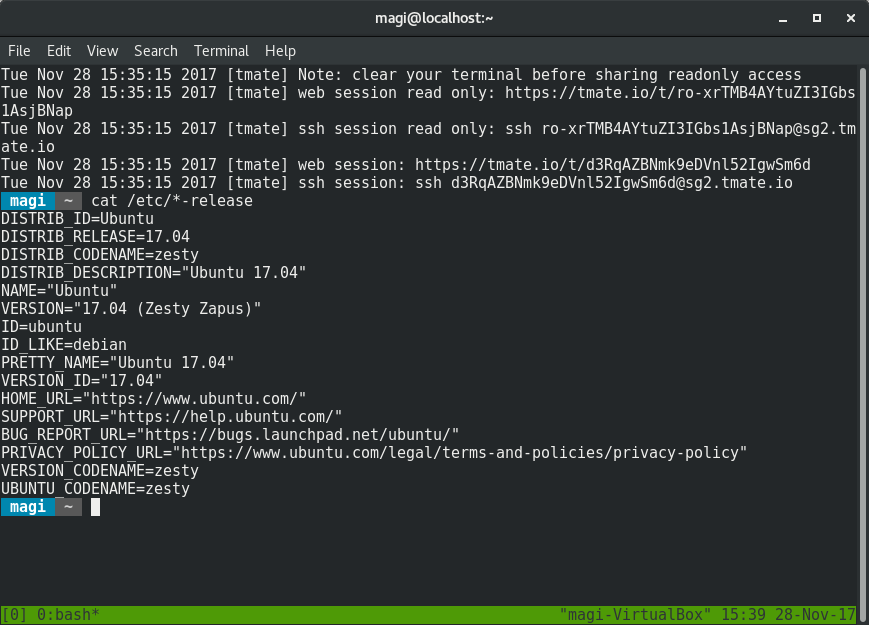
$ tmate show-messages
The show-messages command of tmate will display the log information of tmate, which contains the content of the ssh connection.
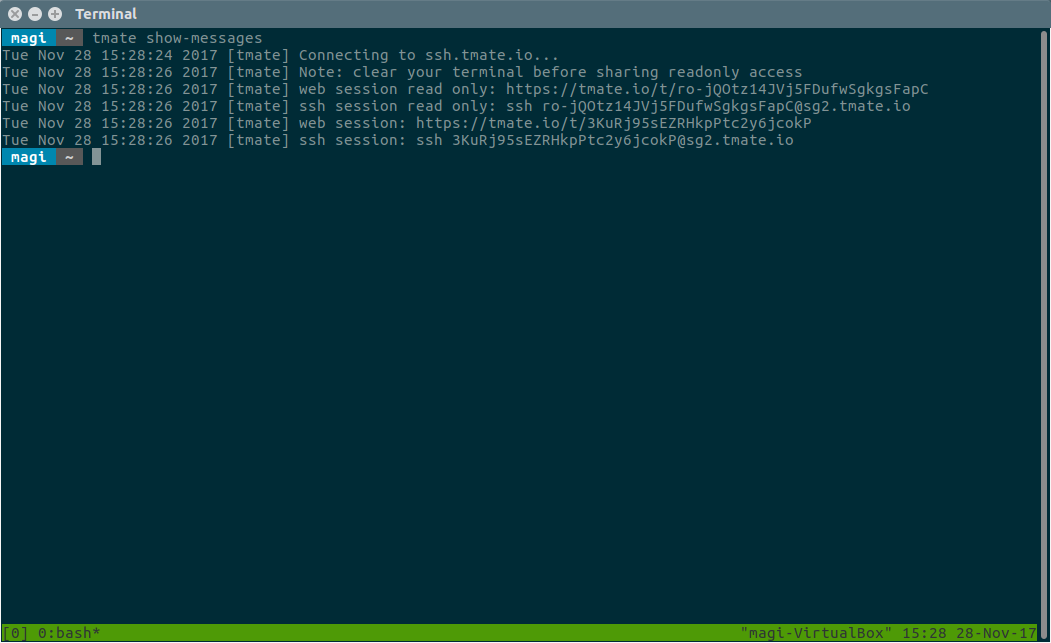
Now, share your SSH session ID with your friends or colleagues to allow them to view the terminal session. In addition to the SSH session ID, you can also share the web URL.
In addition, you can also choose whether to share a read-only session or a read-write session.
Just run the SSH terminal ID you got from your friend on the terminal. Something like this.
$ ssh session: ssh [email protected]
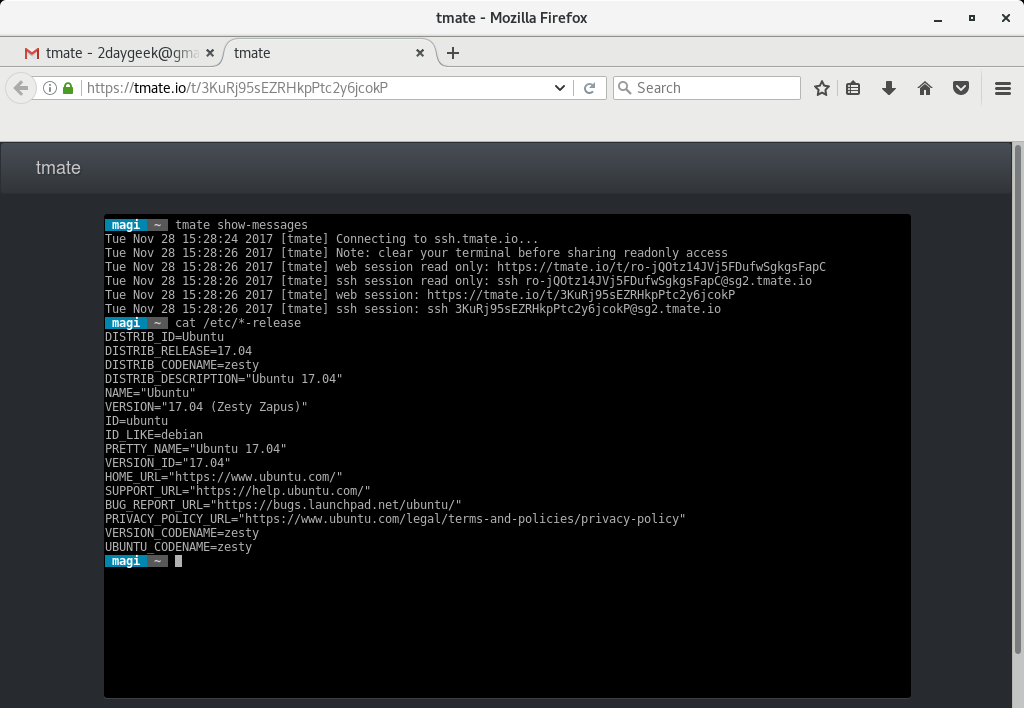
Just open the browser and visit the URL your friend gave you. Like below.
Just enter exit to exit the session.
[Source System Output] [exited] [Remote System Output] [server exited] Connection to sg2.tmate.io closed by remote host。 Connection to sg2.tmate.io closed。
The above is the detailed content of Quick terminal session sharing tool:tmate. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use docker desktop
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:45 AM
How to use Docker Desktop? Docker Desktop is a tool for running Docker containers on local machines. The steps to use include: 1. Install Docker Desktop; 2. Start Docker Desktop; 3. Create Docker image (using Dockerfile); 4. Build Docker image (using docker build); 5. Run Docker container (using docker run).
 Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
Difference between centos and ubuntu
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:09 PM
The key differences between CentOS and Ubuntu are: origin (CentOS originates from Red Hat, for enterprises; Ubuntu originates from Debian, for individuals), package management (CentOS uses yum, focusing on stability; Ubuntu uses apt, for high update frequency), support cycle (CentOS provides 10 years of support, Ubuntu provides 5 years of LTS support), community support (CentOS focuses on stability, Ubuntu provides a wide range of tutorials and documents), uses (CentOS is biased towards servers, Ubuntu is suitable for servers and desktops), other differences include installation simplicity (CentOS is thin)
 What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
What to do if the docker image fails
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:21 AM
Troubleshooting steps for failed Docker image build: Check Dockerfile syntax and dependency version. Check if the build context contains the required source code and dependencies. View the build log for error details. Use the --target option to build a hierarchical phase to identify failure points. Make sure to use the latest version of Docker engine. Build the image with --t [image-name]:debug mode to debug the problem. Check disk space and make sure it is sufficient. Disable SELinux to prevent interference with the build process. Ask community platforms for help, provide Dockerfiles and build log descriptions for more specific suggestions.
 How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to view the docker process
Apr 15, 2025 am 11:48 AM
Docker process viewing method: 1. Docker CLI command: docker ps; 2. Systemd CLI command: systemctl status docker; 3. Docker Compose CLI command: docker-compose ps; 4. Process Explorer (Windows); 5. /proc directory (Linux).
 What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
What computer configuration is required for vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
VS Code system requirements: Operating system: Windows 10 and above, macOS 10.12 and above, Linux distribution processor: minimum 1.6 GHz, recommended 2.0 GHz and above memory: minimum 512 MB, recommended 4 GB and above storage space: minimum 250 MB, recommended 1 GB and above other requirements: stable network connection, Xorg/Wayland (Linux)
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
vscode cannot install extension
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
The reasons for the installation of VS Code extensions may be: network instability, insufficient permissions, system compatibility issues, VS Code version is too old, antivirus software or firewall interference. By checking network connections, permissions, log files, updating VS Code, disabling security software, and restarting VS Code or computers, you can gradually troubleshoot and resolve issues.




