 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
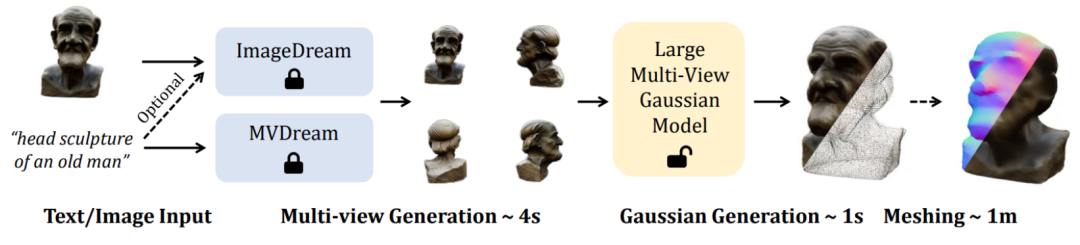
 Large multi-view Gaussian model LGM: produces high-quality 3D objects in 5 seconds, available for trial play
Large multi-view Gaussian model LGM: produces high-quality 3D objects in 5 seconds, available for trial play
Large multi-view Gaussian model LGM: produces high-quality 3D objects in 5 seconds, available for trial play
В ответ на продолжающийся рост спроса на инструменты 3D-творчества в Метавселенной в последнее время наблюдается большой интерес к созданию трехмерного контента (3D AIGC). В то же время создание 3D-контента также значительно продвинулось по качеству и скорости.
Хотя текущие генеративные модели с прямой связью могут генерировать 3D-объекты за секунды, их разрешение ограничено интенсивными вычислениями, необходимыми во время обучения, что приводит к низкому качеству генерации Контента. Возникает вопрос: можно ли создать высококачественный 3D-объект с высоким разрешением всего за 5 секунд?

В этой статье исследователи из Пекинского университета, Наньянского технологического университета S-Lab и Шанхайской лаборатории искусственного интеллекта предложили
новую структуру LGM , а именно Большая Гауссова Модель, позволяет создавать трехмерные объекты высокого разрешения и высокого качества из однопросмотровых изображений или ввода текста всего за 5 секунд.
В настоящее время код и веса модели находятся в открытом исходном коде. Исследователи также предоставляют онлайн-демонстрацию, которую каждый может попробовать. 
- ##Название статьи: LGM: Большая многоракурсная гауссова модель для создания 3D-контента высокого разрешения
- Домашняя страница проекта: https://me.kiui.moe/lgm/
- Код: https://github.com/3DTopia/LGM
- Документ: https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.05054
- Онлайн-демо: https://huggingface.co/spaces/ashawkey/LGM
Для достижения такой цели исследователи сталкиваются со следующими двумя проблемами:
При ограниченном объеме вычислений Эффективное трехмерное представление : Существующие работы по созданию 3D-изображений используют NeRF на основе трех плоскостей в качестве конвейера трехмерного представления и рендеринга, что значительно ограничивает плотное моделирование сцены и технологию объемного рендеринга с трассировкой лучей. Его разрешение обучения ( 128×128) делает текстуру окончательно сгенерированного контента размытой и некачественной.
3D-магистральная сеть генерации с высоким разрешением
#: Существующая работа по 3D-генерации использует плотные трансформаторы в качестве магистральной сети для обеспечения достаточной плотности Количество параметры используются для моделирования универсальных объектов, но это в определенной степени жертвует разрешением обучения, что приводит к низкому качеству конечного трехмерного объекта.
С этой целью в данной статье предлагается новый метод синтеза трехмерных представлений высокого разрешения из четырехракурсных изображений, а затем Перспективных изображений или одно- преобразование изображения в многоракурсные модели изображений для поддержки высококачественных задач преобразования текста в 3D и изображения в 3D.
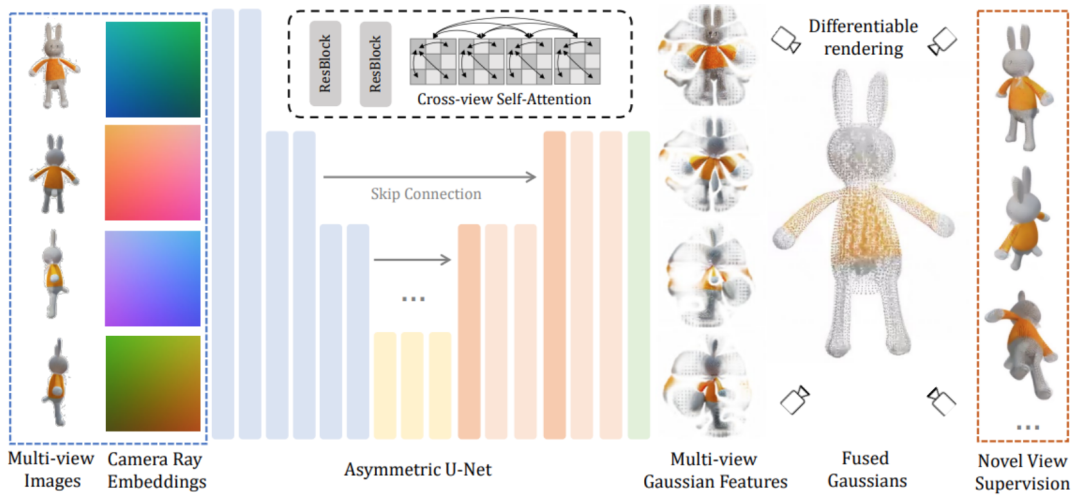
##########################Технически ###LGM основной модуль представляет собой большую многовидовую гауссову модель###. Вдохновленный гауссовским распылением, этот метод использует эффективную и легкую асимметричную сеть U-Net в качестве магистральной сети для прямого прогнозирования гауссовских примитивов высокого разрешения на основе четырехракурсных изображений и, наконец, рендеринга изображений под любым углом обзора. ############ В частности, магистральная сеть U-Net принимает изображения с четырех точек зрения и соответствующие координаты Плакера и выводит фиксированное количество гауссовских функций с нескольких точек зрения. Этот набор гауссовских функций напрямую объединяется с конечным гауссовским элементом, и изображения под разными углами обзора получаются посредством дифференцируемого рендеринга. ############В этом процессе используется механизм перекрестного просмотра для достижения корреляционного моделирования между различными представлениями на картах объектов с низким разрешением, сохраняя при этом меньшие вычислительные затраты. #####################Стоит отметить, что эффективно обучить такую модель в высоком разрешении непросто. Чтобы добиться надежного обучения, исследователи по-прежнему сталкиваются со следующими двумя проблемами. ######First, the three-dimensional consistent multi-view images rendered in the objaverse data set are used in the training phase, while in the inference phase, existing models are directly used to synthesize multi-perspective images from text or images. Since multi-view pictures synthesized based on the model always have the problem of multi-view inconsistency, in order to bridge the gap in this domain, this article proposes a data enhancement strategy based on grid distortion: in the image space, images from three views are Apply random distortion to simulate multi-view inconsistencies.
The second reason is that the multi-view images generated in the inference stage do not strictly guarantee the consistency of the three-dimensional geometry of the camera perspective, so this article also randomly perturbs the camera poses from the three perspectives To simulate this phenomenon, make the model more robust in the inference stage.
Finally, the generated Gaussian primitives are rendered into corresponding images through differentiable rendering, and learned directly end-to-end on the two-dimensional images through supervised learning.
After training is completed, LGM can achieve high-quality Text-to-3D and Image-to-3D through the existing image-to-multi-view or text-to-multi-view diffusion model. Task.

Given the same input text or image, this method can generate a variety of high-quality 3D models.

In order to further support downstream graphics tasks, the researchers also proposed an efficient method to convert the generated Gaussian representation into a smooth and banded representation. Texture Mesh:
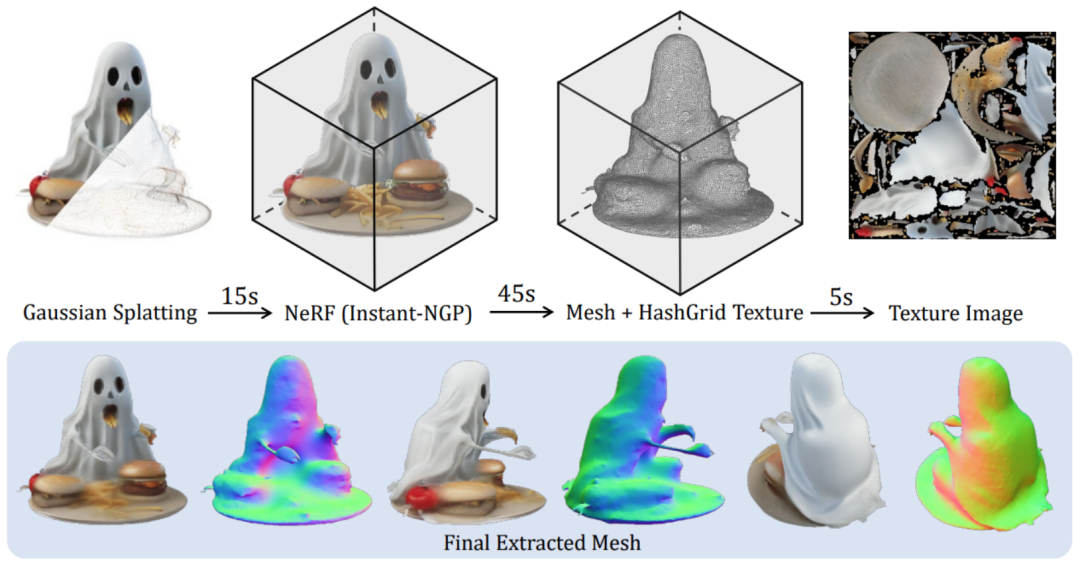
Please refer to the original paper for more details.
The above is the detailed content of Large multi-view Gaussian model LGM: produces high-quality 3D objects in 5 seconds, available for trial play. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Installing MySQL on CentOS involves the following steps: Adding the appropriate MySQL yum source. Execute the yum install mysql-server command to install the MySQL server. Use the mysql_secure_installation command to make security settings, such as setting the root user password. Customize the MySQL configuration file as needed. Tune MySQL parameters and optimize databases for performance.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to choose a GitLab database in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:39 PM
How to choose a GitLab database in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:39 PM
When installing and configuring GitLab on a CentOS system, the choice of database is crucial. GitLab is compatible with multiple databases, but PostgreSQL and MySQL (or MariaDB) are most commonly used. This article analyzes database selection factors and provides detailed installation and configuration steps. Database Selection Guide When choosing a database, you need to consider the following factors: PostgreSQL: GitLab's default database is powerful, has high scalability, supports complex queries and transaction processing, and is suitable for large application scenarios. MySQL/MariaDB: a popular relational database widely used in Web applications, with stable and reliable performance. MongoDB:NoSQL database, specializes in
 How to operate distributed training of PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
How to operate distributed training of PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
PyTorch distributed training on CentOS system requires the following steps: PyTorch installation: The premise is that Python and pip are installed in CentOS system. Depending on your CUDA version, get the appropriate installation command from the PyTorch official website. For CPU-only training, you can use the following command: pipinstalltorchtorchvisiontorchaudio If you need GPU support, make sure that the corresponding version of CUDA and cuDNN are installed and use the corresponding PyTorch version for installation. Distributed environment configuration: Distributed training usually requires multiple machines or single-machine multiple GPUs. Place



