 web3.0
web3.0
 Annual overview of the Cosmos ecosystem: well-known projects emerge and core developers continue to grow
Annual overview of the Cosmos ecosystem: well-known projects emerge and core developers continue to grow
Annual overview of the Cosmos ecosystem: well-known projects emerge and core developers continue to grow
Original author: Xangle
Original compilation: Felix, PANews
2023 In 2016, the Cosmos ecosystem grew rapidly, and its unique interoperability and modular structure attracted a large number of developers and projects, bringing new possibilities to blockchain technology.
This article will explore the major changes, technology updates, and new projects within the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023. At the same time, there will also be an in-depth study of technological advancements and market changes in the Cosmos ecosystem, as well as Cosmos' redefinition of the existing blockchain paradigm.
1. Infrastructure
1.1 Major update of Cosmos SDK
The modules managed by Cosmos SDK are mainly used to develop chains in the Cosmos ecosystem. Below are the major updates to the SDK released in 2023.
Version 0.47 Update
CometBFT has been upgraded to the latest version 0.47, as a new branch of the Tendermint consensus engine, now included in the Cosmos SDK. This update does not introduce major changes and is mainly designed to support the smooth migration of blockchains previously using Tendermint to CometBFT.
Version 0.50 Update
ABCI 2.0: ABCI is the interface responsible for data exchange between the consensus engine and the application layer responsible for different functions on the chain. The consensus engine CometBFT (Tendermint) is responsible for block generation and transaction broadcasting, which is the process of determining the order of transactions. Due to the design of ABCI, there are limitations in processing transactions in the required order in the mempool. To overcome this problem, ABCI 2.0 adds a new process called "PrepareProposal" to determine the order of transactions in the mempool and pass it to CometBFT.
Optimistic Execution: In the previous Cosmos SDK, all validators needed to reach consensus to execute transactions and submit the results to the chain. This move slowed down the execution of transactions, and to overcome this issue, a feature called “Optimistic Execution” was introduced. This feature allows transactions to be executed and submitted without the consent of all validators, thereby increasing transaction throughput.
SDK Modules: The Cosmos SDK contains various modules for application development. Previously, each module's update followed the updated version of the SDK, so it was difficult to track the update history of each module. In version 0.50, version control of each module is implemented independently, making it easier to track update records. In addition, the data storage model Store and IAVL have been decoupled so that they can be updated independently.
1.2 Cosmos on Metamask
Since there are multiple chains in the Cosmos ecosystem, each chain has an independent address even if the mnemonic words are the same. Although the Keplr wallet is currently used for integration and management, it requires the use of a new wallet application, providing a poor user experience and raising the barrier to entry.
Cosmos is working on projects to solve this problem. Against this background, Metamask implements full support for Snap, allowing custom features to be added to Metamask. Transactions can now be created on Cosmos-based chains, including Leap wallets. In other words, the technical foundation has been laid, and users familiar with EVM-based chains can be more easily attracted to the Cosmos ecosystem.
##Leap Wallet(https://cosmos.leapwallet.io/portfolio/overview)
1.3 MultiVM
Unfortunately, the Cosmos SDK does not support virtual machines for smart contracts. Therefore, several projects have emerged to develop virtual machines that have been verified and used in other blockchains, or there are projects to develop virtual machines unique to the Cosmos ecosystem. Some people have tried to integrate various virtual machines (such as EVM, WasmVM, SolanaVM, MoveVM, etc.) with the Cosmos SDK, and have highly praised some virtual machines. If more commonly used virtual machines are supported, it will be easier for dApp developers to enter the Cosmos ecosystem. 2. ProjectsThe following are some interesting and eye-catching projects that will appear in the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023.2.1 Celestia
The most popular project in the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023 is undoubtedly Celestia. Celestia is a representative modular blockchain project that roughly divides the functions of the blockchain into four parts:Execution: The ability to process transactions and change chain state.
Settlement: Verify transactions processed by the computing layer.
Data Availability: Stores information from transactions and blocks and ensures it is always available.
Consensus: The ability to determine transaction validity or the order in which transactions are included in a block
Among these features, Celestia focuses on Data availability. The combination of Celestia and the word "L2" triggered the Rollup craze in the Cosmos ecosystem. For this purpose, a framework called "Rollkit" has been created and supported, which supports ABCI between Celestia and Cosmos SDK.
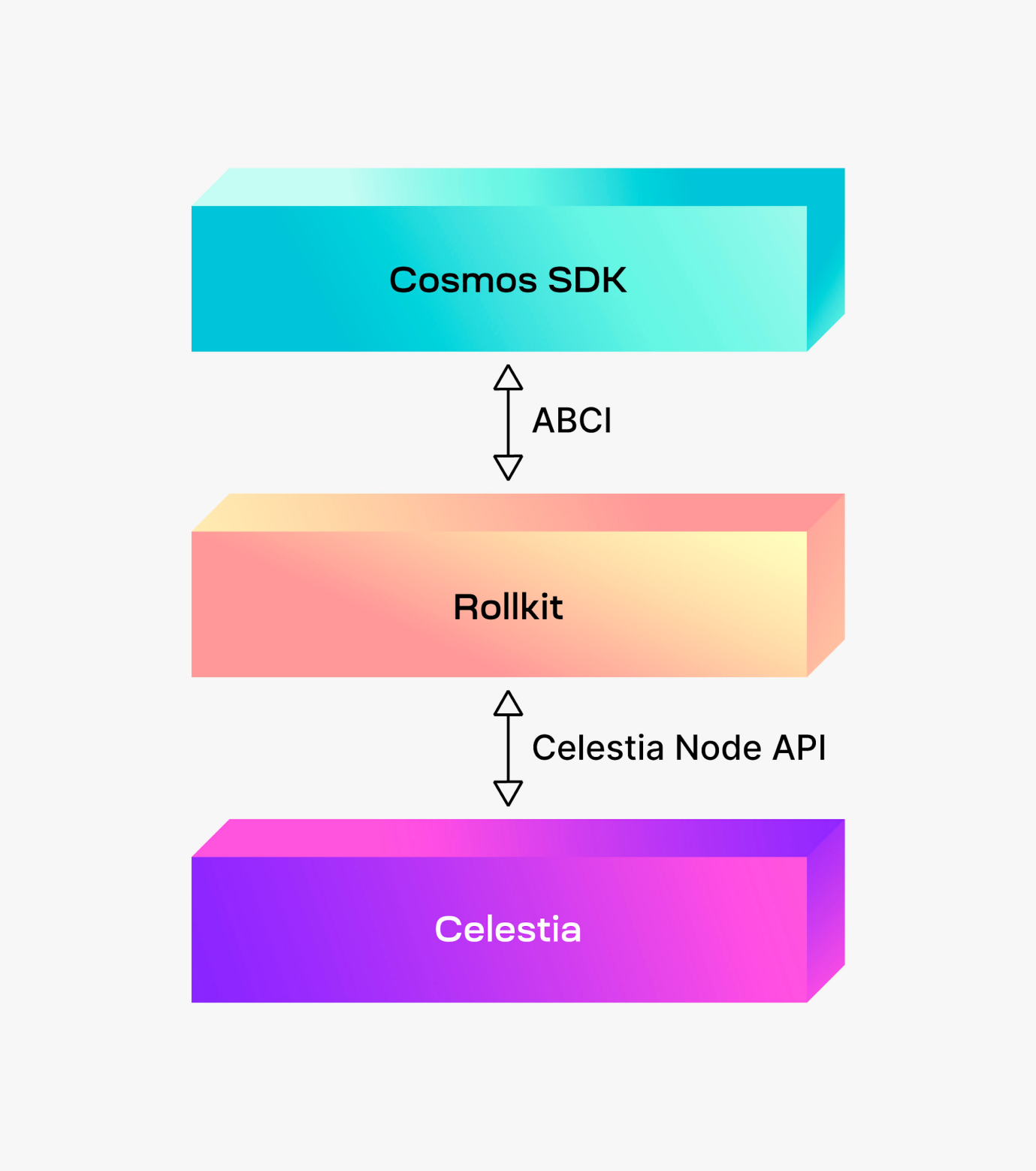
##Celestia Rollkit ( https://docs.celestia.org/developers/rollkit )
Rollkit replaces Cosmos’ consensus engine Tendermint (more precisely CometBFT) and allows Celestia and the Cosmos SDK to communicate directly. Rollkit allows Sovereign Rollup by aggregating transactions in a block and leveraging Celestia’s consensus engine and data availability.2.2 Skip Protocol
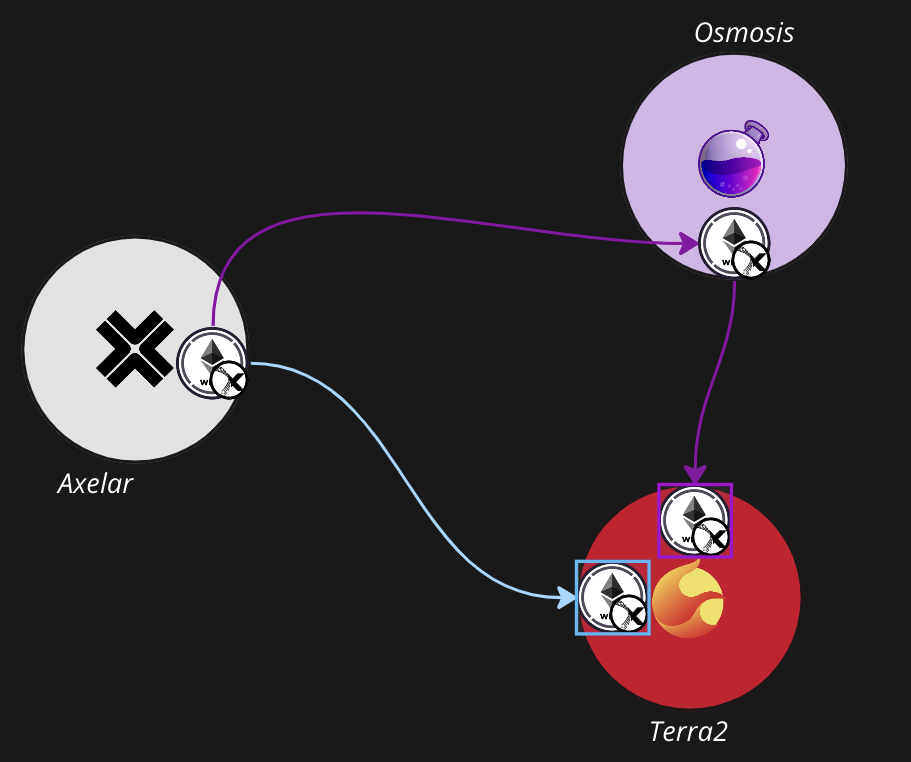
Skip Protocol is a project with the vision of "sovereign transaction infrastructure for sovereign blockchains". This protocol can improve the user experience of sovereign blockchains, make the order of transaction processing transparent, prevent malicious MEV, and improve the quality of the network. Among user experience improvements, the project aims to solve the problem of the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. IBC is a protocol for trading assets between different chains within Cosmos. In order to transfer assets via IBC, a communication "channel" must be created, and each channel needs to be given a unique ID for each connected chain. The picture below shows an example of ETH being sent from Axelar to Terra2.
##Skip API ( https://api-docs.skip.money/docs/ibc-routing-algorithm ) In addition, Skip proposes an optimal routing algorithm for delivering assets in the Cosmos ecosystem and provides a better user experience by determining the Denomination of assets.
Skip Protocol also provides various APIs that are very useful for developing blockchains based on the Cosmos SDK, such as multi-chain transaction tracking. Skip also proposed to the community that Skip’s functions should be included in the Cosmos SDK to contribute to ecological development.
2.3 Other Projects
Sei
Sei is positioned as a chain that specializes in transactions and aims to become a fast Layer1 instead of Rollup is also a major trend in blockchain development in 2023. Sei focuses on improving the performance of the chain by leveraging various technologies.
Injective
Injective is committed to building a blockchain ecosystem specifically for financial applications. Injective has established partnerships with Figment and Binance, and supports various dapps such as Helix and Hydro to join the Injective ecosystem.
dYdX
dYdX is considered the most successful DEX and has been successfully migrated to Layer1 using the Cosmos SDK.
dYdX strengthens governance through its own token.Stride
Stride is a liquidity staking protocol similar to Ethereum Lido. In the Cosmos ecosystem, liquidity staking is inherently difficult because assets are scattered across multiple chains. Stride aims to achieve multi-chain liquidity staking in the Cosmos ecosystem by leveraging ICA (Inter-Chain Account), ICQ (Inter-Chain Query) and ICS (Inter-Chain Security).
Coreum
Coreum is an enterprise-oriented Layer1 blockchain that supports Wasm-based smart contracts, RWA tokenization, NeoBanking applications, and more.
3. On-chain performance
3.1 Development activity
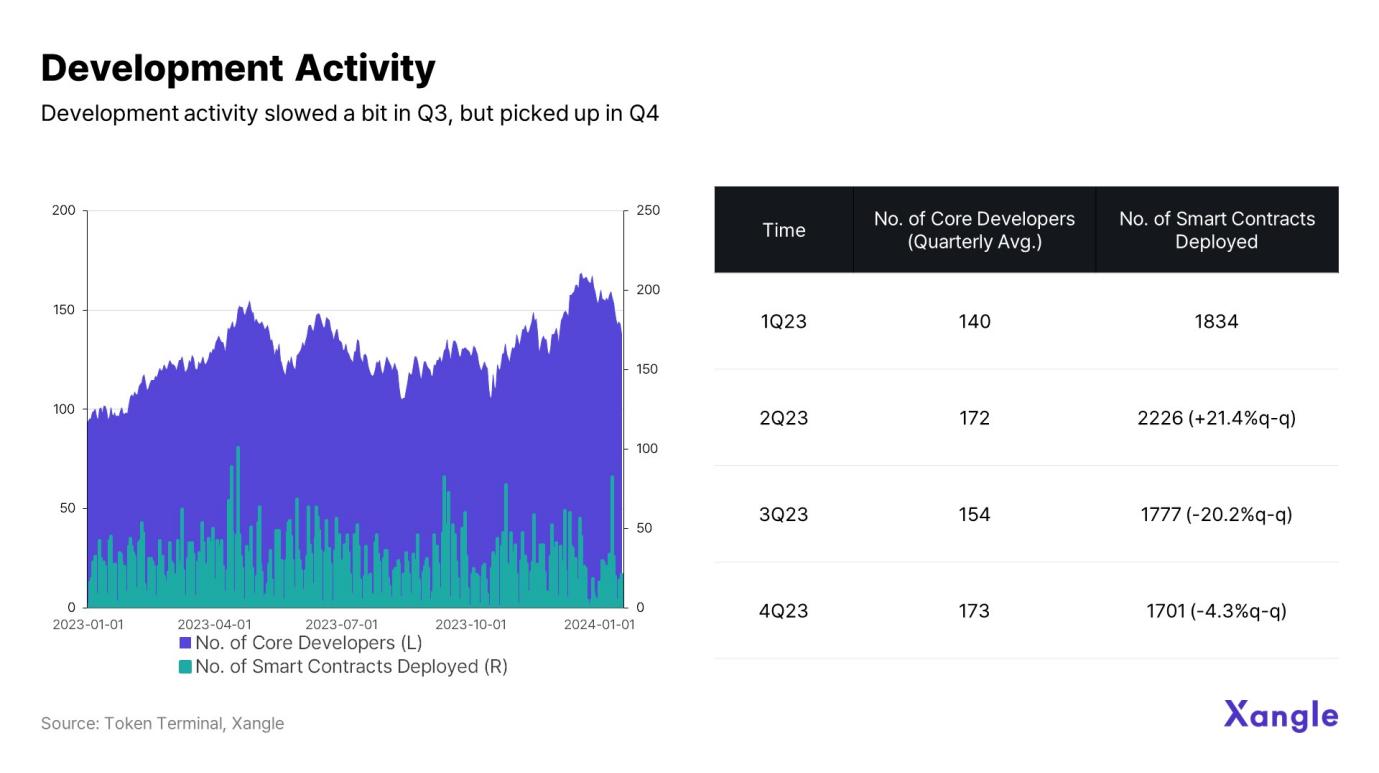
Although development activity on the Cosmos network remains healthy overall , but Q2 in 2023 will have the largest number of smart contract deployments (2226) and the highest growth rate (21.4%). The number of core developers is gradually increasing, which is also a sign of active ecological infrastructure construction.
Meanwhile, the number of smart contracts deployed in Q2 and Q3 last year was 2,226 and 1,777 respectively, up from 1,701 in the fourth quarter. While development activity did slow down compared to the previous two quarters, activity levels continue to hold up given the decline at the end of Q4.
3.2 Network Activity
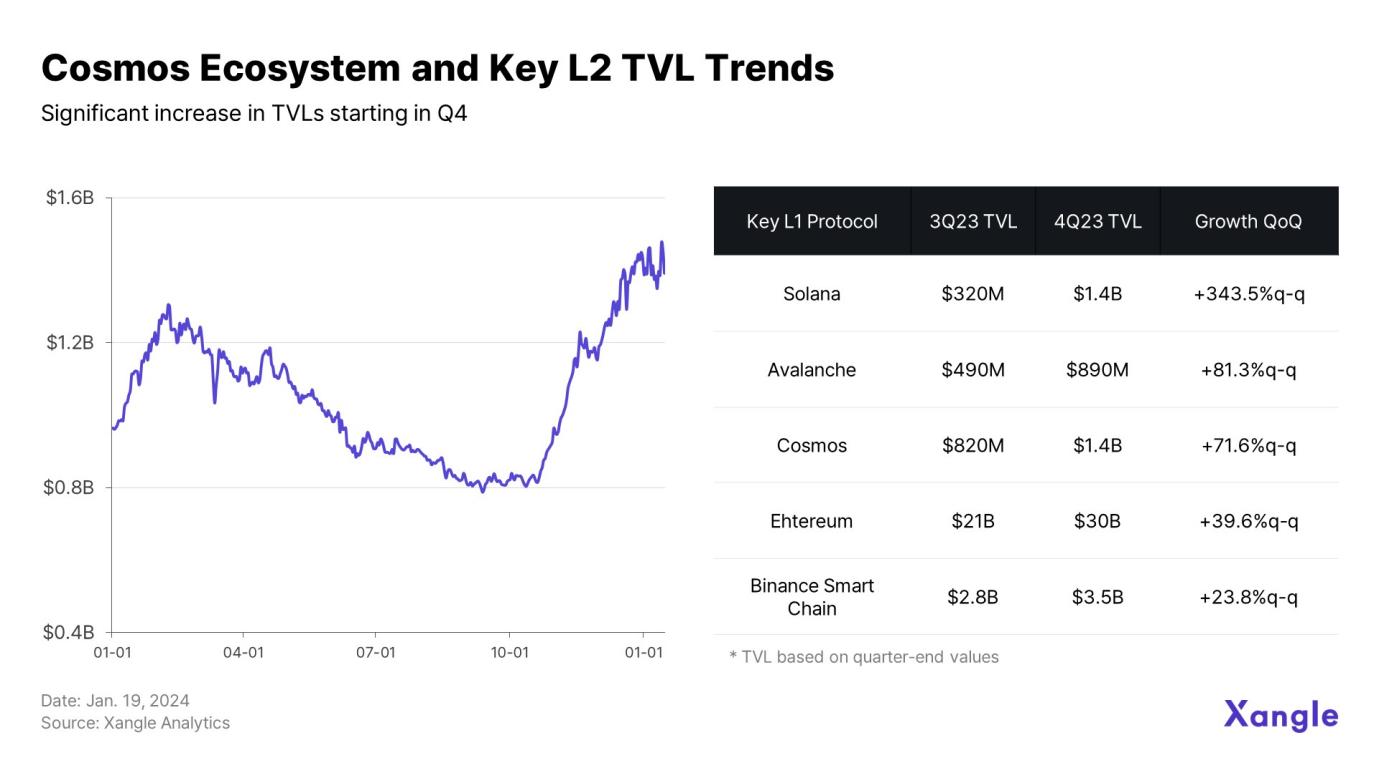
The most notable aspect of Cosmos network activity is that development activity in Q2 and Q3 translated into Q4 overall ecological growth. As shown in the figure, TVL in the Cosmos ecosystem continued to decline in Q3, but then increased significantly in Q4.
The explosive growth of TVL in the Cosmos ecosystem in the fourth quarter can be attributed to two factors. The first was the influx of liquidity in Layer 1 narratives in mid-October. In the second half of the year, a large amount of funds flowed into the Layer 1 ecosystem, and the explosive performance of Solana, Cosmos, and Avalanche drove the overall TVL increase.
In addition, the developer-friendly infrastructure environment, including the Cosmos SDK, and the huge blockchain connection network built on the IBC ecosystem have brought practical benefits to users. By observing the TVL trend, you will find that this is not just a temporary increase, but a continuing trend. Market satisfaction with the protocol's maturity may drive Layer 1 liquidity, boost Cosmos' development and reduce user churn.
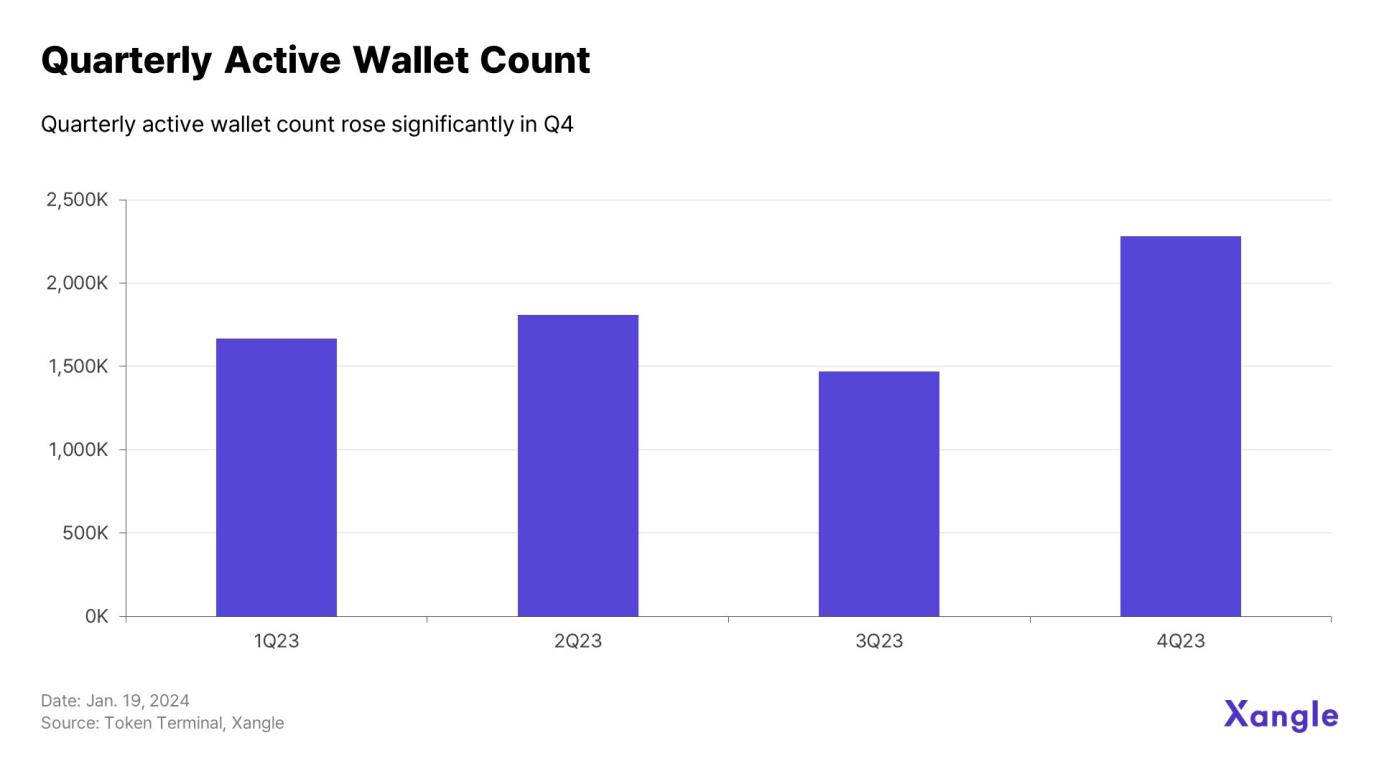
Compared with the worst-performing Q3 (1,470,050), the number of active wallets in Q4 also increased by nearly 55%, reaching 2,280,335. Reflecting the vitality of the ecology. The interoperability of the Cosmos IBC ecosystem drives increased on-chain activity.
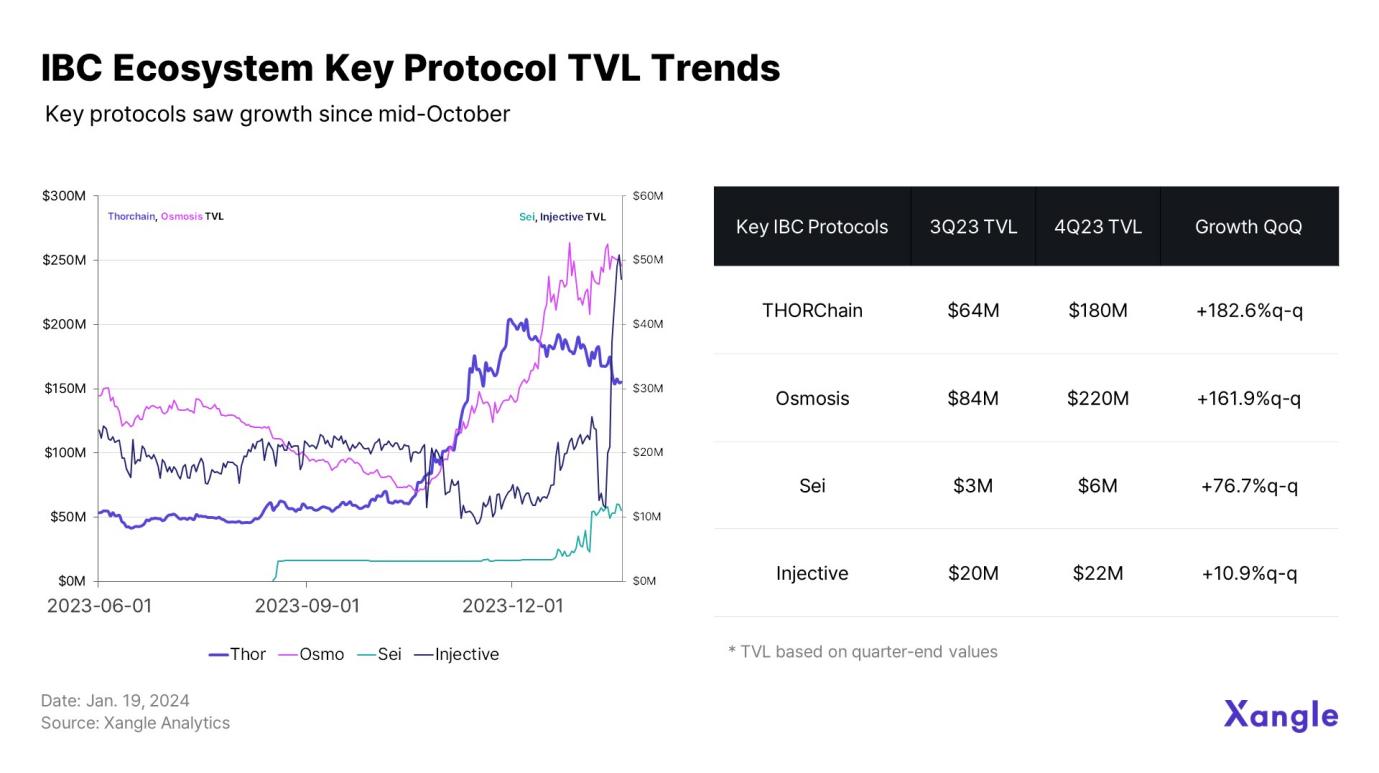
In addition, judging from the TVL trends of key protocols in the IBC ecosystem, the continued hype of protocols based on the Cosmos SDK in the second half of the year also played a role in revitalizing the ecosystem.
3.3 Network Security
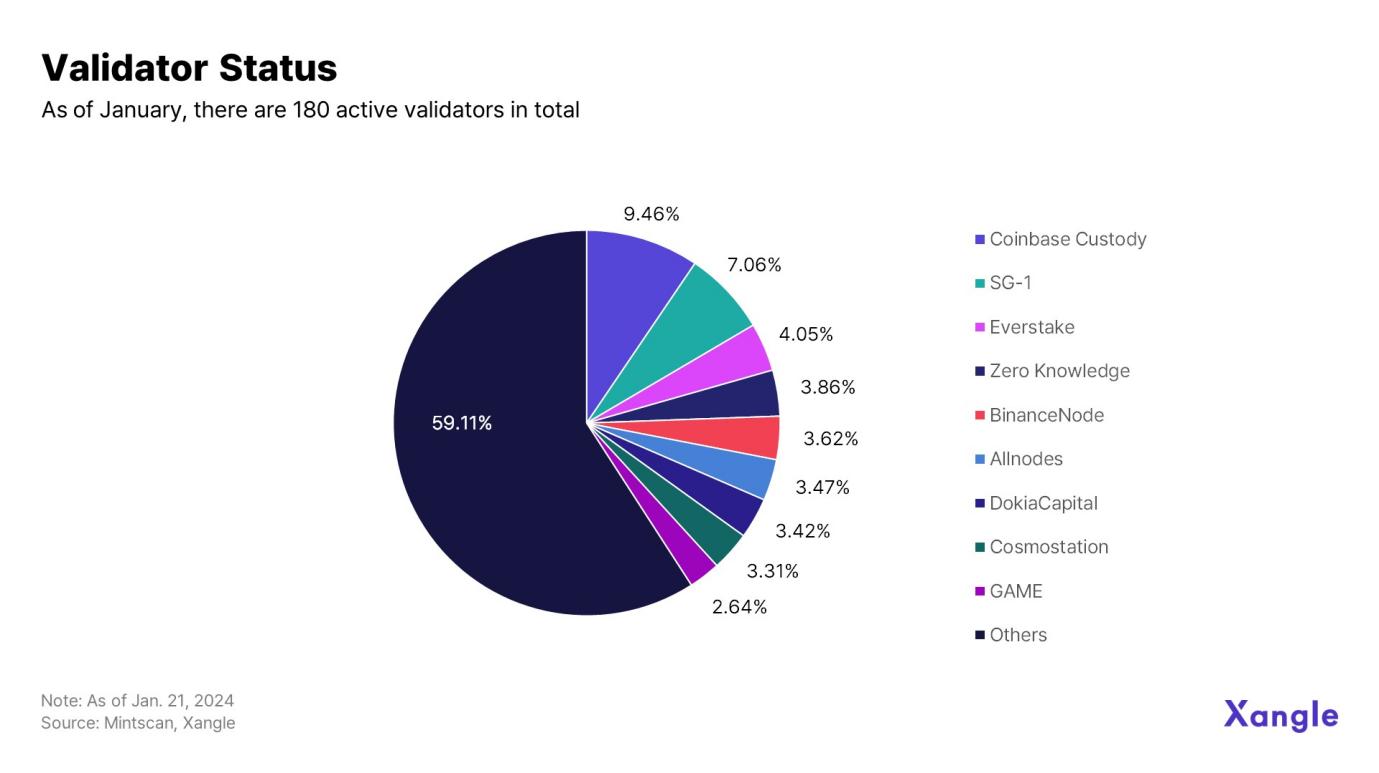
Cosmos currently has a total of 180 active validators. The top 9 validators hold 40.89% of the ATOM supply. There are currently 2.44 billion ATOMs pledged on Cosmos, accounting for approximately 65% of the total supply.
4. Conclusion
2023 is a milestone year for the Cosmos ecosystem, witnessing the development and major changes of several projects. These changes show that Cosmos is not just an area of blockchain technology, but is driving innovation across the entire blockchain ecosystem.
Celestia, Skip Protocol and other well-known projects demonstrate the diversity and flexibility of the Cosmos ecosystem and how it continues to evolve. These projects pioneer new use cases for blockchain technology and help create more efficient, user-friendly blockchain environments.
The growth and development of the Cosmos ecosystem has increased excitement about the future of blockchain technology. Opening the door to new opportunities for developers, users and investors, and paving the way for continued innovation for years to come. It is expected that the Cosmos ecosystem will continue to maintain this positive trend in the next few years, and new technical challenges and opportunities will continue to emerge in the process.
The above is the detailed content of Annual overview of the Cosmos ecosystem: well-known projects emerge and core developers continue to grow. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 What is Ouyi for? What is Ouyi
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
What is Ouyi for? What is Ouyi
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:18 PM
OKX is a global digital asset trading platform. Its main functions include: 1. Buying and selling digital assets (spot trading), 2. Trading between digital assets, 3. Providing market conditions and data, 4. Providing diversified trading products (such as derivatives), 5. Providing asset value-added services, 6. Convenient asset management.
 How to roll positions in digital currency? What are the digital currency rolling platforms?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
How to roll positions in digital currency? What are the digital currency rolling platforms?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Digital currency rolling positions is an investment strategy that uses lending to amplify trading leverage to increase returns. This article explains the digital currency rolling process in detail, including key steps such as selecting trading platforms that support rolling (such as Binance, OKEx, gate.io, Huobi, Bybit, etc.), opening a leverage account, setting a leverage multiple, borrowing funds for trading, and real-time monitoring of the market and adjusting positions or adding margin to avoid liquidation. However, rolling position trading is extremely risky, and investors need to operate with caution and formulate complete risk management strategies. To learn more about digital currency rolling tips, please continue reading.
 How to calculate the transaction fee of gate.io trading platform?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
How to calculate the transaction fee of gate.io trading platform?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
The handling fees of the Gate.io trading platform vary according to factors such as transaction type, transaction pair, and user VIP level. The default fee rate for spot trading is 0.15% (VIP0 level, Maker and Taker), but the VIP level will be adjusted based on the user's 30-day trading volume and GT position. The higher the level, the lower the fee rate will be. It supports GT platform coin deduction, and you can enjoy a minimum discount of 55% off. The default rate for contract transactions is Maker 0.02%, Taker 0.05% (VIP0 level), which is also affected by VIP level, and different contract types and leverages
 Tutorial on how to register, use and cancel Ouyi okex account
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
Tutorial on how to register, use and cancel Ouyi okex account
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:21 PM
This article introduces in detail the registration, use and cancellation procedures of Ouyi OKEx account. To register, you need to download the APP, enter your mobile phone number or email address to register, and complete real-name authentication. The usage covers the operation steps such as login, recharge and withdrawal, transaction and security settings. To cancel an account, you need to contact Ouyi OKEx customer service, provide necessary information and wait for processing, and finally obtain the account cancellation confirmation. Through this article, users can easily master the complete life cycle management of Ouyi OKEx account and conduct digital asset transactions safely and conveniently.
 Binance binance computer version entrance Binance binance computer version PC official website login entrance
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
Binance binance computer version entrance Binance binance computer version PC official website login entrance
Mar 31, 2025 pm 04:36 PM
This article provides a complete guide to login and registration on Binance PC version. First, we explained in detail the steps for logging in Binance PC version: search for "Binance Official Website" in the browser, click the login button, enter the email and password (enable 2FA to enter the verification code) to log in. Secondly, the article explains the registration process: click the "Register" button, fill in the email address, set a strong password, and verify the email address to complete the registration. Finally, the article also emphasizes account security, reminding users to pay attention to the official domain name, network environment, and regularly updating passwords to ensure account security and better use of various functions provided by Binance PC version, such as viewing market conditions, conducting transactions and managing assets.
 What are the recommended websites for virtual currency app software?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
What are the recommended websites for virtual currency app software?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 09:06 PM
This article recommends ten well-known virtual currency-related APP recommendation websites, including Binance Academy, OKX Learn, CoinGecko, CryptoSlate, CoinDesk, Investopedia, CoinMarketCap, Huobi University, Coinbase Learn and CryptoCompare. These websites not only provide information such as virtual currency market data, price trend analysis, etc., but also provide rich learning resources, including basic blockchain knowledge, trading strategies, and tutorials and reviews of various trading platform APPs, helping users better understand and make use of them
 Currency Trading Network Official Website Collection 2025
Mar 31, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
Currency Trading Network Official Website Collection 2025
Mar 31, 2025 pm 03:57 PM
It ranks among the top in the world, supports all categories of transactions such as spot, contracts, and Web3 wallets. It has high security and low handling fees. A comprehensive trading platform with a long history, known for its compliance and high liquidity, supports multilingual services. The industry leader covers currency trading, leverage, options, etc., with strong liquidity and supports BNB deduction fees.
 On which platform is web3 transaction?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
On which platform is web3 transaction?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 07:54 PM
This article lists the top ten well-known Web3 trading platforms, including Binance, OKX, Gate.io, Kraken, Bybit, Coinbase, KuCoin, Bitget, Gemini and Bitstamp. The article compares the characteristics of each platform in detail, such as the number of currencies, trading types (spot, futures, options, NFT, etc.), handling fees, security, compliance, user groups, etc., aiming to help investors choose the most suitable trading platform. Whether it is high-frequency traders, contract trading enthusiasts, or investors who focus on compliance and security, they can find reference information from it.


